Rotational or Angular Motion
... When this skater brings in his arms, he begins to spin faster. He has decreased his radius of rotation, so his moment of inertia is decreased. By the law of conservation of angular momentum, a decrease in moment of inertia means an increase in angular speed. www.youtube.com [Search “one foot spin”] ...
... When this skater brings in his arms, he begins to spin faster. He has decreased his radius of rotation, so his moment of inertia is decreased. By the law of conservation of angular momentum, a decrease in moment of inertia means an increase in angular speed. www.youtube.com [Search “one foot spin”] ...
Preview Sample 1
... 1. The need for precision and exact understanding should be emphasized as the various terms such as speed, velocity, rate, distance, acceleration, and others are presented. Stress the reasoning behind each equation, for example, that velocity is a ratio that describes a property of objects in motion ...
... 1. The need for precision and exact understanding should be emphasized as the various terms such as speed, velocity, rate, distance, acceleration, and others are presented. Stress the reasoning behind each equation, for example, that velocity is a ratio that describes a property of objects in motion ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 12: Keeping momentum
... When a bullet hits the wall, its velocity is very much reduced. The wall does not move, although the force on the ball is the same as the force on the wall (Newton’s 3rd law: Fwall-bullet=-Fbullet-wall). ...
... When a bullet hits the wall, its velocity is very much reduced. The wall does not move, although the force on the ball is the same as the force on the wall (Newton’s 3rd law: Fwall-bullet=-Fbullet-wall). ...
Lecture 21 April 4, 2017
... connection to point P so as to allow torque-free operation. Small ocsillations are considered as usual. In our notation, the equation of motion is ...
... connection to point P so as to allow torque-free operation. Small ocsillations are considered as usual. In our notation, the equation of motion is ...
Physics 2
... Forces and Motion 19. If two objects interact what must the forces be? 20. What is the name given to the force formed by a group of forces working together? 21. How does this cause a change of state of rest: ...
... Forces and Motion 19. If two objects interact what must the forces be? 20. What is the name given to the force formed by a group of forces working together? 21. How does this cause a change of state of rest: ...
Sample Questions
... where L0 = nl0 , and γ, l0 and θ are constants, and L the length of the rubber band. Which of the two possibilities are acceptable? Why? For the acceptable choice, deduce the dependence of the tension f upon T and L/n; that is determine f (T, L/n). 2) The probability of observing a closed equilibrat ...
... where L0 = nl0 , and γ, l0 and θ are constants, and L the length of the rubber band. Which of the two possibilities are acceptable? Why? For the acceptable choice, deduce the dependence of the tension f upon T and L/n; that is determine f (T, L/n). 2) The probability of observing a closed equilibrat ...
Physics 111 Problem Set 8, Chapter 9
... dropped from the same point at t = 100 ms. (a) How far below the release point is the center of mass of the two stones at t = 300 ms? (Neither stone has yet reached the ground.) (b) How fast is the center of mass of the two-stone system moving at that time? ...
... dropped from the same point at t = 100 ms. (a) How far below the release point is the center of mass of the two stones at t = 300 ms? (Neither stone has yet reached the ground.) (b) How fast is the center of mass of the two-stone system moving at that time? ...
V - USU Physics
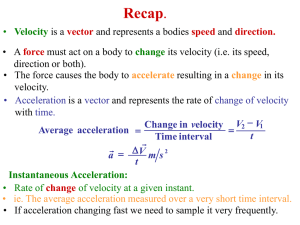
... • Velocity is a vector and represents a bodies speed and direction. • A force must act on a body to change its velocity (i.e. its speed, direction or both). • The force causes the body to accelerate resulting in a change in its velocity. • Acceleration is a vector and represents the rate of change o ...
... • Velocity is a vector and represents a bodies speed and direction. • A force must act on a body to change its velocity (i.e. its speed, direction or both). • The force causes the body to accelerate resulting in a change in its velocity. • Acceleration is a vector and represents the rate of change o ...
