Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on an object 4. Explain the cause of acceleration of any object. 5. Explain the difference b ...
... 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on an object 4. Explain the cause of acceleration of any object. 5. Explain the difference b ...
Circular.Rotary Motion
... causes rotation. • The magnitude of torque is the product of the force and the lever arm. Because force is measured in newtons, and distance is measured in meters, torque is measured in newton-meters ...
... causes rotation. • The magnitude of torque is the product of the force and the lever arm. Because force is measured in newtons, and distance is measured in meters, torque is measured in newton-meters ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Newton’s First Law of Motion “Objects tend to keep on doing whatever it is that they are doing unless another force acts on them” The Law of Inertia!! ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion “Objects tend to keep on doing whatever it is that they are doing unless another force acts on them” The Law of Inertia!! ...
momentum
... Newton built upon the work of others... -1686, Sir Issac Newton publishes his book Principia in which he describes 3 laws relating forces to motion of objects -did not discover all 3 laws himself, but combined previous discoveries by other scientists and explained them in a way that people could un ...
... Newton built upon the work of others... -1686, Sir Issac Newton publishes his book Principia in which he describes 3 laws relating forces to motion of objects -did not discover all 3 laws himself, but combined previous discoveries by other scientists and explained them in a way that people could un ...
Worksheet 4
... The startup screen from “One-D Motion” on the display of the axis which runs from 30 m at the bottom of the screen to +=30m at the top. Notice that the body starts at x = 0 at t = 0. Set the force to +4.00 N and the mass of the body to 2.00 kg. Make sure the axes are displayed and the force is on. R ...
... The startup screen from “One-D Motion” on the display of the axis which runs from 30 m at the bottom of the screen to +=30m at the top. Notice that the body starts at x = 0 at t = 0. Set the force to +4.00 N and the mass of the body to 2.00 kg. Make sure the axes are displayed and the force is on. R ...
Newton Laws Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward force on the exhaust gases. The gases exert an equal and opposite upward force on the rocket. c. When a swimmer pushe ...
... objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward force on the exhaust gases. The gases exert an equal and opposite upward force on the rocket. c. When a swimmer pushe ...
Chapter 10
... Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit of torque: (N.m) Sign of : Positive torque for counterclockwise rotation : Negative torque for clockwise rotation ...
... Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit of torque: (N.m) Sign of : Positive torque for counterclockwise rotation : Negative torque for clockwise rotation ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... should NOT be used!!) At time t = 0, it starts from rest (initial angular velocity ω0 = 0) & begins to rotate counterclockwise about an axis passing through center of the sphere & perpendicular to the page. The figure looks down at the rotation plane, with rotation in the counter-clockwise direction ...
... should NOT be used!!) At time t = 0, it starts from rest (initial angular velocity ω0 = 0) & begins to rotate counterclockwise about an axis passing through center of the sphere & perpendicular to the page. The figure looks down at the rotation plane, with rotation in the counter-clockwise direction ...
Newton s Second and Third Laws and Gravity
... lifeline breaks, your jets run out of fuel, your radio goes dead, and you miss the shuttle. To get back safely, you should: 1) use a swimming motion with your arms and legs 2) throw the hammer at the shuttle to get someone s attention 3) throw the hammer away from the shuttle 4) make a hammering mot ...
... lifeline breaks, your jets run out of fuel, your radio goes dead, and you miss the shuttle. To get back safely, you should: 1) use a swimming motion with your arms and legs 2) throw the hammer at the shuttle to get someone s attention 3) throw the hammer away from the shuttle 4) make a hammering mot ...
PHY820 Homework Set 5
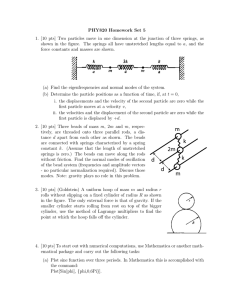
... modes. Note: gravity plays no role in this problem. 3. [10 pts] (Goldstein) A uniform hoop of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on a fixed cylinder of radius R as shown in the figure. The only external force is that of gravity. If the smaller cylinder starts rolling from rest on top of the ...
... modes. Note: gravity plays no role in this problem. 3. [10 pts] (Goldstein) A uniform hoop of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on a fixed cylinder of radius R as shown in the figure. The only external force is that of gravity. If the smaller cylinder starts rolling from rest on top of the ...
Aristotle`s Laws of Motion
... boulder is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force the boulder exerts on the person--EVEN IF THE BOULDER ...
... boulder is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force the boulder exerts on the person--EVEN IF THE BOULDER ...