Fall Final Review
... Newton’s 3rd Law displacement vs distance friction free body diagrams velocity vs speed inertia inversely proportional acceleration net force directly proportional free fall mass impulse momentum weight work / energy / power air resistance Newton’s 1st Law action/reaction force pairs Short Answer Qu ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law displacement vs distance friction free body diagrams velocity vs speed inertia inversely proportional acceleration net force directly proportional free fall mass impulse momentum weight work / energy / power air resistance Newton’s 1st Law action/reaction force pairs Short Answer Qu ...
8th 2014 midterm
... 46) What is: a) a measure of the distance an object travels in a unit of time? b) An object’s distance in a certain direction from a reference point. c) The rate of change of position in which the same distance is traveled each second. d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by t ...
... 46) What is: a) a measure of the distance an object travels in a unit of time? b) An object’s distance in a certain direction from a reference point. c) The rate of change of position in which the same distance is traveled each second. d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by t ...
Motion, Forces &Machines PowerPoint presentation
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
Static Friction
... Law of action-reaction for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction mg = FN Law of gravitation - all bodies are attracted to one another with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... Law of action-reaction for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction mg = FN Law of gravitation - all bodies are attracted to one another with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
CH 3 Forces
... What was the mass of another horse that was running at a velocity of 18.0 m/s if his “p” was 7500 kg·m/s? Law of Conservation of Momentum– the total amount of p of a group of objects does not change unless outside forces act on the objects. ...
... What was the mass of another horse that was running at a velocity of 18.0 m/s if his “p” was 7500 kg·m/s? Law of Conservation of Momentum– the total amount of p of a group of objects does not change unless outside forces act on the objects. ...
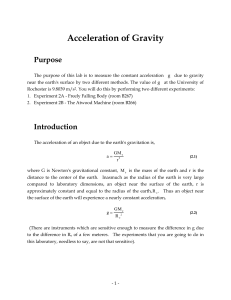
Prelab Homework - University of Rochester
... to the difference in Re of a few meteres. The experiments that you are going to do in this laboratory, needless to say, are not that sensitive). ...
... to the difference in Re of a few meteres. The experiments that you are going to do in this laboratory, needless to say, are not that sensitive). ...
Physics Unit Review
... What is a reference point (also called frame of reference)? An object that appears to stay in place A change in position relative to a reference point is known as _motion___________. Write the formula for speed. D/t What is the average speed of a jet plane that flies 7200 km in 9 hours? 800 km/hr Ho ...
... What is a reference point (also called frame of reference)? An object that appears to stay in place A change in position relative to a reference point is known as _motion___________. Write the formula for speed. D/t What is the average speed of a jet plane that flies 7200 km in 9 hours? 800 km/hr Ho ...
rotation
... Constant Angular Acceleration Kinematics The equations for 1-D motion with constant acceleration are a result the dv definitions of the quantities; because a dt it immediately follows that v v0 at if acceleration is constant. Since the angular variables θ, ω, α are related to each other in ex ...
... Constant Angular Acceleration Kinematics The equations for 1-D motion with constant acceleration are a result the dv definitions of the quantities; because a dt it immediately follows that v v0 at if acceleration is constant. Since the angular variables θ, ω, α are related to each other in ex ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 12. Two like parallel forces P and Q (P>Q) act at A and B respectively. If the magnitude of the forces are interchanged, show that the point of application of the resultant of AB will be displaced P−Q through the distance . AB . P+Q 13. A particle is placed on a rough inclined plane, inclined at an ...
... 12. Two like parallel forces P and Q (P>Q) act at A and B respectively. If the magnitude of the forces are interchanged, show that the point of application of the resultant of AB will be displaced P−Q through the distance . AB . P+Q 13. A particle is placed on a rough inclined plane, inclined at an ...
File - TuHS Physical Science
... a. acts in the direction of motion. b. equals the weight of the box. c. is usually greater than static friction. d. acts in the direction opposite of motion. ____ 11. If you know your mass, how could you calculate your weight? ...
... a. acts in the direction of motion. b. equals the weight of the box. c. is usually greater than static friction. d. acts in the direction opposite of motion. ____ 11. If you know your mass, how could you calculate your weight? ...
Unit 3 Powerpoint
... to solve any problem involving onedimensional motion with a constant acceleration You may need to use two of the equations to solve one problem Many times there is more than one way to solve a problem ...
... to solve any problem involving onedimensional motion with a constant acceleration You may need to use two of the equations to solve one problem Many times there is more than one way to solve a problem ...
24 Slides
... • For a collision occurring between object 1 and object 2 in an isolated system, the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision MV = MV ...
... • For a collision occurring between object 1 and object 2 in an isolated system, the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision MV = MV ...
Ch. 12 Test Review Write the complete definition for the following
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...