Newton`s Laws Webquest
... _________________ is a push or pull on an object. ____________________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ____________________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in _____ ...
... _________________ is a push or pull on an object. ____________________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ____________________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in _____ ...
File - Mr. Purdy`s Rocket Science
... Describing and Measuring Motion • A reference point is a place or object used for comparison to determine if something is in motion. • An object is in motion if it changes position relative to the reference point. ...
... Describing and Measuring Motion • A reference point is a place or object used for comparison to determine if something is in motion. • An object is in motion if it changes position relative to the reference point. ...
Lesson 18 notes – Orbits - science
... An orbit is the (usually elliptical) path described by one celestial body in its revolution about another. The time it takes for one complete revolution is called the period T. The closer a body is to the object it is orbiting the faster it will go. This is because as you move closer to an object wi ...
... An orbit is the (usually elliptical) path described by one celestial body in its revolution about another. The time it takes for one complete revolution is called the period T. The closer a body is to the object it is orbiting the faster it will go. This is because as you move closer to an object wi ...
Circular Motion & Gravity
... some force is pulling it away from the axis of rotation • Thus, inertia is often mistaken for “centrifugal force” ...
... some force is pulling it away from the axis of rotation • Thus, inertia is often mistaken for “centrifugal force” ...
Step 1
... (get rid of) a variable. To simply add this time will not eliminate a variable. If there was a –2x in the 1st equation, the x’s would be eliminated when we add. So we will multiply the 1st equation by a – 2. ...
... (get rid of) a variable. To simply add this time will not eliminate a variable. If there was a –2x in the 1st equation, the x’s would be eliminated when we add. So we will multiply the 1st equation by a – 2. ...
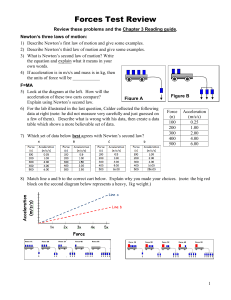
1020 Test review
... That force is the ball’s weight Since earth’s gravity produces the ball’s weight, that weight points toward the earth’s center The ball’s weight causes it to accelerate toward the earth’s center ...
... That force is the ball’s weight Since earth’s gravity produces the ball’s weight, that weight points toward the earth’s center The ball’s weight causes it to accelerate toward the earth’s center ...
Newton`s Three Laws
... This means that for every force there is a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. That is to say that whenever an object pushes another object it gets pushed back in the opposite direction equally hard. ...
... This means that for every force there is a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. That is to say that whenever an object pushes another object it gets pushed back in the opposite direction equally hard. ...
Motion of a charged particle under the action of a magnetic field
... You place a slab of copper, 2.0 mm thick and 1.5 cm wide, in a uniform magnetic field with magnetic field with magnitude 0.40 T. When you run a 75-A current in the +x direction, you find by careful measurement that the potential at the left side of the slab is 0.81V higher than at the right side o ...
... You place a slab of copper, 2.0 mm thick and 1.5 cm wide, in a uniform magnetic field with magnetic field with magnitude 0.40 T. When you run a 75-A current in the +x direction, you find by careful measurement that the potential at the left side of the slab is 0.81V higher than at the right side o ...
forces - jpsaos
... Kinds of Forces Gravitational Force: Attractive force that exists between all objects. The gravitational force between the Earth and the moon keeps the moon in orbit. It may be the most evident but it is the weakest of all the forces. ...
... Kinds of Forces Gravitational Force: Attractive force that exists between all objects. The gravitational force between the Earth and the moon keeps the moon in orbit. It may be the most evident but it is the weakest of all the forces. ...
Solutions for class #1 from Yosunism website Problem 4.
... There is no tangential acceleration (since otherwise it would slide and not roll---the frictional force balances the forward acceleration force). However, there is a centripetal acceleration that pulls the particles back in a circle, as in choice (C). This acceleration propels the tangential velocit ...
... There is no tangential acceleration (since otherwise it would slide and not roll---the frictional force balances the forward acceleration force). However, there is a centripetal acceleration that pulls the particles back in a circle, as in choice (C). This acceleration propels the tangential velocit ...
Scalar Field Theories with Screening Mechanisms
... the ratio of the gravitational coupling to the scalar coupling and (ϕ∞ − ϕc )/M is the depth of the scalars potential well. If M ∼ Mp then this expression is just the ratio of the force of the scalar field to the force of gravity and so, for large objects, the scalar force must be weaker than gravit ...
... the ratio of the gravitational coupling to the scalar coupling and (ϕ∞ − ϕc )/M is the depth of the scalars potential well. If M ∼ Mp then this expression is just the ratio of the force of the scalar field to the force of gravity and so, for large objects, the scalar force must be weaker than gravit ...
The First Law of Motion
... -- weight -- the amount of mass PLUS the force of gravity acting on an object -Force is calculated using units of _____________ AND ___________ (or g) these units combine into a unit called a _______________ (mass + acceleration) D. The Second Law of Motion ***The acceleration of an object is in t ...
... -- weight -- the amount of mass PLUS the force of gravity acting on an object -Force is calculated using units of _____________ AND ___________ (or g) these units combine into a unit called a _______________ (mass + acceleration) D. The Second Law of Motion ***The acceleration of an object is in t ...
Jeopardy Motion Newtons Review
... meters per second. The projectile arrives at its maximum altitude in 3.0 seconds. As the projectile rises and then falls back to the ground, its acceleration a: decreases, then increases b: increases, then decreases c: increase only d: remains the Same ...
... meters per second. The projectile arrives at its maximum altitude in 3.0 seconds. As the projectile rises and then falls back to the ground, its acceleration a: decreases, then increases b: increases, then decreases c: increase only d: remains the Same ...
Today`s Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... • Describe the Celestial Sphere and how astronomers use angular measurement to locate objects in the night sky. • Account for the apparent motions of the Sun and the stars in terms of the actual motion of the Earth. Explain why our planet has seasons. • Understand the changing appearance of the Moon ...
... • Describe the Celestial Sphere and how astronomers use angular measurement to locate objects in the night sky. • Account for the apparent motions of the Sun and the stars in terms of the actual motion of the Earth. Explain why our planet has seasons. • Understand the changing appearance of the Moon ...