Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
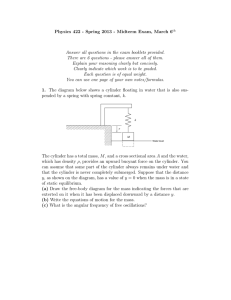
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
waves2 - World of Teaching
... cpforce at the top of the loop ( ST ) • The rest of the cpforce is provided by the weight of the rider ...
... cpforce at the top of the loop ( ST ) • The rest of the cpforce is provided by the weight of the rider ...
Physics Review for Unit Test
... Trajectory: The path of a projectile or other moving body through space. Free fall: The fall of an object such that the only force acting upon it is that of gravity. Explain what a launch angle is. • A launch angle is the initial elevation angle of an object with respect to the ground before it is p ...
... Trajectory: The path of a projectile or other moving body through space. Free fall: The fall of an object such that the only force acting upon it is that of gravity. Explain what a launch angle is. • A launch angle is the initial elevation angle of an object with respect to the ground before it is p ...
F g - Humble ISD
... straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint – As l ...
... straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint – As l ...
Unit 06 Test Study Guide Part I. Force and Motion Review the Unit
... Force = mass x acceleration; this law shows the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. 6. What causes the force (weight) of an object at rest to increase as its mass increases, if the object is at rest? The acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s/s) acts on the object’s mass, increasing its fo ...
... Force = mass x acceleration; this law shows the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. 6. What causes the force (weight) of an object at rest to increase as its mass increases, if the object is at rest? The acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s/s) acts on the object’s mass, increasing its fo ...
Newton`s Laws - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... An inertial frame is either at rest or in uniform motion but there can be no acceleration A non-inertial frame of reference is one in which Newton’s Laws are not valid Accelerating frames of reference are always noninertial ...
... An inertial frame is either at rest or in uniform motion but there can be no acceleration A non-inertial frame of reference is one in which Newton’s Laws are not valid Accelerating frames of reference are always noninertial ...
Rotational Motion Test Review
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
Motion
... mi/hr, but what is average velocity? Since we start and stop at the same location, displacement is zero Velocity must also be zero. ...
... mi/hr, but what is average velocity? Since we start and stop at the same location, displacement is zero Velocity must also be zero. ...
MT 5500 - Loyola College
... 13. Derive the Cartesian equation of a catenary. 14. Show that the resultant of two simple harmonic motions of the same period in the same straight line is also a simple harmonic motion. Find the amplitude and epoch. 15. Obtain the radial and transverse components of velocity and acceleration in pol ...
... 13. Derive the Cartesian equation of a catenary. 14. Show that the resultant of two simple harmonic motions of the same period in the same straight line is also a simple harmonic motion. Find the amplitude and epoch. 15. Obtain the radial and transverse components of velocity and acceleration in pol ...
Unit Objectives
... a dimensional check on any equation. 3. Know the three most common basic physical quantities in physics and their units. 4. Be familiar with the most common metric prefixes. 5. Be able to perform calculations, using proper significant digits and scientific notation. 6. Convert quantities from one sy ...
... a dimensional check on any equation. 3. Know the three most common basic physical quantities in physics and their units. 4. Be familiar with the most common metric prefixes. 5. Be able to perform calculations, using proper significant digits and scientific notation. 6. Convert quantities from one sy ...
Day 3
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.























