Newton's Laws powerpoint - South Webster High School
... Deceleration is negative acceleration or slowing down Centripetal acceleration changing direction ...
... Deceleration is negative acceleration or slowing down Centripetal acceleration changing direction ...
Name____________________________________
... 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed or direction changes d. neither its speed nor its direction changes. 16. W ...
... 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed or direction changes d. neither its speed nor its direction changes. 16. W ...
11B Rotation
... each have a mass of 3 kg and a radius of 20 cm. Compare their rotational inertias. ...
... each have a mass of 3 kg and a radius of 20 cm. Compare their rotational inertias. ...
Force and Drag 1. Define the newton
... The weight W of the block is already shown on the figure. Complete the diagram by showing the normal contact (reaction) force N and the frictional force F acting on the block ...
... The weight W of the block is already shown on the figure. Complete the diagram by showing the normal contact (reaction) force N and the frictional force F acting on the block ...
Answer - Plain Local Schools
... vectors. Therefore, the direction of the acceleration, or the change in velocity, will be in the same direction as the net force. You can also look at this equation from the opposite perspective. A net force applied to an object changes an object’s velocity (produces an acceleration), and is frequen ...
... vectors. Therefore, the direction of the acceleration, or the change in velocity, will be in the same direction as the net force. You can also look at this equation from the opposite perspective. A net force applied to an object changes an object’s velocity (produces an acceleration), and is frequen ...
Name: Date: Period: Study Guide for Quiz Directions: Answer each
... 5. What is the equation for Newton’s second Law? 6. What is the equation for momentum? 7. When you are paddling on a paddleboard and the board goes forward, this is an example of which Newton’s Law? ...
... 5. What is the equation for Newton’s second Law? 6. What is the equation for momentum? 7. When you are paddling on a paddleboard and the board goes forward, this is an example of which Newton’s Law? ...
Notes
... the same angular velocity. Angles (angular displacements, that is) are generally measured in radians, and therefore all other angular quantities are expressed in radians as well. Any equation dealing with rotation can be found from its straight-line motion equivalent by substituting the correspondin ...
... the same angular velocity. Angles (angular displacements, that is) are generally measured in radians, and therefore all other angular quantities are expressed in radians as well. Any equation dealing with rotation can be found from its straight-line motion equivalent by substituting the correspondin ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
... reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
... reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
Matt Katz Newton`s Laws Newton`s First Law • AKA law of ineria • A
... Mass = force of gravity divided by gravity = 59.7 kg. B) On the moon the scale would read 95.5 N. ...
... Mass = force of gravity divided by gravity = 59.7 kg. B) On the moon the scale would read 95.5 N. ...
Molecular Dynamics
... Berendsens method for Langevin dynamics with adjustable friction coeffcient and zero random force bi = bi0 ( T0/T -1) if T >T0 bi is positive -> cooling if T heating
Dynamics is initialized with random vi s drawn from a
...
... Berendsens method for Langevin dynamics with adjustable friction coeffcient and zero random force bi = bi0 ( T0/T -1) if T >T0 bi is positive -> cooling if T
FMALiveForcesMotionPC
... Isaac Newton comes in to help with his First Law of Motion: Objects at rest (or in motion) stay that way unless acted on by an outside Force. ...
... Isaac Newton comes in to help with his First Law of Motion: Objects at rest (or in motion) stay that way unless acted on by an outside Force. ...
Torque - Studentportalen
... perpendicular distance from O to the line of action of the force (see figure). • The torque of a force with respect to O is the product of the force and its lever arm. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... perpendicular distance from O to the line of action of the force (see figure). • The torque of a force with respect to O is the product of the force and its lever arm. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Print Newton`s Laws problem set #1
... a. What is its acceleration? b. What is its weight in newtons? c. What is its speed just before hitting the ground? 2) What net external force is required to give a 25 kg suitcase an acceleration of 2.2m/s/s to the right? Draw a Free Body diagram of the suitcase. 3) You pull on the tail of a 200kg b ...
... a. What is its acceleration? b. What is its weight in newtons? c. What is its speed just before hitting the ground? 2) What net external force is required to give a 25 kg suitcase an acceleration of 2.2m/s/s to the right? Draw a Free Body diagram of the suitcase. 3) You pull on the tail of a 200kg b ...
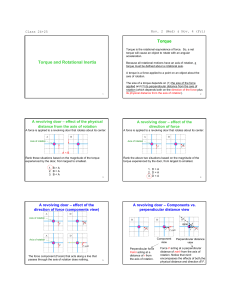
Torque and Rotational Inertia Torque
... The drawing shows an A-shaped ladder. Both sides of the ladder are equal in length. This ladder is standing on a frictionless horizontal surface, and only the crossbar (which has a negligible mass) of the "A" keeps the ladder from collapsing. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 14.0 kg. Determin ...
... The drawing shows an A-shaped ladder. Both sides of the ladder are equal in length. This ladder is standing on a frictionless horizontal surface, and only the crossbar (which has a negligible mass) of the "A" keeps the ladder from collapsing. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 14.0 kg. Determin ...
AP-1 Cutnell 00-05 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... Newton’s First Law objects resist acceleration. Law of inertia. The mass of an object is a quantitative measure of inertia. ...
... Newton’s First Law objects resist acceleration. Law of inertia. The mass of an object is a quantitative measure of inertia. ...
Newton`s three laws of motion are…
... The force acting on a body is equal to the product of its mass times its acceleration, ...
... The force acting on a body is equal to the product of its mass times its acceleration, ...
Chapter 4 - Sharyland ISD
... in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. ...
... in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. ...