Laws of Motion - SCHOOLinSITES
... tendency of an object to resist being moved or if object is moving, to resist a change in speed or direction until an outside force acts on object. All objects resist changes in motion related to an object’s mass. Objects with small mass have less inertia than objects with large mass ...
... tendency of an object to resist being moved or if object is moving, to resist a change in speed or direction until an outside force acts on object. All objects resist changes in motion related to an object’s mass. Objects with small mass have less inertia than objects with large mass ...
Lecture Notes: Chapter 2 Motion
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
P20 Course Summary
... 20–C1.1k describe uniform circular motion as a special case of two-dimensional motion 20–C1.2k explain, qualitatively and quantitatively, that the acceleration in uniform circular motion is directed toward the centre of a circle 20–C1.3k explain, quantitatively, the relationships among speed, freque ...
... 20–C1.1k describe uniform circular motion as a special case of two-dimensional motion 20–C1.2k explain, qualitatively and quantitatively, that the acceleration in uniform circular motion is directed toward the centre of a circle 20–C1.3k explain, quantitatively, the relationships among speed, freque ...
POSITION-TIME GRAPHS WORKSHEET #2
... 1. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its greatest speed? 2. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its least (nonzero) speed? 3. During which time interval(s) (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart at rest? 4. During w ...
... 1. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its greatest speed? 2. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its least (nonzero) speed? 3. During which time interval(s) (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart at rest? 4. During w ...
Now
... The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitational pull on another object. • Small mass = small pull • Large mass = large pull ...
... The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitational pull on another object. • Small mass = small pull • Large mass = large pull ...
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics
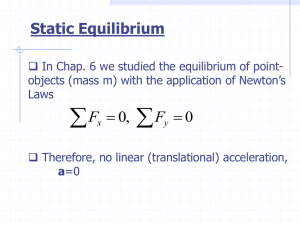
... In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
... In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
Physics Level Force and Motion Review 2010
... Matching: Match the term to the correct definition. 1. Normal Force (FN) a. When all forces are balanced and acceleration is zero 2. Net Force (Fnet) b. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force 3. g c. Objects remain at rest or moving at a constant velocity unless acted ...
... Matching: Match the term to the correct definition. 1. Normal Force (FN) a. When all forces are balanced and acceleration is zero 2. Net Force (Fnet) b. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force 3. g c. Objects remain at rest or moving at a constant velocity unless acted ...
Document
... (hydrochloric acid) solution for a chemistry experiment. There is a bottle of 10% HCl solution and a bottle of 40% HCl solution in the lab. How much of each solution should he use to obtain the required amount of 25% HCl solution? A. 0 mL of 10% solution, 10 mL of 40% solution B. 6 mL of 10% solutio ...
... (hydrochloric acid) solution for a chemistry experiment. There is a bottle of 10% HCl solution and a bottle of 40% HCl solution in the lab. How much of each solution should he use to obtain the required amount of 25% HCl solution? A. 0 mL of 10% solution, 10 mL of 40% solution B. 6 mL of 10% solutio ...
Document
... the dependence from the distance “r”: this is 1/r in one case and 1/r2 in the other. Note moreover that B being equal to the vector product of ε’ and E must be orthogonal to both. Another remark: E and B are orthogonal….. The wave parts of E and B, of course! For the other parts, customarily called ...
... the dependence from the distance “r”: this is 1/r in one case and 1/r2 in the other. Note moreover that B being equal to the vector product of ε’ and E must be orthogonal to both. Another remark: E and B are orthogonal….. The wave parts of E and B, of course! For the other parts, customarily called ...
Ch 3 semester 2 review study guide
... 34. An object’s __________________ is the measure of the force of gravity on that object. 35. The amount of gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the ______________ between them. 36. Weight is measured in units called _______________, while mass is measured in units cal ...
... 34. An object’s __________________ is the measure of the force of gravity on that object. 35. The amount of gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the ______________ between them. 36. Weight is measured in units called _______________, while mass is measured in units cal ...
motion
... 8.How high must a body be lifted to gain an amount of p.energy equal to the K.E it has ,when moving at speed 20m/s .[g = 9.8m/s2]Ans. 20.4m 9.The force constant of a spring is 60N/m.If abullet of 30gm is shot by the gun ,so that its spring is compressed by 12cm. calculate the velocity of the ball?[ ...
... 8.How high must a body be lifted to gain an amount of p.energy equal to the K.E it has ,when moving at speed 20m/s .[g = 9.8m/s2]Ans. 20.4m 9.The force constant of a spring is 60N/m.If abullet of 30gm is shot by the gun ,so that its spring is compressed by 12cm. calculate the velocity of the ball?[ ...