Chapter 3: Laws of Motion
... Leaning Tower of Pisa to see which would fall faster. Suppose the balls had masses of 1.0 kg and 10 kg. a. Use the equation for weight to calculate the force of gravity on each ball. b. Use your answers from part a and Newton’s second law to calculate each ball’s ...
... Leaning Tower of Pisa to see which would fall faster. Suppose the balls had masses of 1.0 kg and 10 kg. a. Use the equation for weight to calculate the force of gravity on each ball. b. Use your answers from part a and Newton’s second law to calculate each ball’s ...
Chapter 2: MOTION AND SPEED
... Sometimes you may want to know not only your distance, but also your direction from a reference point. ...
... Sometimes you may want to know not only your distance, but also your direction from a reference point. ...
centripetal force - Worth County Schools
... You are not flung out, your body simply wants to keep moving in straight line motion! ...
... You are not flung out, your body simply wants to keep moving in straight line motion! ...
Sample Test Questions
... 6. [1] The graph shows the velocity of a particle as a function of time. Calculate the distance the particle moves from 0 to 8 seconds. ...
... 6. [1] The graph shows the velocity of a particle as a function of time. Calculate the distance the particle moves from 0 to 8 seconds. ...
Circular Motion
... Tangential speed • For example, consider a pair of horses sideby-side on a carousel. • Each completes one full circle in the same time period, but the horse on the outside covers more distance than the inside horse does, so the outside horse has a greater tangential speed. ...
... Tangential speed • For example, consider a pair of horses sideby-side on a carousel. • Each completes one full circle in the same time period, but the horse on the outside covers more distance than the inside horse does, so the outside horse has a greater tangential speed. ...
Chapter AA
... where it is clear that we use the latest value of v (computed in the first line) to update the position x (computed in the second line). So these computations start from a given acceleration, update the speed then update the position of the object. There’s one small issue. Where does the acceleratio ...
... where it is clear that we use the latest value of v (computed in the first line) to update the position x (computed in the second line). So these computations start from a given acceleration, update the speed then update the position of the object. There’s one small issue. Where does the acceleratio ...
File
... When drawing a free-body diagram, remember that only gravitational and electrical forces act without contact. Surfaces exert 2 forces on objects – normal forces are perpendicular and friction forces are parallel to the surface. Friction is a resistive force, so it always points opposite the motion ...
... When drawing a free-body diagram, remember that only gravitational and electrical forces act without contact. Surfaces exert 2 forces on objects – normal forces are perpendicular and friction forces are parallel to the surface. Friction is a resistive force, so it always points opposite the motion ...
Force
... -friction acts in a direction opposite to the direction of the motion -2 Factors that affect the force of friction - how hard the surfaces push together -types of surfaces involved -4 Types of Friction -Static Friction -Sliding Friction -Rolling Friction -Fluid Friction Gravity -Law of Universal Gra ...
... -friction acts in a direction opposite to the direction of the motion -2 Factors that affect the force of friction - how hard the surfaces push together -types of surfaces involved -4 Types of Friction -Static Friction -Sliding Friction -Rolling Friction -Fluid Friction Gravity -Law of Universal Gra ...
Terminal Velocity - Northern Illinois University
... The downhill course is 2.5 km long with a drop of 800 m The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.052 The speed gun clocks the skier at a maximum of 130 km/h An average skier is about 80 kg ...
... The downhill course is 2.5 km long with a drop of 800 m The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.052 The speed gun clocks the skier at a maximum of 130 km/h An average skier is about 80 kg ...
Physics for the Sciences 07:150:193 Fall 2003
... • Mass: The measure of how difficult it is to change object’s velocity (sluggishness or inertia of the object). It is a scalar. SI unit of mass is a kilogram, kg • Weight: The force the Earth is pulling the object with. Weight is a vector quantity, it has a magnitude and direction, the unit of weigh ...
... • Mass: The measure of how difficult it is to change object’s velocity (sluggishness or inertia of the object). It is a scalar. SI unit of mass is a kilogram, kg • Weight: The force the Earth is pulling the object with. Weight is a vector quantity, it has a magnitude and direction, the unit of weigh ...
m(kg) - University of Iowa Physics
... • When two objects collide they exert forces on each other that last only a short time • We call these short lasting, but usually strong forces IMPULSIVE forces. • For example when I hit a nail with a hammer, I exert an impulsive force ...
... • When two objects collide they exert forces on each other that last only a short time • We call these short lasting, but usually strong forces IMPULSIVE forces. • For example when I hit a nail with a hammer, I exert an impulsive force ...
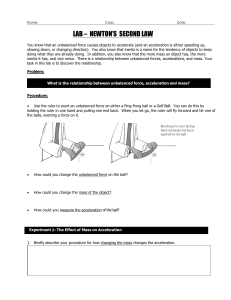
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... According to the equation, applying a larger net force to an object results in a larger acceleration. This is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is be ...
... According to the equation, applying a larger net force to an object results in a larger acceleration. This is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is be ...
CONForces
... STRAIGHT LINE unless acted upon by an outside force. ◦ Simply put…objects like to keep doing what they’re doing. ...
... STRAIGHT LINE unless acted upon by an outside force. ◦ Simply put…objects like to keep doing what they’re doing. ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
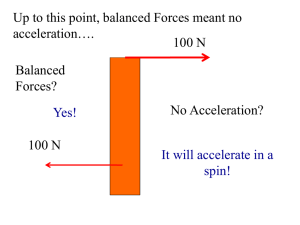
... “I'm confused when net force should equal 0 and when it should not.” Harlow answer: Net force is zero when the acceleration is zero. “how an object is still in motion but have a net force of zero is a little hard to grasp.” Harlow note: Don’t confuse velocity with acceleration! ...
... “I'm confused when net force should equal 0 and when it should not.” Harlow answer: Net force is zero when the acceleration is zero. “how an object is still in motion but have a net force of zero is a little hard to grasp.” Harlow note: Don’t confuse velocity with acceleration! ...
Exploring Newtons` Second Law using Simulations
... Newtons’ Second Law using a Simulations Name: Background: Newton’s second law states that when a force acts upon an object, it will cause the object to accelerate. The greater the force, the greater the acceleration. The simulation forces-1d allows you to explore the relationship between force, mass ...
... Newtons’ Second Law using a Simulations Name: Background: Newton’s second law states that when a force acts upon an object, it will cause the object to accelerate. The greater the force, the greater the acceleration. The simulation forces-1d allows you to explore the relationship between force, mass ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...