Chapters 4&5
... train exceeded the 45-km/h speed limit for this curve. You interview a passenger who had been standing and holding onto a strap; she noticed that an unused strap was hanging at about a 15° angle to the vertical just before the accident. What do you conclude? ...
... train exceeded the 45-km/h speed limit for this curve. You interview a passenger who had been standing and holding onto a strap; she noticed that an unused strap was hanging at about a 15° angle to the vertical just before the accident. What do you conclude? ...
Mechanics notes
... i) What is the tangential velocity of the stone? ii) What is the centripetal acceleration of the stone? iii)Show whether the string will break. iv)If the stone is now spun in a vertical plane at the same speed show whether the string will ...
... i) What is the tangential velocity of the stone? ii) What is the centripetal acceleration of the stone? iii)Show whether the string will break. iv)If the stone is now spun in a vertical plane at the same speed show whether the string will ...
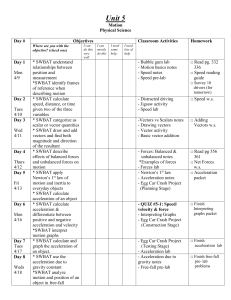
Tri 3 Study Guide 2014
... What is density? ____________________________________________________________________ By comparing densities, you can predict if an object will sink or float: o An object that is more dense than the fluid it is in will _________________ (sink or float) o An object that is less dense than the flu ...
... What is density? ____________________________________________________________________ By comparing densities, you can predict if an object will sink or float: o An object that is more dense than the fluid it is in will _________________ (sink or float) o An object that is less dense than the flu ...
Physics of Rolling Ball Coasters
... When using physics to determine values like acceleration, there are often two perfectly correct approaches: one is using energy (like we just did), and a second is by using forces. While energy is often simpler computationally, it is not always as satisfying. For this next situation, the previous ap ...
... When using physics to determine values like acceleration, there are often two perfectly correct approaches: one is using energy (like we just did), and a second is by using forces. While energy is often simpler computationally, it is not always as satisfying. For this next situation, the previous ap ...
in m/s 2
... 1) What is the speed during the first 20 seconds? 2) How far is the object from the start after 60 seconds? 3) What is the speed during the last 40 seconds? 4) When was the object travelling the fastest? ...
... 1) What is the speed during the first 20 seconds? 2) How far is the object from the start after 60 seconds? 3) What is the speed during the last 40 seconds? 4) When was the object travelling the fastest? ...
Essential Question
... An object will have greater acceleration if a _____________ force is applied to it. An object with less mass will accelerate faster. An example of Newton’s Second Law of Motion: A baseball and a bowling ball are both hit with the same bat and the same force. The baseball will have a greater acce ...
... An object will have greater acceleration if a _____________ force is applied to it. An object with less mass will accelerate faster. An example of Newton’s Second Law of Motion: A baseball and a bowling ball are both hit with the same bat and the same force. The baseball will have a greater acce ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - CEC
... Now let’s introduce the second part of Newton’s first law, which is that objects in motion tend to stay in motion until something hits them. An example of this is what happens if an astronaut throws something while in outer space. The item will continue in the same direction and at the same speed un ...
... Now let’s introduce the second part of Newton’s first law, which is that objects in motion tend to stay in motion until something hits them. An example of this is what happens if an astronaut throws something while in outer space. The item will continue in the same direction and at the same speed un ...
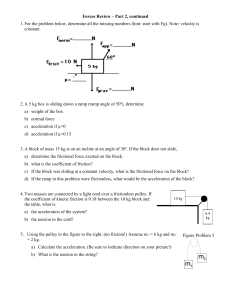
Review Forces Part 2
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
Chap.5 - KFUPM Faculty List
... A block of mass 2.0 kg is being pushed by a force parallel to the ground as shown in Figure 8. The block is observed to have an acceleration of 1.0 m/s 2 down the incline. Assume the incline is frictionless. Calculate the magnitude of the force. (Hint: Write equations of motion along the x-axis and ...
... A block of mass 2.0 kg is being pushed by a force parallel to the ground as shown in Figure 8. The block is observed to have an acceleration of 1.0 m/s 2 down the incline. Assume the incline is frictionless. Calculate the magnitude of the force. (Hint: Write equations of motion along the x-axis and ...
Circular Motion
... When an object moves in a circle, the net force toward the center of the circle is called the centripetal force To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration (such as tension on a string). Then you can apply Newton’s ...
... When an object moves in a circle, the net force toward the center of the circle is called the centripetal force To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration (such as tension on a string). Then you can apply Newton’s ...
Lecture7_Wheels
... strikes a stationary billiard ball head-on. A. The cue ball rebounds backward, while its target is sent moving forward. B. The cue ball stops while its target continues forward with the speed v. C. The cue ball and target ball roll forward together with a speed
... strikes a stationary billiard ball head-on. A. The cue ball rebounds backward, while its target is sent moving forward. B. The cue ball stops while its target continues forward with the speed v. C. The cue ball and target ball roll forward together with a speed
Chapter 10.3-10.5
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion • This means that if an object is not moving, it will not move until a force acts on it. • If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. • Gravity and friction are unbalanced f ...
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion • This means that if an object is not moving, it will not move until a force acts on it. • If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. • Gravity and friction are unbalanced f ...