Newton`s Laws: Explaining Motion
... Notice that, in paraphrasing Newton’s first law, we have used the term velocity rather than the term speed. Constant velocity implies that neither the direction nor the magnitude of the velocity changes. When the object is at rest, its velocity is zero, and that value remains constant in the absence ...
... Notice that, in paraphrasing Newton’s first law, we have used the term velocity rather than the term speed. Constant velocity implies that neither the direction nor the magnitude of the velocity changes. When the object is at rest, its velocity is zero, and that value remains constant in the absence ...
Molecular dynamics
... We will need to take precautions if we want all the states to be of same temperature. We will discuss this in the future. If the particles are not spherical, things get more complicated. There are numerical methods tailored to this type of application for maximum numerical efficiency. If the number ...
... We will need to take precautions if we want all the states to be of same temperature. We will discuss this in the future. If the particles are not spherical, things get more complicated. There are numerical methods tailored to this type of application for maximum numerical efficiency. If the number ...
Review Questions
... A falling person is gaining momentum all the way down as gravity pulls on them. When they reach the ground and stop, whatever they hit has to impart just the right amount of impulse to take away all their momentum. If they had 1000 kg·m/s of momentum, they would need to receive –1000 N·s of impulse ...
... A falling person is gaining momentum all the way down as gravity pulls on them. When they reach the ground and stop, whatever they hit has to impart just the right amount of impulse to take away all their momentum. If they had 1000 kg·m/s of momentum, they would need to receive –1000 N·s of impulse ...
PH202 Chapter 14 solutions
... sine and cosine functions. For example, if the block is released at a distance position, its displacement ...
... sine and cosine functions. For example, if the block is released at a distance position, its displacement ...
Assignment 1 Chapter 8: Planar Forces
... Weight down, friction up; force of your hand onto wall; (normal) force of wallout. Normal force is perpendicualr to the weight. Weight is equal (and opposite to friction force, which is the coefficient of ...
... Weight down, friction up; force of your hand onto wall; (normal) force of wallout. Normal force is perpendicualr to the weight. Weight is equal (and opposite to friction force, which is the coefficient of ...
PM PPT
... Of these three equations, the top equation is the most commonly used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
... Of these three equations, the top equation is the most commonly used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
p - Effingham County Schools
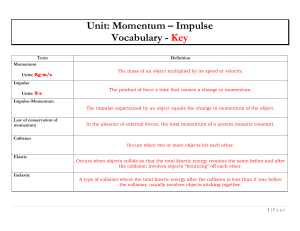
... The product of the object’s mass, m, and the object’s velocity, v, is defined as the momentum of the object. Momentum is measured in kg·m/s. An object’s momentum, also known as linear momentum, is represented by the following equation: ...
... The product of the object’s mass, m, and the object’s velocity, v, is defined as the momentum of the object. Momentum is measured in kg·m/s. An object’s momentum, also known as linear momentum, is represented by the following equation: ...
Physics Study Guide - Barnstable Academy
... 1. Which one of the following steps is NOT a part of the scientific method? a. Perform experiments to test the predictions. b. Repeat the experiments until the answers match the predictions. c. Formulate a general rule based on the predictions and experimental outcome. d. Make a guess about the answ ...
... 1. Which one of the following steps is NOT a part of the scientific method? a. Perform experiments to test the predictions. b. Repeat the experiments until the answers match the predictions. c. Formulate a general rule based on the predictions and experimental outcome. d. Make a guess about the answ ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... of the rocket increases. Give three reasons for this increase in acceleration. (c) Explain in terms of Newton’s laws of motion why a rocket can travel from the Earth to the Moon and for most of the journey not burn up any fuel. ...
... of the rocket increases. Give three reasons for this increase in acceleration. (c) Explain in terms of Newton’s laws of motion why a rocket can travel from the Earth to the Moon and for most of the journey not burn up any fuel. ...
Centripetal Acceleration
... which points directly toward the center of rotation (the center of the circular path). This pointing is shown with the vector diagram in the gure. ...
... which points directly toward the center of rotation (the center of the circular path). This pointing is shown with the vector diagram in the gure. ...
Chap 3 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... b. Violent motion has an external cause c. Violent motion is the result of forces that push or pull d. Violent motion is thought to be either straight up or straight down ____ 11. You and a friend are jumping on a trampoline. Why does Earth, which is rapidly orbiting around the sun, not move under y ...
... b. Violent motion has an external cause c. Violent motion is the result of forces that push or pull d. Violent motion is thought to be either straight up or straight down ____ 11. You and a friend are jumping on a trampoline. Why does Earth, which is rapidly orbiting around the sun, not move under y ...
Lecture Presentation
... the hinges with a 240 N force directed 20° away from being perpendicular to the door. There’s a natural pivot point, the hinges. What torque does Ryan exert? How could he exert more torque? PREPARE In FIGURE 7.20 the radial line is shown drawn from the pivot—the hinge—through the point at which the ...
... the hinges with a 240 N force directed 20° away from being perpendicular to the door. There’s a natural pivot point, the hinges. What torque does Ryan exert? How could he exert more torque? PREPARE In FIGURE 7.20 the radial line is shown drawn from the pivot—the hinge—through the point at which the ...