Newtons 1st Law notes
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
... Balanced Forces Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
PDF#10
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
Document
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
Unit 1
... If we tie a mass to a string and swing the mass around in a circle, some force is required to keep the mass from flying off in a straight line This is a centripetal force, a force directed towards the center of the system The tension in the string provides this force. Newton determined that this for ...
... If we tie a mass to a string and swing the mass around in a circle, some force is required to keep the mass from flying off in a straight line This is a centripetal force, a force directed towards the center of the system The tension in the string provides this force. Newton determined that this for ...
Physics 235 Chapter 8 Central-Force Motion
... Two-Body Systems with a Central Force: Conserved Quantities Since we have assumed that the potential U depends only on the relative position between the two objects, the system poses spherical symmetry. As we have seen in Chapter 7, this type of symmetry implies that the angular momentum of the syst ...
... Two-Body Systems with a Central Force: Conserved Quantities Since we have assumed that the potential U depends only on the relative position between the two objects, the system poses spherical symmetry. As we have seen in Chapter 7, this type of symmetry implies that the angular momentum of the syst ...
Document
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
Kinetics: Work, Energy and Power 193 8.6 Spatial (3D) Mechanical
... where q and w are the 3D angular displacement and angular velocities of the rigid body, respectively. Note, even though angular displacement is not a vector, q, represents the angular displacement of the body about each axis. In other words, qx, represents the amount of rotation about the X axis. Th ...
... where q and w are the 3D angular displacement and angular velocities of the rigid body, respectively. Note, even though angular displacement is not a vector, q, represents the angular displacement of the body about each axis. In other words, qx, represents the amount of rotation about the X axis. Th ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Date ___________ Algebra I Period ___________ How do we “solve” a system of equations??? By finding the point where two or more equations ________________. ...
... Date ___________ Algebra I Period ___________ How do we “solve” a system of equations??? By finding the point where two or more equations ________________. ...
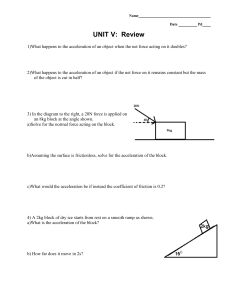
Unit 5 Review
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Chapter 4 Newtons Laws
... ability to change motion. • Objects need a force applied to them in order to change their motion. • A force is also called a ...
... ability to change motion. • Objects need a force applied to them in order to change their motion. • A force is also called a ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... ie: the greater the mass, the greater the inertia an object possesses, the harder it is to change the object’s motion ...
... ie: the greater the mass, the greater the inertia an object possesses, the harder it is to change the object’s motion ...
Block 3 Drill Set - PHYS 242, General Physics II
... Slide this paper under the door of Marteena 308 any time before 7:50 AM Friday, February 3, or give it to me in Marteena 312 by 8:00 AM that day. Use one different equation from the Block 3 objectives for each problem. 1. An electric field does 9.63 MeV of work in moving a very small charged particl ...
... Slide this paper under the door of Marteena 308 any time before 7:50 AM Friday, February 3, or give it to me in Marteena 312 by 8:00 AM that day. Use one different equation from the Block 3 objectives for each problem. 1. An electric field does 9.63 MeV of work in moving a very small charged particl ...
0002_hsm11a1_te_0201tr.indd
... a. Write and solve an equation to find the average number of people the center is planning to feed each hour. b. During the first hour and a half, the center fed 270 people. Write and solve ...
... a. Write and solve an equation to find the average number of people the center is planning to feed each hour. b. During the first hour and a half, the center fed 270 people. Write and solve ...
Science GHST Review
... Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation (EM) EM spectrum shows the forms of radiation in order of increasing frequency and decreasing ...
... Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation (EM) EM spectrum shows the forms of radiation in order of increasing frequency and decreasing ...
L#4
... with a bead of mass m free to slide along the hoop. We wish to determine the ODE that governs θ(t) This problem is a natural for spherical coordinates. The bead has spherical coordinates: r(t) = R constant. It has azimuthal coordinate φ = Ω t specified. Its other spherical coordinate is θ(t) which ...
... with a bead of mass m free to slide along the hoop. We wish to determine the ODE that governs θ(t) This problem is a natural for spherical coordinates. The bead has spherical coordinates: r(t) = R constant. It has azimuthal coordinate φ = Ω t specified. Its other spherical coordinate is θ(t) which ...