Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Chapter 12
... Regardless of the number of forces that are acting, if an object is in translational equilibrium and if the net torque is zero about one axis, then the net torque must also be zero about any other axis. The axis can pass through a point that is inside or outside the boundaries of the object. Conside ...
... Regardless of the number of forces that are acting, if an object is in translational equilibrium and if the net torque is zero about one axis, then the net torque must also be zero about any other axis. The axis can pass through a point that is inside or outside the boundaries of the object. Conside ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
... Conceptual Example Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Answe ...
acceleration
... A) What force causes a bicycle to stop? o Friction caused by brakes pushing on tires o Friction caused by tires pushing on road 6 ...
... A) What force causes a bicycle to stop? o Friction caused by brakes pushing on tires o Friction caused by tires pushing on road 6 ...
Section 4.3 - CPO Science
... down, the speed decreases so the car covers less distance each second. The position vs. time graph gets shallower with time. ...
... down, the speed decreases so the car covers less distance each second. The position vs. time graph gets shallower with time. ...
Revision of Mechanics Basics
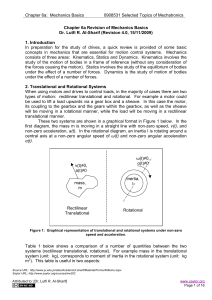
... The equation F=ma is equivalent to the equation T=I α. When a body of mass m (kg) is subjected to a Force F (N) it is accelerated by acceleration a (m/s2). Similarly, when a body that can rotate around an axis and has a moment of inertia of I (kg m2) is subjected to a torque T (N m), its rotational ...
... The equation F=ma is equivalent to the equation T=I α. When a body of mass m (kg) is subjected to a Force F (N) it is accelerated by acceleration a (m/s2). Similarly, when a body that can rotate around an axis and has a moment of inertia of I (kg m2) is subjected to a torque T (N m), its rotational ...
see link - engin1000
... algebra by hand). Instead, however, we will use MATLAB to do this for us. For this purpose, we need to turn the equation into a constraint on the accelerations, instead of the position of the particle. To get such an equation, we can differentiate both sides of the constraint with respect to ...
... algebra by hand). Instead, however, we will use MATLAB to do this for us. For this purpose, we need to turn the equation into a constraint on the accelerations, instead of the position of the particle. To get such an equation, we can differentiate both sides of the constraint with respect to ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 16.
... kinetic energy (1/2 mv2) except that instead of being proportional to the the mass m of the object, the rotational kinetic energy is proportional to the moment of inertia I of the object: Note: units of I: kg m2 I mi ri 2 or I r 2 dm i ...
... kinetic energy (1/2 mv2) except that instead of being proportional to the the mass m of the object, the rotational kinetic energy is proportional to the moment of inertia I of the object: Note: units of I: kg m2 I mi ri 2 or I r 2 dm i ...
Preview Sample 1
... You may not wish to dwell on friction to the extent presented in Section 2.1, although kinetic friction is mentioned by name in later chapters. See the interesting article “Soft Matter in a Tight Spot” by Steve Granick in the July 1999 Physics Today about current work on friction and lubrication—he ...
... You may not wish to dwell on friction to the extent presented in Section 2.1, although kinetic friction is mentioned by name in later chapters. See the interesting article “Soft Matter in a Tight Spot” by Steve Granick in the July 1999 Physics Today about current work on friction and lubrication—he ...
PHYSICS
... 7. A cannon shoots a projectile at 200 m/sec at an angle of 30 degrees above horizontal. The horizontal range of the cannon is a. 1764 m b. 3530 m c. 7058 m d. 2040 m e. 4080 m 8. A marble moving at 2 m/sec rolls off a tabletop that is 1 m high. It hits the ground how many m from the edge of the tab ...
... 7. A cannon shoots a projectile at 200 m/sec at an angle of 30 degrees above horizontal. The horizontal range of the cannon is a. 1764 m b. 3530 m c. 7058 m d. 2040 m e. 4080 m 8. A marble moving at 2 m/sec rolls off a tabletop that is 1 m high. It hits the ground how many m from the edge of the tab ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over a pothole in the road. Let’s assume that mass is evenly distributed to all four springs. The total mass of the sys ...
... springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over a pothole in the road. Let’s assume that mass is evenly distributed to all four springs. The total mass of the sys ...
Newton`s Laws Review Sheet
... Your weight is a measure of how hard gravity pulls down on you. Your mass is a measure of how difficult you are to accelerate. Since these two properties are directly related, it can be hard to tell the difference. One example that illustrates the difference is considering the difference between pus ...
... Your weight is a measure of how hard gravity pulls down on you. Your mass is a measure of how difficult you are to accelerate. Since these two properties are directly related, it can be hard to tell the difference. One example that illustrates the difference is considering the difference between pus ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...