review for exam
... __b__ 21. A rock is thrown straight upward with an initial velocity of 19.6 m/s where the downward acceleration due to gravity is - 9.81 m/s2 What time interval elapses between the rocks being thrown and its return to the original launch point? a. 10.0 s c. 8.00 s b. 4.0 s d. 2.00 s __d__ 22. A mode ...
... __b__ 21. A rock is thrown straight upward with an initial velocity of 19.6 m/s where the downward acceleration due to gravity is - 9.81 m/s2 What time interval elapses between the rocks being thrown and its return to the original launch point? a. 10.0 s c. 8.00 s b. 4.0 s d. 2.00 s __d__ 22. A mode ...
Phys 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
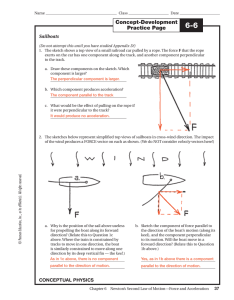
... Solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. 6. Two people are on a carnival ride that uses centripetal and frictional forces to hold its riders in place inside a rotating drum. How do the velocity, acceleration, and force acting on the people differ if one person has twice the mass of ...
... Solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. 6. Two people are on a carnival ride that uses centripetal and frictional forces to hold its riders in place inside a rotating drum. How do the velocity, acceleration, and force acting on the people differ if one person has twice the mass of ...
Powerpoint for Today
... • Does this mean that Newton's laws do not apply? – The acceleration due to Earth's rotation is much smaller than the accelerations we experience from other types of motion. • In most situations, we can assume that Earth is not rotating and, therefore, does count as an inertial reference frame. © 20 ...
... • Does this mean that Newton's laws do not apply? – The acceleration due to Earth's rotation is much smaller than the accelerations we experience from other types of motion. • In most situations, we can assume that Earth is not rotating and, therefore, does count as an inertial reference frame. © 20 ...
pdf file - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... an object to changes in its motion due to a force ► Recall: mass is a scalar quantity Units of mass ...
... an object to changes in its motion due to a force ► Recall: mass is a scalar quantity Units of mass ...
PowerPoints
... • Mass is a property of objects, producing a reluctance to accelerate, called inertia • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No ...
... • Mass is a property of objects, producing a reluctance to accelerate, called inertia • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No ...
Physics - Circular Motion
... circular motion. • Centrifugal force represents the effects of inertia that arise in connection with rotation and which are experienced as an outward force away from the center of rotation. ...
... circular motion. • Centrifugal force represents the effects of inertia that arise in connection with rotation and which are experienced as an outward force away from the center of rotation. ...
Vocabulary Chapter 3: Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... objects through his experiments with inclined planes. He found that balls rolling down inclines rolled faster and faster. Their speed changed as they rolled. He further noticed the balls gained the same amount of velocity in equal time intervals. You experience what Galileo called acceleration every ...
... objects through his experiments with inclined planes. He found that balls rolling down inclines rolled faster and faster. Their speed changed as they rolled. He further noticed the balls gained the same amount of velocity in equal time intervals. You experience what Galileo called acceleration every ...
Liang`s first semester Physics final practice
... acceleration of 7.0 m/s2. This means that during this leap they are pushing against the floor with a force of: a. 2.2 x 10 2 N b. 5.6 x 10 2 N c. 7.8 x 10 2 N d. 1.3 x 10 3 N e. none of these. A rock has been tossed straight upward in this room. What is the net external force acting upon the rock wh ...
... acceleration of 7.0 m/s2. This means that during this leap they are pushing against the floor with a force of: a. 2.2 x 10 2 N b. 5.6 x 10 2 N c. 7.8 x 10 2 N d. 1.3 x 10 3 N e. none of these. A rock has been tossed straight upward in this room. What is the net external force acting upon the rock wh ...
Newton’s 3 Laws and Free Body Diagrams
... in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? ...
... in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? ...
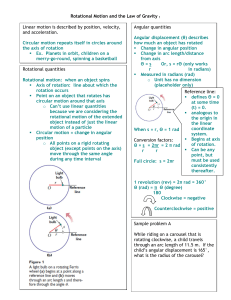
Circular Motion (AIS).
... Objects moving in circular (or nearly circular) paths are often measured in radians rather than degrees. In the diagram, the angle θ, in radians, is defined as follows ...
... Objects moving in circular (or nearly circular) paths are often measured in radians rather than degrees. In the diagram, the angle θ, in radians, is defined as follows ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... Newton’s second law applies. – For example, a “stationary” reference frame or one that moves with constant velocity. – This is sort of a circular argument but it is still useful. ...
... Newton’s second law applies. – For example, a “stationary” reference frame or one that moves with constant velocity. – This is sort of a circular argument but it is still useful. ...
File
... I will be able to Define the force due to gravity. State the 2 key factors that the amount of gravitational force depends upon. Describe how gravitational force changes, as it relates to the mass of and distance between 2 objects. Explain why gravity is a long range force effecting the motio ...
... I will be able to Define the force due to gravity. State the 2 key factors that the amount of gravitational force depends upon. Describe how gravitational force changes, as it relates to the mass of and distance between 2 objects. Explain why gravity is a long range force effecting the motio ...