Momentum and Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension
... In any collision or explosion, the total momentum is always conserved. This principle proves to be very useful in predicting what will happen when objects collide or explode. Actually, the principle of the Conservation of Momentum is a direct consequence of Newton’s Third Law of Motion that we learn ...
... In any collision or explosion, the total momentum is always conserved. This principle proves to be very useful in predicting what will happen when objects collide or explode. Actually, the principle of the Conservation of Momentum is a direct consequence of Newton’s Third Law of Motion that we learn ...
Table of Contents
... In terms of manipulation of numbers, these steps appear fine but for the step in which is eliminated. Dividing by zero is clearly shown to produce an incorrect answer. Differential equations may have conditions leading to similar issues, but for now it is sufficient to understand the solution techni ...
... In terms of manipulation of numbers, these steps appear fine but for the step in which is eliminated. Dividing by zero is clearly shown to produce an incorrect answer. Differential equations may have conditions leading to similar issues, but for now it is sufficient to understand the solution techni ...
CHAPTER 1 Forces in action
... A graph of velocity versus time provides information about the velocity and acceleration at any instant of time during the interval described by the graph. It also provides information about the displacement between any two instants. The instantaneous acceleration of an object at an instant of time ...
... A graph of velocity versus time provides information about the velocity and acceleration at any instant of time during the interval described by the graph. It also provides information about the displacement between any two instants. The instantaneous acceleration of an object at an instant of time ...
Gravity and Inertia (Rec. 1.23.14) (* file)
... true relative aether velocity to an orbiting satellite is the vector sum of two velocity vectors at right angles to each other as in Figure 5-1 below. In order for the gradient of v2 to vanish for an orbiting object, the magnitude of vnet must remain constant for a small change in the position (in t ...
... true relative aether velocity to an orbiting satellite is the vector sum of two velocity vectors at right angles to each other as in Figure 5-1 below. In order for the gradient of v2 to vanish for an orbiting object, the magnitude of vnet must remain constant for a small change in the position (in t ...
chapter 7
... a. If a single object has kinetic energy, it must have a velocity; therefore, it must have linear momentum as well. b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinet ...
... a. If a single object has kinetic energy, it must have a velocity; therefore, it must have linear momentum as well. b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinet ...
am-ii_unit-v-1
... • Apply Newton’s second law to find normal force by the track at point 2. A 2000 lb car starts from rest at point 1 • Apply principle of work and energy to and moves without friction down the determine velocity at point 3. track shown. • Apply Newton’s second law to find Determine: minimum radius of ...
... • Apply Newton’s second law to find normal force by the track at point 2. A 2000 lb car starts from rest at point 1 • Apply principle of work and energy to and moves without friction down the determine velocity at point 3. track shown. • Apply Newton’s second law to find Determine: minimum radius of ...
Ch15 - Oscillations
... 15.14 Identify that for a simple harmonic oscillator 15.16 Given data about the the acceleration a at any position x and velocity v instant is always given by at one instant, determine the product of a negative the phase t and constant and the phase constant . displacement x just then. 15.15 F ...
... 15.14 Identify that for a simple harmonic oscillator 15.16 Given data about the the acceleration a at any position x and velocity v instant is always given by at one instant, determine the product of a negative the phase t and constant and the phase constant . displacement x just then. 15.15 F ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... So, this is the kinetic energy, then potential energy, and this should be equal to 0. So, if you differentiate we will get m l square theta dot theta double dot plus m g l. This will be sin theta, because minus will get cancelled is equal to 0. So, if we take out the common term from here, we can wr ...
... So, this is the kinetic energy, then potential energy, and this should be equal to 0. So, if you differentiate we will get m l square theta dot theta double dot plus m g l. This will be sin theta, because minus will get cancelled is equal to 0. So, if we take out the common term from here, we can wr ...
FE ANS
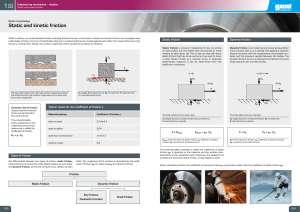
... normal (vertical) component, magnitude N , and a horizontal frictional component, magnitude F. The frictional component is directed forward when the car is moving with constant velocity or when it is accelerating forward. The frictional force may be directed backwards when the brakes are applied and ...
... normal (vertical) component, magnitude N , and a horizontal frictional component, magnitude F. The frictional component is directed forward when the car is moving with constant velocity or when it is accelerating forward. The frictional force may be directed backwards when the brakes are applied and ...
Chapter 4: Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... An object’s mass is a measure of its inertia. The more mass, the more force is required to obtain a given acceleration. The net force is just the vector sum of all of the forces acting on the body, often written as F. ...
... An object’s mass is a measure of its inertia. The more mass, the more force is required to obtain a given acceleration. The net force is just the vector sum of all of the forces acting on the body, often written as F. ...