Chapter 7 Rotational Motion 7.1 Angular Quantities Homework # 51
... c.) What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? d.) How long did it take to reach this speed? 05. A train that has wheels with a diameter of 91.44 cm (36 inches used for 100 ton capacity cars) slows down from 82.5 km/h to 32.5 km/h as the train approaches a town. The wheels of the train make 95. ...
... c.) What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? d.) How long did it take to reach this speed? 05. A train that has wheels with a diameter of 91.44 cm (36 inches used for 100 ton capacity cars) slows down from 82.5 km/h to 32.5 km/h as the train approaches a town. The wheels of the train make 95. ...
Chapter 3
... 10. Which of the following is a type of linear motion? a. angular motion b. curvilinear motion c. angulolinear motion d. curviangular motion 11. Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between linear and angular motion? a. angular motion of the joints produces linear ...
... 10. Which of the following is a type of linear motion? a. angular motion b. curvilinear motion c. angulolinear motion d. curviangular motion 11. Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between linear and angular motion? a. angular motion of the joints produces linear ...
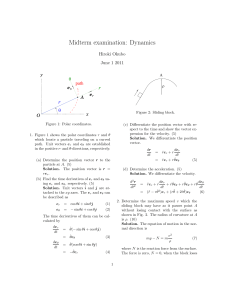
Midterm examination: Dynamics
... 2. Determine the maximum speed v which the sliding block may have as it passes point A without losing contact with the surface as shown in Fig. 2. The radius of curvature at A is ρ. (10) Solution. The equation of motion in the normal direction is ...
... 2. Determine the maximum speed v which the sliding block may have as it passes point A without losing contact with the surface as shown in Fig. 2. The radius of curvature at A is ρ. (10) Solution. The equation of motion in the normal direction is ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... an object and the acceleration. • It states: F = M x A • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ ...
... an object and the acceleration. • It states: F = M x A • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion Section 3
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...
HW6.1 – This is a lot of work!
... WORK (make FBDs with the displacement vector shown clearly in order to calculate work) 1. A student holds her 1.5-kg psychology textbook out of a second floor classroom window until her arm is tired; then she releases it. a) How much work is done on the book by the student in simply holding it out t ...
... WORK (make FBDs with the displacement vector shown clearly in order to calculate work) 1. A student holds her 1.5-kg psychology textbook out of a second floor classroom window until her arm is tired; then she releases it. a) How much work is done on the book by the student in simply holding it out t ...
8-7 Gravitational Potential Energy and Escape Velocity 8
... A box of empty film canisters is allowed to fall from a rocket traveling outward from Earth at a speed of 1800 m/s when 1600 km above the Earth’s surface. The package eventually falls to the Earth. Estimate its speed just before impact. ...
... A box of empty film canisters is allowed to fall from a rocket traveling outward from Earth at a speed of 1800 m/s when 1600 km above the Earth’s surface. The package eventually falls to the Earth. Estimate its speed just before impact. ...
HP UNIT 5 work & energy - student handout
... A conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken…only matters on initial and final positions. ie; Gravity & spring force. A non-conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a ...
... A conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken…only matters on initial and final positions. ie; Gravity & spring force. A non-conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a ...
lecture 18 mechanical energy
... A block of mass m = 1.6 kg slides with an initial speed of v0 = 0.950 m/s on a frictionless, horizontal surface until it encounters a spring with a force constant of k = 902 N/m. The block comes to rest after compressing the spring by x = 4.00 cm. Find the spring potential energy U, kinetic energy o ...
... A block of mass m = 1.6 kg slides with an initial speed of v0 = 0.950 m/s on a frictionless, horizontal surface until it encounters a spring with a force constant of k = 902 N/m. The block comes to rest after compressing the spring by x = 4.00 cm. Find the spring potential energy U, kinetic energy o ...
ANSWERS FOR AMSTI FINAL EXAM
... 27. OCCURS WHEN ACTING FORCES CAUSE THE SPEED OF A FALLING OBJECT TO REMAIN CONSTANT. 28. THE FORCE THAT OPPOSES AN OBJECT’S MOVEMENT THROUGH AIR. 29. A NUMBER THAT IS USED TO PREDICT FRICTIONAL FORCES BETWEEN TWO SURFACES. 30. SURFACE TYPES IN CONTACT. 31. OCCURS WHEN TWO OBJECTS RUB AGAINST EACH O ...
... 27. OCCURS WHEN ACTING FORCES CAUSE THE SPEED OF A FALLING OBJECT TO REMAIN CONSTANT. 28. THE FORCE THAT OPPOSES AN OBJECT’S MOVEMENT THROUGH AIR. 29. A NUMBER THAT IS USED TO PREDICT FRICTIONAL FORCES BETWEEN TWO SURFACES. 30. SURFACE TYPES IN CONTACT. 31. OCCURS WHEN TWO OBJECTS RUB AGAINST EACH O ...
Harmonic Motion
... The motion can be described as a function of time. • x = r cos wt • y = r sin wt ...
... The motion can be described as a function of time. • x = r cos wt • y = r sin wt ...
PHYS 101 Lecture 10 - Simon Fraser University
... The total work is zero, since the forces cancel out in the direction of motion. Similarly, ΔK = 0 since the object is at rest at the top and bottom. The work we have done on the block has not resulted in a change in kinetic energy! Even though this is a nice consistent picture, we find it unsatisfac ...
... The total work is zero, since the forces cancel out in the direction of motion. Similarly, ΔK = 0 since the object is at rest at the top and bottom. The work we have done on the block has not resulted in a change in kinetic energy! Even though this is a nice consistent picture, we find it unsatisfac ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.