Newton`s Laws and the Nature of Matter
... Your weight is the upward force exerted on the soles of your feet (if you're standing) by the surface of the Earth. The gravitational force down and your weight (an upwards force) balance and you do not accelerate. You are in equilibrium. Suppose you use M to represent your mass, and m to represent ...
... Your weight is the upward force exerted on the soles of your feet (if you're standing) by the surface of the Earth. The gravitational force down and your weight (an upwards force) balance and you do not accelerate. You are in equilibrium. Suppose you use M to represent your mass, and m to represent ...
013 Energy, Work and Power
... A 80 kg child stands on a trampoline and causes the trampoline to sag by 1 m. a) What is the child’s weight? b) What is the trampoline’s spring constant? ...
... A 80 kg child stands on a trampoline and causes the trampoline to sag by 1 m. a) What is the child’s weight? b) What is the trampoline’s spring constant? ...
TODAY:
... narrow part. (Larger v so more distance covered by the wide end). Now, if you tape two together, at their wide ends, and let them roll along two meter sticks (“tracks”), they will stay stably on the tracks. Why? When they roll off center, they self-correct: say they roll to the left, then the wider ...
... narrow part. (Larger v so more distance covered by the wide end). Now, if you tape two together, at their wide ends, and let them roll along two meter sticks (“tracks”), they will stay stably on the tracks. Why? When they roll off center, they self-correct: say they roll to the left, then the wider ...
Force and Motion
... Gravity – A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses Law of Universal Gravitation- All objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. The size of the force depends on the masses of the objects and the ...
... Gravity – A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses Law of Universal Gravitation- All objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. The size of the force depends on the masses of the objects and the ...
sept17
... following a straight path. So, at time t = 0 the car’s speed is 0 m/sec. After one second of acceleration, the car’s speed is 10 m/sec (velocity 10 m/sec south). After two seconds, the car’s speed is 20 m/sec. ...
... following a straight path. So, at time t = 0 the car’s speed is 0 m/sec. After one second of acceleration, the car’s speed is 10 m/sec (velocity 10 m/sec south). After two seconds, the car’s speed is 20 m/sec. ...
4, 7, 9, 13, 15 / 2, 6, 17, 18, 24, 29, 41, 48, 51, 54, 74
... The time required for a particle in simple harmonic motion to travel through one complete cycle (the period) is independent of the amplitude of the motion, even though at larger amplitudes the particle travels further. This is possible because, at larger amplitudes, the maximum speed of the particle ...
... The time required for a particle in simple harmonic motion to travel through one complete cycle (the period) is independent of the amplitude of the motion, even though at larger amplitudes the particle travels further. This is possible because, at larger amplitudes, the maximum speed of the particle ...
Ch. 8. Energy
... 12. How do you measure hang time for an athlete who jumped 1 m high? 13. What is the maximum height jumped by an athlete who has a hang time of 0.8 s. ...
... 12. How do you measure hang time for an athlete who jumped 1 m high? 13. What is the maximum height jumped by an athlete who has a hang time of 0.8 s. ...
peden (jp5559) – Simple Harmonic Motion – peden
... An object moves up and down the y-axis with an acceleration given as a function of time t by the expression a = A sin ω t, where A and ω are constants. ...
... An object moves up and down the y-axis with an acceleration given as a function of time t by the expression a = A sin ω t, where A and ω are constants. ...
Ch 5 Work and Energy
... - If you are holding a book still in the air, you are doing no work - If you are sitting in a chair, gravity is doing no work. ...
... - If you are holding a book still in the air, you are doing no work - If you are sitting in a chair, gravity is doing no work. ...
Notes: Position, Displacement, Speed, and Velocity
... Instantaneous Speed: the speed at any instant (in time) o What tool can you use to determine the instantaneous speed of a moving car? ...
... Instantaneous Speed: the speed at any instant (in time) o What tool can you use to determine the instantaneous speed of a moving car? ...
Physics S1 ideas overview (1)
... 57. What is the difference between rotation and revolution? Provide an example of each. 58. A child is on a merry-go-round: which is rotating? Which is revolving? ...
... 57. What is the difference between rotation and revolution? Provide an example of each. 58. A child is on a merry-go-round: which is rotating? Which is revolving? ...
W - crashwhite.com
... W net = ΔK : net work is equal to the change in kinetic energy K = 12 mv 2 : kinetic energy of an object is equal to one-half the mass times velocity squared U = mgh : gravitational potential energy is equal to mass times gravitational acceleration times distance from “ground” K = 12 kx2 : elastic p ...
... W net = ΔK : net work is equal to the change in kinetic energy K = 12 mv 2 : kinetic energy of an object is equal to one-half the mass times velocity squared U = mgh : gravitational potential energy is equal to mass times gravitational acceleration times distance from “ground” K = 12 kx2 : elastic p ...
MA Syllabus Summary Blank
... compare instantaneous and average speed with instantaneous and average velocity ...
... compare instantaneous and average speed with instantaneous and average velocity ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
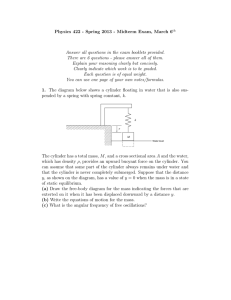
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.