Notes: Free Body Diagrams
... A normal force occurs when a surface pushes back on an object. For example, you are sitting in your chair, pushing down on the chair. The chair is pushing up the exact same amount. That means if your weight is pressing 500 N down, the chair is pushing up 500 N. For flat surfaces only, the force of g ...
... A normal force occurs when a surface pushes back on an object. For example, you are sitting in your chair, pushing down on the chair. The chair is pushing up the exact same amount. That means if your weight is pressing 500 N down, the chair is pushing up 500 N. For flat surfaces only, the force of g ...
1. Activity #1: Calibrating Force sensors
... 1.7 Click again on the Sensors icon. Left click on DIN 2 and make sure it is highlighted. Repeat steps 1.1-1.6 except change the Label and Short label to Force2 and F2 respectively. You have now informed the computer that a second SFS has been connected to the interface box in socket DIN 2 and given ...
... 1.7 Click again on the Sensors icon. Left click on DIN 2 and make sure it is highlighted. Repeat steps 1.1-1.6 except change the Label and Short label to Force2 and F2 respectively. You have now informed the computer that a second SFS has been connected to the interface box in socket DIN 2 and given ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... Note that inertia is a property of matter, not a reason for the behavior of matter. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Note that inertia is a property of matter, not a reason for the behavior of matter. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
8-2 Simple Harmonic Motion 8-3 The Force Law for Simple
... torsion pendulum. The element of elasticity is associated with the twisting of a suspension wire. If we rotate the desk by some angular displacement from its rest position (where the reference line is at 0 ) and release it, it will oscillate about that position in angular simple harmonic motio ...
... torsion pendulum. The element of elasticity is associated with the twisting of a suspension wire. If we rotate the desk by some angular displacement from its rest position (where the reference line is at 0 ) and release it, it will oscillate about that position in angular simple harmonic motio ...
Newton`s Law of Motion
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
Chapter 6 - AstroStop
... Remember that the car and the truck exert equal but oppositely directed forces upon each other. What about the drivers? The truck driver undergoes the same acceleration as the truck, that is ...
... Remember that the car and the truck exert equal but oppositely directed forces upon each other. What about the drivers? The truck driver undergoes the same acceleration as the truck, that is ...
Newton`s Law of Motion
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
ÿþK i n e m a t i c s S o l u t i o n s
... Hi!! Idea 3: The interactions of an obiect with other obiects Essential Knowledge 3.A.I: An observer in a particular reference frame can describe the motion of an object using such quautitics as position, displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. a. Displacement, velocity, and accel ...
... Hi!! Idea 3: The interactions of an obiect with other obiects Essential Knowledge 3.A.I: An observer in a particular reference frame can describe the motion of an object using such quautitics as position, displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. a. Displacement, velocity, and accel ...
Phys 2050 HOMEWORK
... 13. A particle moving along the x axis in simple harmonic motion starts from its equilibrium position, the origin, at t 5 0 and moves to the right. The amplitude of its motion is 2.00 cm, and the frequency is 1.50 Hz. (a) Find an expression for the position of the particle as a function of time. Det ...
... 13. A particle moving along the x axis in simple harmonic motion starts from its equilibrium position, the origin, at t 5 0 and moves to the right. The amplitude of its motion is 2.00 cm, and the frequency is 1.50 Hz. (a) Find an expression for the position of the particle as a function of time. Det ...
B (2) - TSG@MIT Physics
... Bicycle Wheel and Rotating Stool: The demonstrator sits on a rotating stool and holds a spinning bicycle wheel equipped with handles on each end of its axle. The wheel is held in a vertical plane passing through axis of the stool. If the spinning wheel is turned into a horizontal plane, will rotate ...
... Bicycle Wheel and Rotating Stool: The demonstrator sits on a rotating stool and holds a spinning bicycle wheel equipped with handles on each end of its axle. The wheel is held in a vertical plane passing through axis of the stool. If the spinning wheel is turned into a horizontal plane, will rotate ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
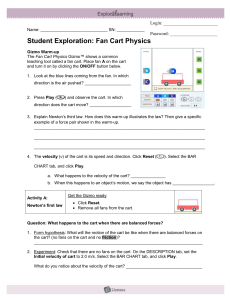
... C. What does this tell us about the forces acting upon the cart? _________________________ 5. Draw conclusions: Explain Newton’s first law. How do experiments 2 and 3 illustrate this law? _________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... C. What does this tell us about the forces acting upon the cart? _________________________ 5. Draw conclusions: Explain Newton’s first law. How do experiments 2 and 3 illustrate this law? _________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
Widener University
... km/h eastward, as measured by a suddenly nervous crew member who stands alongside the cheetah’s path. The change in the animal’s velocity takes 2.0 s. What is its acceleration from the perspective of: a) the cameraman? b) the nervous crew member? ...
... km/h eastward, as measured by a suddenly nervous crew member who stands alongside the cheetah’s path. The change in the animal’s velocity takes 2.0 s. What is its acceleration from the perspective of: a) the cameraman? b) the nervous crew member? ...
Chapter 9 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Force and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated. The techniques developed in this chapter will enable you to understand and analyze these situations in a simple way. Will develop momentum versions of analysis ...
... Force and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated. The techniques developed in this chapter will enable you to understand and analyze these situations in a simple way. Will develop momentum versions of analysis ...
Period 5 Activity Sheet: Forces and Newton’s Laws
... under the pennies without toppling them. How high a stack of pennies can you pull the paper out from under? ___________ Explain why it is possible to pull the paper from under the pennies in terms of Newton’s first law and the frictional forces acting between the bottom penny and the sheet of paper. ...
... under the pennies without toppling them. How high a stack of pennies can you pull the paper out from under? ___________ Explain why it is possible to pull the paper from under the pennies in terms of Newton’s first law and the frictional forces acting between the bottom penny and the sheet of paper. ...
chapter09
... Force and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated. The techniques developed in this chapter will enable you to understand and analyze these situations in a simple way. Will develop momentum versions of analysis ...
... Force and acceleration are related by Newton’s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated. The techniques developed in this chapter will enable you to understand and analyze these situations in a simple way. Will develop momentum versions of analysis ...
Phys101 Final Code: 20 Term: 123 Monday, July 29, 2013 Page: 1
... As shown in Figure 2, a block with mass M = 3.00 kg is lying on a smooth surface and is attached to another block of mass m = 2.00 kg by means of a light, inextensible string which passes over a massless pulley. What force F acting on the block M at angle θ = 60o above the horizontal will hold both ...
... As shown in Figure 2, a block with mass M = 3.00 kg is lying on a smooth surface and is attached to another block of mass m = 2.00 kg by means of a light, inextensible string which passes over a massless pulley. What force F acting on the block M at angle θ = 60o above the horizontal will hold both ...
AP Physics Pacing Curriculum
... should include uniform circular motion and projectile motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potential energy, and microscopic internal energy. Examples should include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and kinetic energy. 4.C.1.1 The student is abl ...
... should include uniform circular motion and projectile motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potential energy, and microscopic internal energy. Examples should include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and kinetic energy. 4.C.1.1 The student is abl ...