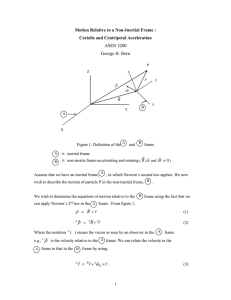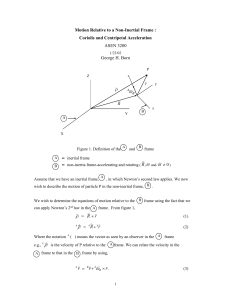
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... 3.B.1: If an object of interest interacts with several other objects, the net force is the vector sum of the individual forces. ...
... 3.B.1: If an object of interest interacts with several other objects, the net force is the vector sum of the individual forces. ...
Example 6.1 The Conical Pendulum A small ball of mass m is
... banking, as in the next example! Notice that the maximum speed does not depend on the mass of the car, which is why curved highways do not need multiple speed limits to cover the various masses of vehicles using the road. WHAT IF? Suppose a car travels this curve on a wet day and begins to skid on t ...
... banking, as in the next example! Notice that the maximum speed does not depend on the mass of the car, which is why curved highways do not need multiple speed limits to cover the various masses of vehicles using the road. WHAT IF? Suppose a car travels this curve on a wet day and begins to skid on t ...
Lectures in physics Part 1: Mechanics Przemysław Borys 7.11.2013
... 1. Scalars and vectors. In physics we use different quantities to describe the observed phenomena. Among them the most important are scalars and vectors. Scalars are simply the numbers, which describe for example the temperature, mass, density, energy. Other physical phenomena cannot be described i ...
... 1. Scalars and vectors. In physics we use different quantities to describe the observed phenomena. Among them the most important are scalars and vectors. Scalars are simply the numbers, which describe for example the temperature, mass, density, energy. Other physical phenomena cannot be described i ...
Chap4-Conceptual Modules
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
Physics - Calderglen High School
... (c) Explain why there is a change in kinetic energy. 13. A skater is spinning at 3.0 rad s-1 with her arms and one leg outstretched. The angular speed is increased to 25 rad s-1 when she draws her arms and leg in. (a) Explain why this movement of her arms and leg affects the rotational speed. (b) He ...
... (c) Explain why there is a change in kinetic energy. 13. A skater is spinning at 3.0 rad s-1 with her arms and one leg outstretched. The angular speed is increased to 25 rad s-1 when she draws her arms and leg in. (a) Explain why this movement of her arms and leg affects the rotational speed. (b) He ...
4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... This form for the frictional force is an approximation; the actual phenomenon is very complicated. The coefficient of friction may vary somewhat with speed; there may be some dependence on the surface area of the objects. Also, remember that these equations are for the magnitude of the frictional fo ...
... This form for the frictional force is an approximation; the actual phenomenon is very complicated. The coefficient of friction may vary somewhat with speed; there may be some dependence on the surface area of the objects. Also, remember that these equations are for the magnitude of the frictional fo ...
VU2 Movement 2008
... – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
... – kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy close to the Earth’s surface; – potential energy and kinetic energy in springs; ...
Unit 2 - aqaphysics.co.uk
... The diagram shows two balls that are released at the same time, one is released and the other has a horizontal velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of ...
... The diagram shows two balls that are released at the same time, one is released and the other has a horizontal velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of ...
Forces and Motion
... • When an object is in free fall it will accelerate due to gravity at 10ms-2. • When objects fall from a large height they do not continue to accelerate but eventually reach a constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balan ...
... • When an object is in free fall it will accelerate due to gravity at 10ms-2. • When objects fall from a large height they do not continue to accelerate but eventually reach a constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balan ...