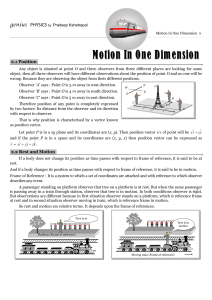
Physics 231 Topic 3: Forces & Laws of Motion
... If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass: F=ma Third Law: If two objects interact, the force exerted by the first object on ...
... If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass: F=ma Third Law: If two objects interact, the force exerted by the first object on ...
Introduction - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... So distance |Displacement|. (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacemen ...
... So distance |Displacement|. (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacemen ...
ANSWERS
... 10 - 15 s: The brakes are applied. The forward velocity component decreases and the component of acceleration is negative. As the brakes are eased off, the forward velocity decreases at a lower rate, i.e. the magnitude of the (negative) acceleration component is less. Finally as the brakes are appli ...
... 10 - 15 s: The brakes are applied. The forward velocity component decreases and the component of acceleration is negative. As the brakes are eased off, the forward velocity decreases at a lower rate, i.e. the magnitude of the (negative) acceleration component is less. Finally as the brakes are appli ...
Section Check
... Anudja is holding a stuffed dog, with a mass of 0.30 kg, when Sarah decides that she wants it and tries to pull it away from Anudja. If Sarah pulls horizontally on the dog with a force of 10.0 N and Anudja pulls with a horizontal force of 11.0 N, what is the horizontal acceleration of the dog? ...
... Anudja is holding a stuffed dog, with a mass of 0.30 kg, when Sarah decides that she wants it and tries to pull it away from Anudja. If Sarah pulls horizontally on the dog with a force of 10.0 N and Anudja pulls with a horizontal force of 11.0 N, what is the horizontal acceleration of the dog? ...
postlab for week 5: combining forces
... where Frepresents the vector sum of two or more forces. Some textbooks refer to a combination of forces or a combined force as a net force. Other authors write about the resultant force. Combined, resultant, or net force all refer to the same thing. You should note that velocities and accelerations ...
... where Frepresents the vector sum of two or more forces. Some textbooks refer to a combination of forces or a combined force as a net force. Other authors write about the resultant force. Combined, resultant, or net force all refer to the same thing. You should note that velocities and accelerations ...
Circular Motion - cloudfront.net
... ride and has a centripetal acceleration of 17 m/s . What is the girl's tangential speed? 3. Use an example to describe the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration. 4. Identify the forces that contribute to the centripetal force on the object in each of the following examples: a. a ...
... ride and has a centripetal acceleration of 17 m/s . What is the girl's tangential speed? 3. Use an example to describe the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration. 4. Identify the forces that contribute to the centripetal force on the object in each of the following examples: a. a ...
Physics Applet review - Futur-E
... A rock thrown from a tall building sails in a modest orbit that soon intersects the earth not far from its point of launch. If the ball were fired more swiftly to start with, it would travel further. Futher increasing the speed would result in ever larger, rounder elliptical paths and more distant i ...
... A rock thrown from a tall building sails in a modest orbit that soon intersects the earth not far from its point of launch. If the ball were fired more swiftly to start with, it would travel further. Futher increasing the speed would result in ever larger, rounder elliptical paths and more distant i ...
PSI AP Physics I
... Object 2 has a mass of 2.8 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s south. What is the momentum of the system? 28. Three objects in a system are moving as follows: Object 1 has a mass of 5.5 kg with a velocity of 12 m/s east; Object 2 has a mass of 2.2 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s west; and Object 3 has a mass ...
... Object 2 has a mass of 2.8 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s south. What is the momentum of the system? 28. Three objects in a system are moving as follows: Object 1 has a mass of 5.5 kg with a velocity of 12 m/s east; Object 2 has a mass of 2.2 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s west; and Object 3 has a mass ...
Research Methods in Biomechanics
... mechanics that bridges the areas of kinematics and kinetics. It is the process by which forces and moments of force are indirectly determined from the kinematics and inertial properties of moving bodies. In principle, inverse dynamics also applies to stationary bodies, but usually it is applied to b ...
... mechanics that bridges the areas of kinematics and kinetics. It is the process by which forces and moments of force are indirectly determined from the kinematics and inertial properties of moving bodies. In principle, inverse dynamics also applies to stationary bodies, but usually it is applied to b ...
Descriptive Essay: The Night Market
... (i)a word which describes a noun (ii)a word used to show actions (iii)a word used instead of noun An adverb is (i)a word which describes how action are done (ii)a word which is added to the end of the verb (iii)the name of a place or thing A conjunction is a word (i)shown by the sign (ii)a word whic ...
... (i)a word which describes a noun (ii)a word used to show actions (iii)a word used instead of noun An adverb is (i)a word which describes how action are done (ii)a word which is added to the end of the verb (iii)the name of a place or thing A conjunction is a word (i)shown by the sign (ii)a word whic ...
Force is not stored or used up. Because energy can be stored and
... Forces need not be exerted by living things or machines. Transforming energy from one form into another usually requires some kind of living or mechanical mechanism. The concept is not applicable to forces, which are an interaction between objects, not a thing to be transferred or transformed. Incor ...
... Forces need not be exerted by living things or machines. Transforming energy from one form into another usually requires some kind of living or mechanical mechanism. The concept is not applicable to forces, which are an interaction between objects, not a thing to be transferred or transformed. Incor ...
Ch. 7 PP - Lemon Bay High School
... • We will use the convention that the sign of the torque is positive if the rotation is counterclockwise and negative if the rotation is clockwise. Tip: To determine the sign of a torque, imagine that the torque is the only one acting on the object and that the object is free to rotate. Visualize th ...
... • We will use the convention that the sign of the torque is positive if the rotation is counterclockwise and negative if the rotation is clockwise. Tip: To determine the sign of a torque, imagine that the torque is the only one acting on the object and that the object is free to rotate. Visualize th ...
5. Momentum - Rougemont School
... amount of time taken for the person to decelerate in a collision. How does this reduce the risk of serious injury? A longer deceleration means that change in momentum occurs over a longer time. There is therefore a smaller force acting on the person. What features of cars use this principle? ...
... amount of time taken for the person to decelerate in a collision. How does this reduce the risk of serious injury? A longer deceleration means that change in momentum occurs over a longer time. There is therefore a smaller force acting on the person. What features of cars use this principle? ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...