Grade 8 – MAFS.8.EE.3.8 MAFS-FSA Resource
... many possible solutions for y = ax + b. Students can start this process by computing on paper first. The Gizmo can then be used to assess student responses - check the “check solution at point” checkbox on the Gizmo. Gizmo snapshots of each solution can be captured. To extend the learning opportunit ...
... many possible solutions for y = ax + b. Students can start this process by computing on paper first. The Gizmo can then be used to assess student responses - check the “check solution at point” checkbox on the Gizmo. Gizmo snapshots of each solution can be captured. To extend the learning opportunit ...
Sections 6.1-6.5 Review #1
... What point on the image corresponds to this point? ________________ 3. True or False. The image is congruent to the preimage. _______________________ Consider the parabola with the equation y+ 3 = 3(x+ 4)2 4. What is its vertex? __________________ 5. What is the equation of the axis of symmetry? ...
... What point on the image corresponds to this point? ________________ 3. True or False. The image is congruent to the preimage. _______________________ Consider the parabola with the equation y+ 3 = 3(x+ 4)2 4. What is its vertex? __________________ 5. What is the equation of the axis of symmetry? ...
Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces Newton`s Second Law: F=ma In
... What is the direction of the centrifugal force for an object on the Earth? The centrifugal force is a body force and can be combined with the gravity force to give an effective gravity. Effective gravity: g = 9.81 m s-2 at sea level For atmospheric science applications we use effective gravity (g) r ...
... What is the direction of the centrifugal force for an object on the Earth? The centrifugal force is a body force and can be combined with the gravity force to give an effective gravity. Effective gravity: g = 9.81 m s-2 at sea level For atmospheric science applications we use effective gravity (g) r ...
Lecture-15-10
... wooden sign shown below. The left end of the sign is held in place by a bolt, the right end is tied to a rope that makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. If the sign is uniform, 3.20 m long, and has a mass of 16.0 kg, what is (a) the tension in the rope, and (b) the horizontal and vertical com ...
... wooden sign shown below. The left end of the sign is held in place by a bolt, the right end is tied to a rope that makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. If the sign is uniform, 3.20 m long, and has a mass of 16.0 kg, what is (a) the tension in the rope, and (b) the horizontal and vertical com ...
Answers to Sample exam 2004
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
Differential Formulation of Boundary Value Problems
... We are interested in boundary value problems where one must determine a function u representing some meaningful physical variable inside a domain Ω with boundary Γ. We will focus primarily in BVP governed by either Laplace’s Equation ∇2 u = 0 or Poisson’s Equation ∇2 u + f = 0 both subject to suitab ...
... We are interested in boundary value problems where one must determine a function u representing some meaningful physical variable inside a domain Ω with boundary Γ. We will focus primarily in BVP governed by either Laplace’s Equation ∇2 u = 0 or Poisson’s Equation ∇2 u + f = 0 both subject to suitab ...
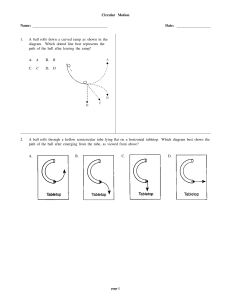
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... D. doubling the mass of one object and doubling the distance between the objects ...
... D. doubling the mass of one object and doubling the distance between the objects ...
Conceptual Physics Ch 7 Newton`s Laws Project
... mass. How can you either increase the force acting on your vehicle or decrease its mass? Draw a diagram of your vehicle. Use labeled arrows to show each place that a force is acting on it. Be sure to include friction forces in your diagram. Brainstorm ways to reduce forces that slow down your vehicl ...
... mass. How can you either increase the force acting on your vehicle or decrease its mass? Draw a diagram of your vehicle. Use labeled arrows to show each place that a force is acting on it. Be sure to include friction forces in your diagram. Brainstorm ways to reduce forces that slow down your vehicl ...
01) A car has a mass of 1000 kilograms
... balanced by a) weight of the displaced air b) force of propelled air c) vertical component of the thrust created by air current striking the lower surface of the plane. d) upward thrust created by the pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the wings. 7. A ball is dropped from a ...
... balanced by a) weight of the displaced air b) force of propelled air c) vertical component of the thrust created by air current striking the lower surface of the plane. d) upward thrust created by the pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the wings. 7. A ball is dropped from a ...
The Nature of Force
... Newton’s third law refers to forces on two different objects. Example: Soccerball If one player hits the ball – force is upward. The ball exerts an equal but opposite downward force on the player. The action and reaction forces are acting on different objects and therefore cannot be added togeth ...
... Newton’s third law refers to forces on two different objects. Example: Soccerball If one player hits the ball – force is upward. The ball exerts an equal but opposite downward force on the player. The action and reaction forces are acting on different objects and therefore cannot be added togeth ...
Chapter 10b
... Four small spheres are mounted on the corners of a frame as shown. a) What is the rotational energy of the system if it is rotated about the z-axis (out of page) with an angular velocity of 5 rad/s b) What is the rotational energy if the system is rotated about the yaxis? (M = 5 kg; m = 2 kg; a = 1. ...
... Four small spheres are mounted on the corners of a frame as shown. a) What is the rotational energy of the system if it is rotated about the z-axis (out of page) with an angular velocity of 5 rad/s b) What is the rotational energy if the system is rotated about the yaxis? (M = 5 kg; m = 2 kg; a = 1. ...
Adiabatic Charged Particle Motion in Rapidly Rotating
... usual diffusionequation cannot be justified.The reasonthat J is no longer conservedis that the guidingcentervelocitycomponent perpendicularto the magneticfield B is comparableto or greater than the componentparallel to B, and after one mirror bounceperiod the guiding centerdoes not return anywhere n ...
... usual diffusionequation cannot be justified.The reasonthat J is no longer conservedis that the guidingcentervelocitycomponent perpendicularto the magneticfield B is comparableto or greater than the componentparallel to B, and after one mirror bounceperiod the guiding centerdoes not return anywhere n ...