South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... explain that if you were inside the rotating frame of reference, you would feel a force pushing you toward the outside of the circle. This is a “false force” called centrifugal force that can simulate gravity. ...
... explain that if you were inside the rotating frame of reference, you would feel a force pushing you toward the outside of the circle. This is a “false force” called centrifugal force that can simulate gravity. ...
Slide 1
... A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a speed v. The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a stationary rod of mass M, length d, pivoted about a frictionless axle through its center. (a) Find the angular speed of the system right after the collision. (b) Determine the fractional loss ...
... A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a speed v. The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a stationary rod of mass M, length d, pivoted about a frictionless axle through its center. (a) Find the angular speed of the system right after the collision. (b) Determine the fractional loss ...
Chapter 4 Motion, Energy, and Gravity
... An object moving on a circle with fixed rotation rate has constant angular velocity (constant degree/sec and direction of rotation). An object moving on a circle with fixed rotation rate has non-zero acceleration. It is changing its direction all the time. The orbital motion of the Earth around ...
... An object moving on a circle with fixed rotation rate has constant angular velocity (constant degree/sec and direction of rotation). An object moving on a circle with fixed rotation rate has non-zero acceleration. It is changing its direction all the time. The orbital motion of the Earth around ...
Course Syllabus
... who wish to pursue a baccalaureate degree in Aeorspace, Mechanical, Civil, Environmental, or Electrical Engineering. Other students from other programs may also take the course if they have the appropriate background. II. Course Student Learning Outcomes: State the student learning outcome(s) for th ...
... who wish to pursue a baccalaureate degree in Aeorspace, Mechanical, Civil, Environmental, or Electrical Engineering. Other students from other programs may also take the course if they have the appropriate background. II. Course Student Learning Outcomes: State the student learning outcome(s) for th ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Notes
... a. The forces on the wall and the ice skater are equal in size and opposite in direction. Although there are two objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward forc ...
... a. The forces on the wall and the ice skater are equal in size and opposite in direction. Although there are two objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward forc ...
Slide 1
... If the velocity of a car traveling around a circular track doubles, its centripetal acceleration would be A) 1/2 as great B) 2 times greater C) 1/4 as great D) 4 times greater ...
... If the velocity of a car traveling around a circular track doubles, its centripetal acceleration would be A) 1/2 as great B) 2 times greater C) 1/4 as great D) 4 times greater ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
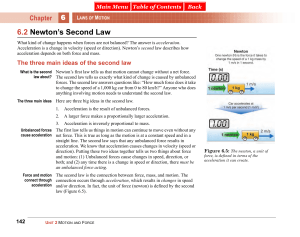
... Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces can also be exerted in the same direction. For example, imagine that your family's car breaks down on the road and you have to push it into a parking lot. If you and your brother or sister both push on the car, the resulting force on the car will be the sum of yo ...
... Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces can also be exerted in the same direction. For example, imagine that your family's car breaks down on the road and you have to push it into a parking lot. If you and your brother or sister both push on the car, the resulting force on the car will be the sum of yo ...
document
... "The net force is always the important thing. If the net force is zero, then Newton's Second Law (and Newton's First Law, too) says that the acceleration of the wagon must be zero." "Yes, I remember Newton's Second Law very well, Old Dobbin.", says Farmer Brown, hopefully. "This physics discussion i ...
... "The net force is always the important thing. If the net force is zero, then Newton's Second Law (and Newton's First Law, too) says that the acceleration of the wagon must be zero." "Yes, I remember Newton's Second Law very well, Old Dobbin.", says Farmer Brown, hopefully. "This physics discussion i ...
Newton`s Laws
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
7 - Tarman Physics
... Which statement is NOT true? A. the weight of the candle = buoyant force B. V is the volume of fluid displaced C. is the density of wax D. there is no normal force on the candle E. all statements are true ...
... Which statement is NOT true? A. the weight of the candle = buoyant force B. V is the volume of fluid displaced C. is the density of wax D. there is no normal force on the candle E. all statements are true ...
determination of the acceleration of an elevator.
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...