Chapter 2: MOTION AND SPEED
... so obvious…the force of the floor being exerted on your feet OR gravity pulling down on your body ...
... so obvious…the force of the floor being exerted on your feet OR gravity pulling down on your body ...
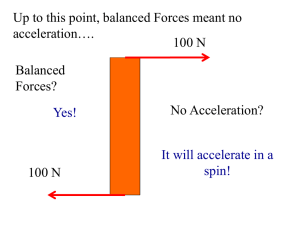
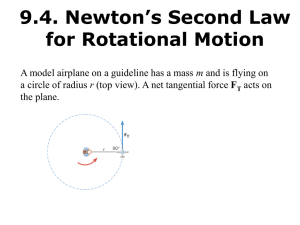
Rotational Motion and Torque
... Symbolized by the Greek letter α (alpha) *All points on a rotating rigid object have the same angular acceleration and the same angular speed as all other points on the object. ...
... Symbolized by the Greek letter α (alpha) *All points on a rotating rigid object have the same angular acceleration and the same angular speed as all other points on the object. ...
PHY131 E1
... A crate rests on a horizontal surface and a woman pulls on it with a 10-N force. Rank the situations shown below according to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface on the crate, least to greatest. ...
... A crate rests on a horizontal surface and a woman pulls on it with a 10-N force. Rank the situations shown below according to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface on the crate, least to greatest. ...
Name of Model
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
F g
... Newton mechanics laws cannot be applied when: 1) The speed of the interacting bodies are a fraction of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure ...
... Newton mechanics laws cannot be applied when: 1) The speed of the interacting bodies are a fraction of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure ...
Ch 2 Motion - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pairs. Of the two forces one force is always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the other. The law of gravitation is also applicable throughout the known universe. All objec ...
... results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pairs. Of the two forces one force is always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the other. The law of gravitation is also applicable throughout the known universe. All objec ...
Forces HW-1
... An astronaut on a space walk discovers that his jet pack no longer works, leaving him stranded 50 m from the spacecraft. If the jet pack is removable, explain how the astronaut can still use it to return to the ship. Two astronauts on a space walk decide to take a break and play catch with a basebal ...
... An astronaut on a space walk discovers that his jet pack no longer works, leaving him stranded 50 m from the spacecraft. If the jet pack is removable, explain how the astronaut can still use it to return to the ship. Two astronauts on a space walk decide to take a break and play catch with a basebal ...
Document
... other attributes that make it desirable to use cylindrical coordinates Equilibrium equations or “Equations of Motion” in cylindrical coordinates (using r, q , and z coordinates) may be expressed in scalar form as: Fr = mar = m(r – rq2) Fq = maq = m(rq – 2rq) ...
... other attributes that make it desirable to use cylindrical coordinates Equilibrium equations or “Equations of Motion” in cylindrical coordinates (using r, q , and z coordinates) may be expressed in scalar form as: Fr = mar = m(r – rq2) Fq = maq = m(rq – 2rq) ...
Part41
... can see that the biceps have to exert a large force to hold up a relatively light weight! What advantage does this give? Note how far the biceps have to contract in order to move the weight! This is the advantage of the elbow setup! In practice, we use clubs and rackets to make this ...
... can see that the biceps have to exert a large force to hold up a relatively light weight! What advantage does this give? Note how far the biceps have to contract in order to move the weight! This is the advantage of the elbow setup! In practice, we use clubs and rackets to make this ...
Comprehensive Final Exam Review 2014
... 15. A race car accelerates uniformly from 7 m/s to 25 m/s at a rate of 8.50 m/s2. What is the displacement during this acceleration? 16. A pilot stops a plane of mass 45000 kg in a distance of 555 m. If the plane had a uniform acceleration of -6.00 m/s2, how fast was the plane moving before the brak ...
... 15. A race car accelerates uniformly from 7 m/s to 25 m/s at a rate of 8.50 m/s2. What is the displacement during this acceleration? 16. A pilot stops a plane of mass 45000 kg in a distance of 555 m. If the plane had a uniform acceleration of -6.00 m/s2, how fast was the plane moving before the brak ...
rotary motion - GEOCITIES.ws
... A tangential force of 5.0 N is applied for 10.0 s to the rim of a 1.5 Kg bicycle wheel having a radius of 25 cm. If the wheel starts from rest, find : (a) The rotational inertia of the wheel, (b) Its angular acceleration, (c) Its angular velocity at 10.0 s, (d) The distance traveled by a point on th ...
... A tangential force of 5.0 N is applied for 10.0 s to the rim of a 1.5 Kg bicycle wheel having a radius of 25 cm. If the wheel starts from rest, find : (a) The rotational inertia of the wheel, (b) Its angular acceleration, (c) Its angular velocity at 10.0 s, (d) The distance traveled by a point on th ...
2nd Term Exam - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... of which 50J was spent to change the box’s kinetic energy, and the remainder was spent to overcome friction. 10. If you push twice as hard against a stationary brick wall, the amount of work you do a) doubles b) is cut in half c) remains constant but non-zero d) remains constant at zero Solution: Si ...
... of which 50J was spent to change the box’s kinetic energy, and the remainder was spent to overcome friction. 10. If you push twice as hard against a stationary brick wall, the amount of work you do a) doubles b) is cut in half c) remains constant but non-zero d) remains constant at zero Solution: Si ...