Chapter 10
... There is an analogy between the kinetic energies associated with linear motion (K = 1/2 mv 2) and the kinetic energy associated with rotational motion (KR= 1/2 I2) Rotational kinetic energy is not a new type of energy, the form is different because it is applied to a rotating object The units of ro ...
... There is an analogy between the kinetic energies associated with linear motion (K = 1/2 mv 2) and the kinetic energy associated with rotational motion (KR= 1/2 I2) Rotational kinetic energy is not a new type of energy, the form is different because it is applied to a rotating object The units of ro ...
Objective:
... c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) Stops the motion of an object. When a car collides with a wall, the car is stopped by the wall. e) Change the direction of motion. When a tennis b ...
... c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) Stops the motion of an object. When a car collides with a wall, the car is stopped by the wall. e) Change the direction of motion. When a tennis b ...
6) Solve the following problems
... uniform velocity in a straight line unless acted upon by a resultant force(……………………….) 3. The tendency of an object to keep either its state of rest or its state of motion at its original velocity uniformly in a straight line (………………………) ...
... uniform velocity in a straight line unless acted upon by a resultant force(……………………….) 3. The tendency of an object to keep either its state of rest or its state of motion at its original velocity uniformly in a straight line (………………………) ...
Forces Vocab
... How does this law apply to a person wearing roller skates pushing off of a wall? 17. ____________________________________ is a property of all moving objects that describes how much force is needed to change its motion. It is a product of mass and velocity p = mv The larger the mass, the (greater/ ...
... How does this law apply to a person wearing roller skates pushing off of a wall? 17. ____________________________________ is a property of all moving objects that describes how much force is needed to change its motion. It is a product of mass and velocity p = mv The larger the mass, the (greater/ ...
Pre-lab on forces
... 1. How does the mass of the car affect the force at which it hits the wall? 2. Do you see any relationship between the mass of the car and its velocity? (If mass increases, does velocity increase?) 3. If a semi-truck and a Honda Civic were to hit a block wall going at the same velocity, which would ...
... 1. How does the mass of the car affect the force at which it hits the wall? 2. Do you see any relationship between the mass of the car and its velocity? (If mass increases, does velocity increase?) 3. If a semi-truck and a Honda Civic were to hit a block wall going at the same velocity, which would ...
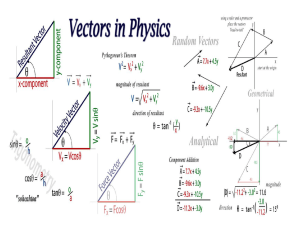
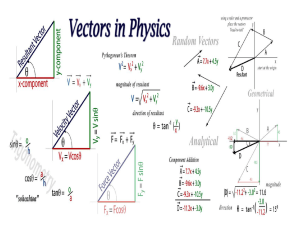
IB Physics Vector Presentation
... Place first vector on graph with tail starting at the origin Place the second vector with the tail at the tip of the first vector Repeat step two for multiple vectors Draw a line from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the final vector. This final -x vector is called the resultant. The order ...
... Place first vector on graph with tail starting at the origin Place the second vector with the tail at the tip of the first vector Repeat step two for multiple vectors Draw a line from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the final vector. This final -x vector is called the resultant. The order ...
PHYSICS
... Place first vector on graph with tail starting at the origin Place the second vector with the tail at the tip of the first vector Repeat step two for multiple vectors Draw a line from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the final vector. This final -x vector is called the resultant. The order ...
... Place first vector on graph with tail starting at the origin Place the second vector with the tail at the tip of the first vector Repeat step two for multiple vectors Draw a line from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the final vector. This final -x vector is called the resultant. The order ...
Momentum and Energy
... 1. The third floor of a house is 8 m above street level. How much work is needed to move a 150 kg refrigerator to the third floor? 1. During a tug-of-war, team A does 2.2 x 105 J of work in pulling team B 8 m. What force did team A exert? 1. A wagon is pulled by a force of 38 N exerted on the handle ...
... 1. The third floor of a house is 8 m above street level. How much work is needed to move a 150 kg refrigerator to the third floor? 1. During a tug-of-war, team A does 2.2 x 105 J of work in pulling team B 8 m. What force did team A exert? 1. A wagon is pulled by a force of 38 N exerted on the handle ...
Fun items for the teaching of mechanics
... a. Express the first law of thermodynamics in terms of U, W and Q which stand for internal energy, work and heat respectively. b. Which part of the body has a displacement contribute to the external work done? c. How can we incorporate the change in mechanical energy (P.E. + K.E.)into the 1st ...
... a. Express the first law of thermodynamics in terms of U, W and Q which stand for internal energy, work and heat respectively. b. Which part of the body has a displacement contribute to the external work done? c. How can we incorporate the change in mechanical energy (P.E. + K.E.)into the 1st ...
Motion PowerPoint #4
... •velocity is a description of both speed and direction of motion. Velocity is a vector. •Two or more vectors can be added by vector addition. •Acceleration = Total distance/Total time, or d/t •The SI unit of speed is meters per second(m/s) •A distance-time graph is a good way to describe motion •The ...
... •velocity is a description of both speed and direction of motion. Velocity is a vector. •Two or more vectors can be added by vector addition. •Acceleration = Total distance/Total time, or d/t •The SI unit of speed is meters per second(m/s) •A distance-time graph is a good way to describe motion •The ...
Newton`s Second Law
... (b) the smaller the mass for a given force the greater the acceleration These results can be summarised as follows: ...
... (b) the smaller the mass for a given force the greater the acceleration These results can be summarised as follows: ...
Conceptual Physics first Semester Review #1
... m/s in 12.0seconds. The total distance traveled by the car in this 12.0 second time interval is A. 36.0m B. 180.m C. 216m D. 252m 9. Who used three laws to explain the way objects move? a. b. c. d. ...
... m/s in 12.0seconds. The total distance traveled by the car in this 12.0 second time interval is A. 36.0m B. 180.m C. 216m D. 252m 9. Who used three laws to explain the way objects move? a. b. c. d. ...
Practice - People Server at UNCW
... planet’s distance from the Sun could then be determined from Kepler’s a) first law; b) second law d) third law. _____ r) When the distance between two masses is cut in half and one of the masses is doubled, the gravitational force between them is _____ the original force. a) half b) the same as b) t ...
... planet’s distance from the Sun could then be determined from Kepler’s a) first law; b) second law d) third law. _____ r) When the distance between two masses is cut in half and one of the masses is doubled, the gravitational force between them is _____ the original force. a) half b) the same as b) t ...
AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... Ex. 9 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a block of wood (mass m2 = 2.50 kg) suspended by a wire. A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m abo ...
... Ex. 9 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a block of wood (mass m2 = 2.50 kg) suspended by a wire. A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m abo ...