1 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 2. Two blocks, joined by a string, have masses o ...
... 1. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 2. Two blocks, joined by a string, have masses o ...
physics midterm review
... Additional Review for Physics Midterm 9) A dog runs down the entire length of his driveway at a constant speed of 4 m/s for 5 s, then uniformly increases her speed to 8 m/s in 4 s. How long is the driveway? ...
... Additional Review for Physics Midterm 9) A dog runs down the entire length of his driveway at a constant speed of 4 m/s for 5 s, then uniformly increases her speed to 8 m/s in 4 s. How long is the driveway? ...
Are You suprised
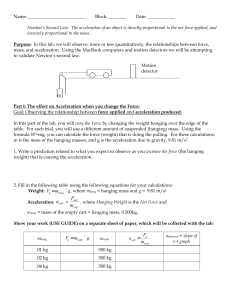
... mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
... mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
3.1-3.2 Circular Motion - York Catholic District School Board
... This could be string, a rod – anything that is attached to the rotating mass that keeps it from flying out of its rotational circle Even gravity – planets move around the sun at a constant speed in a circular motion because the sun’s gravitational pull creates a centripetal force that keeps us in or ...
... This could be string, a rod – anything that is attached to the rotating mass that keeps it from flying out of its rotational circle Even gravity – planets move around the sun at a constant speed in a circular motion because the sun’s gravitational pull creates a centripetal force that keeps us in or ...
Problem set 13
... the principal moments of inertia and the magnitude of angular momentum L. How does α depend on time and L? (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above ...
... the principal moments of inertia and the magnitude of angular momentum L. How does α depend on time and L? (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above ...
Kreutter: Linear Dynamics 7 Newton`s Second Law: Quantitative I
... . In this situation, if we increase c and keep b constant, than a will decrease. If we decrease c and keep b constant, than a will increase. Think about how this is different than if we increase or decrease b. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: We choose a particular object (objects) as our object of in ...
... . In this situation, if we increase c and keep b constant, than a will decrease. If we decrease c and keep b constant, than a will increase. Think about how this is different than if we increase or decrease b. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: We choose a particular object (objects) as our object of in ...
sessnn9
... This means that the acceleration is proportional to the displacement but opposite in sign, and the two quantities are related by the square of the angular frequency. The force law If we want to know what force must act on the particle, we need to know its acceleration and how it varies with time. Us ...
... This means that the acceleration is proportional to the displacement but opposite in sign, and the two quantities are related by the square of the angular frequency. The force law If we want to know what force must act on the particle, we need to know its acceleration and how it varies with time. Us ...
motion - SCHOOLinSITES
... action exerted on a body in order to change body’s state of rest or motion. has magnitude and direction. net force • combination of all forces acting on an object. balanced forces: Objects either do not move or move at constant velocity. unbalanced force any change in an object’s state of mo ...
... action exerted on a body in order to change body’s state of rest or motion. has magnitude and direction. net force • combination of all forces acting on an object. balanced forces: Objects either do not move or move at constant velocity. unbalanced force any change in an object’s state of mo ...
ppt
... Force equation So now, assuming we’ve set up object space right (centre of mass at 0), F=MA If there are no external forces, have F=0 Internal forces must balance out, opposite and equal Thus A=0, thus V=constant ...
... Force equation So now, assuming we’ve set up object space right (centre of mass at 0), F=MA If there are no external forces, have F=0 Internal forces must balance out, opposite and equal Thus A=0, thus V=constant ...