Angular momentum and PH101:Tutorial
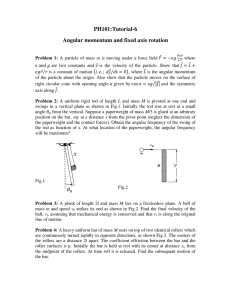
... Problem 6: A cone of height h and base radius R is free to rotate about afixed vertical axis as shown in Fig.5. It has a thin groove cut in the surface. The cone is set rotating freely with angular speed ωo, and a small block of mass m is released in the top of the frictionless groove and allowed to ...
... Problem 6: A cone of height h and base radius R is free to rotate about afixed vertical axis as shown in Fig.5. It has a thin groove cut in the surface. The cone is set rotating freely with angular speed ωo, and a small block of mass m is released in the top of the frictionless groove and allowed to ...
PHYS 1443 * Section 501 Lecture #1
... Example for Moment of Inertia In a system of four small spheres as shown in the figure, assuming the radii are negligible and the rods connecting the particles are massless, compute the moment of inertia and the rotational kinetic energy when the system rotates about the y-axis at angular speed ω. ...
... Example for Moment of Inertia In a system of four small spheres as shown in the figure, assuming the radii are negligible and the rods connecting the particles are massless, compute the moment of inertia and the rotational kinetic energy when the system rotates about the y-axis at angular speed ω. ...
Chapter 19 Outline The First Law of Thermodynamics
... • Kepler’s second law is a natural consequence of the conservation of angular momentum. • There can be no torque because the force is always central (on a line between the masses.) ...
... • Kepler’s second law is a natural consequence of the conservation of angular momentum. • There can be no torque because the force is always central (on a line between the masses.) ...
Question 1 - BrainMass
... As the directions of the vectors are not given we have to surch for max and min possible values of x. The resultant of 500m and 30m is having maximum of 530m when they in same direction and minimum of 470m if they are in apposite directions. When we find resultant 10m with 530 and x value of x shoul ...
... As the directions of the vectors are not given we have to surch for max and min possible values of x. The resultant of 500m and 30m is having maximum of 530m when they in same direction and minimum of 470m if they are in apposite directions. When we find resultant 10m with 530 and x value of x shoul ...
Examples of Lagrange`s Equations
... However, for angular coordinates we saw that the generalized force was the torque, and the generalized momentum was the angular momentum. In any case, when the generalized force is zero (i.e. the Lagrangian is independent of the generalized coordinate qi, then the generalized momentum is conserved. ...
... However, for angular coordinates we saw that the generalized force was the torque, and the generalized momentum was the angular momentum. In any case, when the generalized force is zero (i.e. the Lagrangian is independent of the generalized coordinate qi, then the generalized momentum is conserved. ...
Physics Chapter 1-3 Review
... The reluctance of any object to change its state of motion. Mass is the measure of inertia ...
... The reluctance of any object to change its state of motion. Mass is the measure of inertia ...
Formative 1
... garbage pick-up day. The diagram at the right is a free-body diagram. It uses arrows to represent the forces acting upon the bag. a. Each force is labeled according to type. The magnitude of the force is represented by the size of the arrow. Use the free body diagram to determine the net force actin ...
... garbage pick-up day. The diagram at the right is a free-body diagram. It uses arrows to represent the forces acting upon the bag. a. Each force is labeled according to type. The magnitude of the force is represented by the size of the arrow. Use the free body diagram to determine the net force actin ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... 1. There is no external torque acting on it 2. The shape remains spherical ...
... 1. There is no external torque acting on it 2. The shape remains spherical ...
Monday, April 27, 2009
... 1. There is no external torque acting on it 2. The shape remains spherical ...
... 1. There is no external torque acting on it 2. The shape remains spherical ...
Atwood Lab #5 - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... DSHS AP1 Physics Mathy Ch 4 Forces Lab #5 Atwood Demonstrator ...
... DSHS AP1 Physics Mathy Ch 4 Forces Lab #5 Atwood Demonstrator ...
Newton`s Second Law, X
... • Equations of Motion If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian ...
... • Equations of Motion If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. A Cartesian ...