80 Revision Motion
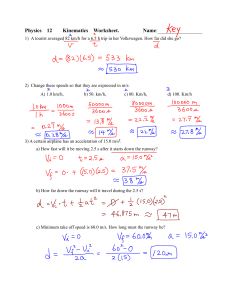
... 16. A pen is dropped from rest and accelerated by gravity on Earth. How far has it dropped in 2s? (ignore air resistance) (A) 9.8m (B) 19.6m (C) 12m (D) Can’t be calculated - insufficient information. 17. A ball is thrown straight upwards into the air at 6m/s. How long before it reaches its peak hei ...
... 16. A pen is dropped from rest and accelerated by gravity on Earth. How far has it dropped in 2s? (ignore air resistance) (A) 9.8m (B) 19.6m (C) 12m (D) Can’t be calculated - insufficient information. 17. A ball is thrown straight upwards into the air at 6m/s. How long before it reaches its peak hei ...
Force and Motion
... 4.5 Free-body Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium Problems we will solve will generally have constant forces and therefore have constant accelerations. This allows us to use the kinematics equations and Newton’s Laws to analyze motion. Free-body Diagrams 1. Sketch the problem. Draw all force vec ...
... 4.5 Free-body Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium Problems we will solve will generally have constant forces and therefore have constant accelerations. This allows us to use the kinematics equations and Newton’s Laws to analyze motion. Free-body Diagrams 1. Sketch the problem. Draw all force vec ...
Force and Motion - Derry Area School District
... 4.5 Free-body Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium Problems we will solve will generally have constant forces and therefore have constant accelerations. This allows us to use the kinematics equations and Newton’s Laws to analyze motion. Free-body Diagrams 1. Sketch the problem. Draw all force vec ...
... 4.5 Free-body Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium Problems we will solve will generally have constant forces and therefore have constant accelerations. This allows us to use the kinematics equations and Newton’s Laws to analyze motion. Free-body Diagrams 1. Sketch the problem. Draw all force vec ...
Kein Folientitel
... Averaging the resulting Vlasov equation gives the evolution for fs0. No assumptions were yet made about the size of the fluctuations, but usually they are assumed to be much smaller than the background. ...
... Averaging the resulting Vlasov equation gives the evolution for fs0. No assumptions were yet made about the size of the fluctuations, but usually they are assumed to be much smaller than the background. ...
4.1 Systems of Linear Equations in two variables
... solve these systems using substitution solve these systems using elimination by addition solve applications of linear systems. ...
... solve these systems using substitution solve these systems using elimination by addition solve applications of linear systems. ...
Linear Constant Coefficients Equations (§ 1.1) Linear Constant
... Theorem (Constant Coefficients) If the constants a, b ∈ R satisfy a 6= 0, then the linear equation y 0 (t) = a y (t) + b has infinitely many solutions, one for each value of c ∈ R, given by b y (t) = c e at − . a ...
... Theorem (Constant Coefficients) If the constants a, b ∈ R satisfy a 6= 0, then the linear equation y 0 (t) = a y (t) + b has infinitely many solutions, one for each value of c ∈ R, given by b y (t) = c e at − . a ...
Chapter 5 Worksheets - School District of La Crosse
... 17. If all the force comes from the right on a tug of war, which way will have the longer arrow? ...
... 17. If all the force comes from the right on a tug of war, which way will have the longer arrow? ...
slide show
... Horizontally: Projectiles move with constant velocity. Vertically: Projectiles accelerate with a constant rate of -9.80 m/s2 or -32.2 ft/s2 ...
... Horizontally: Projectiles move with constant velocity. Vertically: Projectiles accelerate with a constant rate of -9.80 m/s2 or -32.2 ft/s2 ...
UNIVERSITAT POLITÈCNICA DE CATALUNYA
... In that small frequency band the electric susceptibility frequency dependence is assumed to be well described by a Taylor expansion around the carrier frequency roo in which terms up to second order are considered, namely ...
... In that small frequency band the electric susceptibility frequency dependence is assumed to be well described by a Taylor expansion around the carrier frequency roo in which terms up to second order are considered, namely ...
1 - Denton ISD
... The Maplewood Symphony Orchestra sold 146 tickets and collected a total of $1036 in ticket sales. Admission was $5 for children and $8 for adults. Write two equations that would be used to solve the system. Variable: ...
... The Maplewood Symphony Orchestra sold 146 tickets and collected a total of $1036 in ticket sales. Admission was $5 for children and $8 for adults. Write two equations that would be used to solve the system. Variable: ...
Newton`s laws of motion - University of Toronto Physics
... acting on a body determines acceleration, not velocity. This insight leads to Newton's First Law - no force means no acceleration, and hence the body will continue to maintain its velocity. The 'Law of Inertia' apparently occurred to many different natural philosophers independently, for example in ...
... acting on a body determines acceleration, not velocity. This insight leads to Newton's First Law - no force means no acceleration, and hence the body will continue to maintain its velocity. The 'Law of Inertia' apparently occurred to many different natural philosophers independently, for example in ...
0.1 Exponents 0.2 Scientific Notation and Powers of 10 0.3 Algebra
... 4.2 Newton’s First Law Newton’s first law Every object continues either at rest or in constant motion in a straight line, unless it is forced to change that state by forces action on it. An object acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and thus with zero accelerati ...
... 4.2 Newton’s First Law Newton’s first law Every object continues either at rest or in constant motion in a straight line, unless it is forced to change that state by forces action on it. An object acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and thus with zero accelerati ...