Study Guide for Final
... Gravity - the force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass A. The size of gravitational force depends on two things: mass and distance ...
... Gravity - the force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass A. The size of gravitational force depends on two things: mass and distance ...
Forces
... related. More mass = more inertia Inertia is NOT a force. Forces are needed to overcome inertia Newton (1643-1727) expanded on this concept of inertia and developed his 3 laws of motion. These three laws are the foundation for classical mechanics (that is the branch of physics we are studying) ...
... related. More mass = more inertia Inertia is NOT a force. Forces are needed to overcome inertia Newton (1643-1727) expanded on this concept of inertia and developed his 3 laws of motion. These three laws are the foundation for classical mechanics (that is the branch of physics we are studying) ...
07.01.2015 - Erwin Sitompul
... The quantity xm is called the amplitude of the motion. It is a positive constant. The subscript m stands for maximum, because the amplitude is the magnitude of the maximum displacement of the particle in either direction. The cosine function varies between ±1; so the displacement x(t) varies b ...
... The quantity xm is called the amplitude of the motion. It is a positive constant. The subscript m stands for maximum, because the amplitude is the magnitude of the maximum displacement of the particle in either direction. The cosine function varies between ±1; so the displacement x(t) varies b ...
Sects. 4.9 & 4.10
... NOT a derivative of a function Ω(t), which the previous section made a big point does not exist (for finite rotations). Instead, (dΩ/dt) = ω = ratio of 2 infinitesimal quantities. Direction of ω instantaneous axis of rotation direction. ...
... NOT a derivative of a function Ω(t), which the previous section made a big point does not exist (for finite rotations). Instead, (dΩ/dt) = ω = ratio of 2 infinitesimal quantities. Direction of ω instantaneous axis of rotation direction. ...
Photo Assessment Album
... exit tickets to explain what they have learned. Tailor – In order to tailor instruction, I will incorporate Bloom’s Taxonomy and Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences in all of my lessons. This is important in order to meet the various needs of all students. Organize – Managing the Learning Env ...
... exit tickets to explain what they have learned. Tailor – In order to tailor instruction, I will incorporate Bloom’s Taxonomy and Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences in all of my lessons. This is important in order to meet the various needs of all students. Organize – Managing the Learning Env ...
Math 1302 – Test II – Review
... Math 1302 – Test II – Review Tentative review – this will get you started – I need to look over the material Friday and Saturday to make sure I have not forgotten anything else. Check back then and see if anything else has been added. Begins with polynomials – you were tested on but the ideas are ne ...
... Math 1302 – Test II – Review Tentative review – this will get you started – I need to look over the material Friday and Saturday to make sure I have not forgotten anything else. Check back then and see if anything else has been added. Begins with polynomials – you were tested on but the ideas are ne ...
Momentum Notes
... Ex B: Two people are practicing curling. The red stone is sliding on the ice towards the west at 5.0 m/s and has a mass of 17.0 kg. The blue stone has a mass of 20.0 kg and is stationary. After the collision, the red stone moves east at 1.25 m/s. Calculate the velocity of the blue stone after the co ...
... Ex B: Two people are practicing curling. The red stone is sliding on the ice towards the west at 5.0 m/s and has a mass of 17.0 kg. The blue stone has a mass of 20.0 kg and is stationary. After the collision, the red stone moves east at 1.25 m/s. Calculate the velocity of the blue stone after the co ...
Grade 8 – MAFS.8.EE.3.8 MAFS-FSA Resource
... many possible solutions for y = ax + b. Students can start this process by computing on paper first. The Gizmo can then be used to assess student responses - check the “check solution at point” checkbox on the Gizmo. Gizmo snapshots of each solution can be captured. To extend the learning opportunit ...
... many possible solutions for y = ax + b. Students can start this process by computing on paper first. The Gizmo can then be used to assess student responses - check the “check solution at point” checkbox on the Gizmo. Gizmo snapshots of each solution can be captured. To extend the learning opportunit ...