Algebra 2 Lesson 7
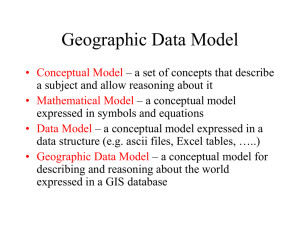
... What is a Radical Equation? • A Radical Equation is an equation that has a variable in a radicand or has a variable with a rational exponent. ...
... What is a Radical Equation? • A Radical Equation is an equation that has a variable in a radicand or has a variable with a rational exponent. ...
Lecture powerpoint
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ F force causes acceleration M mass resists acceleration ...
... • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ F force causes acceleration M mass resists acceleration ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... should not move. This does not happen because action and reaction forces do not _________ ...
... should not move. This does not happen because action and reaction forces do not _________ ...
NewtonDefns
... is the subject that comprises all the manual arts, from which the subject of mechanics as a whole has adopted its name. • But since those who practice the art do not generally work with a high degree of exactness, the whole subject of mechanics is distinguished from geometry by the attribution of ex ...
... is the subject that comprises all the manual arts, from which the subject of mechanics as a whole has adopted its name. • But since those who practice the art do not generally work with a high degree of exactness, the whole subject of mechanics is distinguished from geometry by the attribution of ex ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC ANALOGUE OF A POINT STRUCTURAL
... Since the early studies of Schrödinger [1] on building a classical theory of a particle with spin, a lot of work has been carried out in order to develop models and to analyze physical implications of such particle. The main difficulty of the large number of theoretical studies devoted to this matte ...
... Since the early studies of Schrödinger [1] on building a classical theory of a particle with spin, a lot of work has been carried out in order to develop models and to analyze physical implications of such particle. The main difficulty of the large number of theoretical studies devoted to this matte ...
Content Area: Newtonian Mechanics Unit: 5 Topic (s): Circular
... 4. Combine concepts of weight and universal gravitation to determine the local gravitational acceleration (aka: gravitational field) 5. Distinguish between periodic motion and simple harmonic motion 6. Analyze the acceleration and velocity of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion 7. Solve prob ...
... 4. Combine concepts of weight and universal gravitation to determine the local gravitational acceleration (aka: gravitational field) 5. Distinguish between periodic motion and simple harmonic motion 6. Analyze the acceleration and velocity of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion 7. Solve prob ...
Unit 7 Bell Ringers - Trimble County Schools
... and swung. If the string breaks at Point A, in which direction will the ball be traveling an instant later? ...
... and swung. If the string breaks at Point A, in which direction will the ball be traveling an instant later? ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ F force causes acceleration M mass resists acceleration ...
... • Another form of this equation says: • A= ___ F force causes acceleration M mass resists acceleration ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of one meter per second squared. ...
... or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of one meter per second squared. ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... Sir Isaac Newton • Lived from 1642-1727 in England. • He was a dedicated physicist and mathematician, and is considered to be one of the most brilliant scientists of all time. • He is most famous for his three laws of motion and his universal law of gravitation, but did much more like inventing cal ...
... Sir Isaac Newton • Lived from 1642-1727 in England. • He was a dedicated physicist and mathematician, and is considered to be one of the most brilliant scientists of all time. • He is most famous for his three laws of motion and his universal law of gravitation, but did much more like inventing cal ...
Newton`s First Law
... velocity will naturally remain constant. This means that if an object is moving along, untouched by a force of any kind, it will continue to move along in a perfectly straight line at a constant speed. ...
... velocity will naturally remain constant. This means that if an object is moving along, untouched by a force of any kind, it will continue to move along in a perfectly straight line at a constant speed. ...
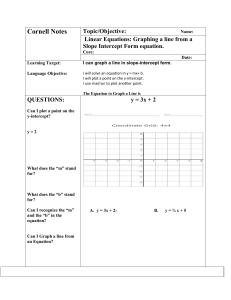
Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Name: Linear Equations: Graphing a
... I will solve an equation in y = mx+ b. I will plot a point on the y-intercept. I use rise/run to plot another point. The Equation to Graph a Line is ...
... I will solve an equation in y = mx+ b. I will plot a point on the y-intercept. I use rise/run to plot another point. The Equation to Graph a Line is ...