Problem set 11
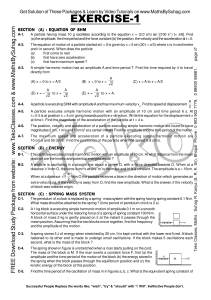
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
MFM1 MACHINE VIBRATION ANALYSIS 1. OSCILLATORY
... time τ, it is called periodic motion. The, repetition time τ is called the period of the oscillation, and its reciprocal, , f = 1/τ, is called the frequency. If the motion is designated by the time function x(t), then any periodic motion must satisfy the relationship x(t) = x(t + τ). The simplest fo ...
... time τ, it is called periodic motion. The, repetition time τ is called the period of the oscillation, and its reciprocal, , f = 1/τ, is called the frequency. If the motion is designated by the time function x(t), then any periodic motion must satisfy the relationship x(t) = x(t + τ). The simplest fo ...
Chapter 9 Rotation
... of the inner portion of the spool. When the spool is freely rotating about that axis, then the torque due to the pulling string causes a counter clockwise rotation. Second, in the situation in which the spool is resting on the horizontal tabletop, one should (for ease of understanding) consider torq ...
... of the inner portion of the spool. When the spool is freely rotating about that axis, then the torque due to the pulling string causes a counter clockwise rotation. Second, in the situation in which the spool is resting on the horizontal tabletop, one should (for ease of understanding) consider torq ...
Ch#15 - KFUPM Faculty List
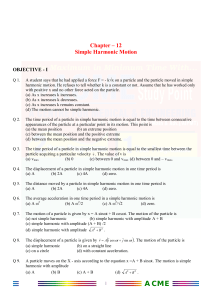
... Q12 A 5.0 kg mass stretches a spring by 10 cm when the mass is attached to the spring. The mass is then displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) i ...
... