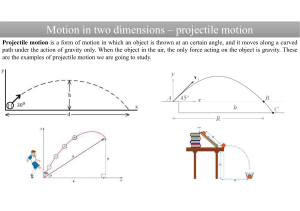
Chapter 2 - Forces In Motion
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
... All forces act in pairs called action-reaction force pairs If a force is exerted, another force occurs that is equal in size and opposite in direction to the first. ...
forces and the laws of motion - PAMS-Doyle
... Momentum • Momentum Mass * Velocity • Measured in kg•m/s • Law of conservation of momentum the total momentum of any group of objects remains the same unless outside forces act on the objects. • Friction is an example of an outside force ...
... Momentum • Momentum Mass * Velocity • Measured in kg•m/s • Law of conservation of momentum the total momentum of any group of objects remains the same unless outside forces act on the objects. • Friction is an example of an outside force ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... This is an introductory college physics course which uses basic calculus in developing some of the fundamental concepts of classical physics. Topics covered are measurement, vector manipulation (including unit vector notation), linear kinematics and dynamics, motion in a plane, and conservation of e ...
... This is an introductory college physics course which uses basic calculus in developing some of the fundamental concepts of classical physics. Topics covered are measurement, vector manipulation (including unit vector notation), linear kinematics and dynamics, motion in a plane, and conservation of e ...
Lecture15
... is opposite the displacement • An object moves with simple harmonic motion whenever its acceleration is proportional to its position and is oppositely directed to the displacement from equilibrium ...
... is opposite the displacement • An object moves with simple harmonic motion whenever its acceleration is proportional to its position and is oppositely directed to the displacement from equilibrium ...
ppt
... Force equation So now, assuming we’ve set up object space right (centre of mass at 0), F=MA If there are no external forces, have F=0 Internal forces must balance out, opposite and equal Thus A=0, thus V=constant ...
... Force equation So now, assuming we’ve set up object space right (centre of mass at 0), F=MA If there are no external forces, have F=0 Internal forces must balance out, opposite and equal Thus A=0, thus V=constant ...
Skills
... In Exercises #2 and #3, the elimination occurred by simply adding the two equations together because one term in the second equation was the additive inverse of a term in the first equation. When this isn’t the case, manipulation of the equations must happen using the multiplication property of equa ...
... In Exercises #2 and #3, the elimination occurred by simply adding the two equations together because one term in the second equation was the additive inverse of a term in the first equation. When this isn’t the case, manipulation of the equations must happen using the multiplication property of equa ...
AP Physics Course Syllabus - Greensburg Salem School District
... college course. Topics covered include mechanics, thermodynamics, electricity and magnetism, waves and optics, and modern physics. Emphasis is placed on both concept development and complex problem solving. Students will work individually and in groups to complete laboratory investigations and probl ...
... college course. Topics covered include mechanics, thermodynamics, electricity and magnetism, waves and optics, and modern physics. Emphasis is placed on both concept development and complex problem solving. Students will work individually and in groups to complete laboratory investigations and probl ...
Newton`s second law File
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION states: ...
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION states: ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d / t 3. Constant speed – speed stays the same the entire trip 4. Average speed – total distance divided by t ...
... 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d / t 3. Constant speed – speed stays the same the entire trip 4. Average speed – total distance divided by t ...
SI Physics 221
... 4) A charged particle carrying charge of -1μC, enters a uniform field of 20N/C. The particle’s motion is perpendicular to the field it enters. If the particle has an initial height of 2 meters, and is traveling at a velocity of 80m/s how far does it travel before it hits the ground? Review Questions ...
... 4) A charged particle carrying charge of -1μC, enters a uniform field of 20N/C. The particle’s motion is perpendicular to the field it enters. If the particle has an initial height of 2 meters, and is traveling at a velocity of 80m/s how far does it travel before it hits the ground? Review Questions ...
1.3 Solving Linear Equations
... sides of an equation by the same term. • Division prop of = - can divide both sides of an equation by the same term. ** So basically, whatever you do to one side of an equation, you MUST do to the other! ...
... sides of an equation by the same term. • Division prop of = - can divide both sides of an equation by the same term. ** So basically, whatever you do to one side of an equation, you MUST do to the other! ...
DYNAMICS
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
Lesson 25 – PowerPoint
... acceleration equation and calculate the velocity for an object under constant acceleration. ...
... acceleration equation and calculate the velocity for an object under constant acceleration. ...
AP Physics B Syllabus
... At appropriate points in the course, each of the above laboratory investigations will be presented to the students in the form of a problem. Very often a demonstration of a physical phenomenon will be presented to the class and an explanation of the event will be requested. Students will be encoura ...
... At appropriate points in the course, each of the above laboratory investigations will be presented to the students in the form of a problem. Very often a demonstration of a physical phenomenon will be presented to the class and an explanation of the event will be requested. Students will be encoura ...
Forces and Motion Learning Outcomes
... 16. Friction is a force that acts between any to surfaces in contact with one another by preventing or slowing motion 17. Matter is everything that takes up space and has mass Ex. Living and non living materials 18. Motion is a change in position 19. Sir Isaac Newton, a 17th century English physicis ...
... 16. Friction is a force that acts between any to surfaces in contact with one another by preventing or slowing motion 17. Matter is everything that takes up space and has mass Ex. Living and non living materials 18. Motion is a change in position 19. Sir Isaac Newton, a 17th century English physicis ...