SPH4U: Forces
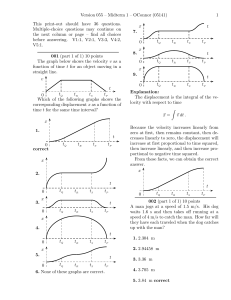
... Reason. Emmy says, “Since the skydiver is moving downwards, the net force should be downwards.” Do you agree or disagree with Emmy? Explain. ...
... Reason. Emmy says, “Since the skydiver is moving downwards, the net force should be downwards.” Do you agree or disagree with Emmy? Explain. ...
Impulse and Momentum Review
... objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system must remain constant. This is another way of stating Newton’s first law, the law of inertia, discussed in chapter 4. ...
... objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system must remain constant. This is another way of stating Newton’s first law, the law of inertia, discussed in chapter 4. ...
3.1 force skiing and external forces
... Skiing, 2009). This is the average of centrifugal and centripetal forces. The faster the skier travels through a turn the greater the centripetal and centrifugal forces. This results in the angle of the resultant force also being more inclined and allows for the skier to incline further. This is imp ...
... Skiing, 2009). This is the average of centrifugal and centripetal forces. The faster the skier travels through a turn the greater the centripetal and centrifugal forces. This results in the angle of the resultant force also being more inclined and allows for the skier to incline further. This is imp ...
Dynamics - Bergen.org
... This means that if we measure the total momentum of a system at any point in time, its momentum will not change if it is not affected by something outside the system. The objects can collide, explode, break apart, stick together, etc. Nothing that happens within the system will change its momentum. ...
... This means that if we measure the total momentum of a system at any point in time, its momentum will not change if it is not affected by something outside the system. The objects can collide, explode, break apart, stick together, etc. Nothing that happens within the system will change its momentum. ...
ROTATIONAL VECTORS AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
... ASSESS The torque vector τ is perpendicular to both r and F . It points in the direction normal to the plane formed by r and F . ...
... ASSESS The torque vector τ is perpendicular to both r and F . It points in the direction normal to the plane formed by r and F . ...
5.0
... Note that the force curve is characterized by two parameters (height and width): the maximum force Fmax and the interaction time ∆t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, ∆t is the time interval during which one cart fee ...
... Note that the force curve is characterized by two parameters (height and width): the maximum force Fmax and the interaction time ∆t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, ∆t is the time interval during which one cart fee ...
Chapter 8 Lecture
... and this is summed up in Newton's Three Laws. These laws also apply to rotational motion. The rotational analogs to Newton's Laws will be presented now. ...
... and this is summed up in Newton's Three Laws. These laws also apply to rotational motion. The rotational analogs to Newton's Laws will be presented now. ...
SPH3U: What is a Force?
... Model the object as a point-particle Represent the external forces acting on the object using vectors that start at the point (the object’s centre of mass). Note: the force vectors do not need to be drawn to scale, but should be drawn roughly according to their relative magnitudes. As a guide, ...
... Model the object as a point-particle Represent the external forces acting on the object using vectors that start at the point (the object’s centre of mass). Note: the force vectors do not need to be drawn to scale, but should be drawn roughly according to their relative magnitudes. As a guide, ...
Momentum - USU Physics
... Example 1: A 100kg boulder rolling towards a castle gate at 3m/s. Momentum boulder: P = m.v = 100 x 3 = 300 kg.m/s Example 2: A 1 kg missile flying towards the castle gate at 300 m/s (speed of sound). Momentum missile: P = m.v = 1 x 300 = 300 kg.m/s • Result: Different objects can have the same mome ...
... Example 1: A 100kg boulder rolling towards a castle gate at 3m/s. Momentum boulder: P = m.v = 100 x 3 = 300 kg.m/s Example 2: A 1 kg missile flying towards the castle gate at 300 m/s (speed of sound). Momentum missile: P = m.v = 1 x 300 = 300 kg.m/s • Result: Different objects can have the same mome ...
oscillations
... time, that is, it is periodic. In your childhood you must have enjoyed rocking in a cradle or swinging on a swing. Both these motions are repetitive in nature but different from the periodic motion of a planet. Here, the object moves to and fro about a mean position. The pendulum of a wall clock exe ...
... time, that is, it is periodic. In your childhood you must have enjoyed rocking in a cradle or swinging on a swing. Both these motions are repetitive in nature but different from the periodic motion of a planet. Here, the object moves to and fro about a mean position. The pendulum of a wall clock exe ...
ENGR-36_Lec-02_Fa12_Forces_as_Vectors_
... This Force Exerted by the Earth is called Weight • While g Varies Somewhat With the Elevation & Location, to a Very Good Approximation – g 9.81 m/s2 32.2 ft/s2 Engineering-36: Engineering Mechanics - Statics ...
... This Force Exerted by the Earth is called Weight • While g Varies Somewhat With the Elevation & Location, to a Very Good Approximation – g 9.81 m/s2 32.2 ft/s2 Engineering-36: Engineering Mechanics - Statics ...