10 Circular Motion - Aurora City Schools
... Types of Speed Linear speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. • The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • The speed of something moving along a circular path is also called tangential speed because the direction of motion is always t ...
... Types of Speed Linear speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. • The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • The speed of something moving along a circular path is also called tangential speed because the direction of motion is always t ...
Ch 6 ppt
... force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net force would always be 0 N and nothing would ever move! ...
... force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net force would always be 0 N and nothing would ever move! ...
Name:
... Know and understand the laws. Be able to apply the laws to a situation – like force and acceleration of a bug going splat on the windshield (equal and opposite forces, etc.) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to calculate acceleration and Fnet. Apply the equation when there is a constant velocity (equilibrium) ...
... Know and understand the laws. Be able to apply the laws to a situation – like force and acceleration of a bug going splat on the windshield (equal and opposite forces, etc.) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to calculate acceleration and Fnet. Apply the equation when there is a constant velocity (equilibrium) ...
Document
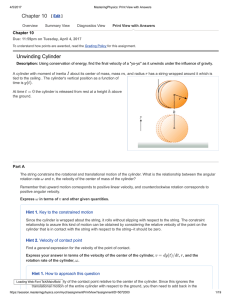
... Example: A block of mass m1 on a rough horizontal surface is pulled with a force FA at an angle θ to the horizontal. A ball of mass m2 is connected to the other side, hanging over a lightweight frictionless pulley. The coefficient of friction is given by μk. Assume m1 will move to the right. Determ ...
... Example: A block of mass m1 on a rough horizontal surface is pulled with a force FA at an angle θ to the horizontal. A ball of mass m2 is connected to the other side, hanging over a lightweight frictionless pulley. The coefficient of friction is given by μk. Assume m1 will move to the right. Determ ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... Circular Motion • When an object moves in a circle at constant speed, we describe it as undergoing uniform circular motion. • Its speed is constant, but its velocity is not because velocity includes direction and the object’s direction is clearly changing. ...
... Circular Motion • When an object moves in a circle at constant speed, we describe it as undergoing uniform circular motion. • Its speed is constant, but its velocity is not because velocity includes direction and the object’s direction is clearly changing. ...
Forces - Lemon Bay High School
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
NEWTON`S LESSON 12
... The perpendicular component of force still balances the normal force since objects do not accelerate perpendicular to the incline. The perpendicular component and the normal force add to 0 N. Yet the frictional force must also be considered when determining the net force. The parallel component and ...
... The perpendicular component of force still balances the normal force since objects do not accelerate perpendicular to the incline. The perpendicular component and the normal force add to 0 N. Yet the frictional force must also be considered when determining the net force. The parallel component and ...
Answers
... Newton's 2nd Law of Motion can be expressed as force equals mass times acceleration. It explains that force causes acceleration and mass resists acceleration. The more mass, the more force you need to make the object move. Acceleration is calculated by dividing change in velocity (final speed – init ...
... Newton's 2nd Law of Motion can be expressed as force equals mass times acceleration. It explains that force causes acceleration and mass resists acceleration. The more mass, the more force you need to make the object move. Acceleration is calculated by dividing change in velocity (final speed – init ...
MOTION, FORCES, AND SIMPLE MACHINES!
... Newton’s SECOND law tells how a net force acting on an object changes the motion of an object. ...
... Newton’s SECOND law tells how a net force acting on an object changes the motion of an object. ...
Lecture notes for Physics 10154: General Physics I
... even though it may look a little different on either side. If both sides must be the same, then they must also have the same units. The basic strategy is to represent all quantities in the equation by their dimensions. For example, x is typically used to represent distance, so it will have dimension ...
... even though it may look a little different on either side. If both sides must be the same, then they must also have the same units. The basic strategy is to represent all quantities in the equation by their dimensions. For example, x is typically used to represent distance, so it will have dimension ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Unbalanced forces cause a chance in an object’s motion. The net force acting on the object causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Changes in motion, that is, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction, are called acceleration. When an object of a certain mass is acted upon by a ...
... Unbalanced forces cause a chance in an object’s motion. The net force acting on the object causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Changes in motion, that is, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction, are called acceleration. When an object of a certain mass is acted upon by a ...
Kinetic Behavior of Flexible Bodies
... the seismic forces modifies its base-fixed behavior. One of the reasons why this happens is that the excitation motions are modified when sliding of the body occurs. In this paper a numerical method that considers coupling between the sliding flexible body and the surface on which it slides is advan ...
... the seismic forces modifies its base-fixed behavior. One of the reasons why this happens is that the excitation motions are modified when sliding of the body occurs. In this paper a numerical method that considers coupling between the sliding flexible body and the surface on which it slides is advan ...
Wednesday, Apr. 3, 2002
... What is a system that has this kind of character? A system consists of a mass and a spring When a spring is stretched from its equilibrium position by a length x, the force acting on the mass is ...
... What is a system that has this kind of character? A system consists of a mass and a spring When a spring is stretched from its equilibrium position by a length x, the force acting on the mass is ...
Export To Word
... derive an equation that related mass, distance, and gravitational force. Use measurements to determine the universal gravitational constant. ...
... derive an equation that related mass, distance, and gravitational force. Use measurements to determine the universal gravitational constant. ...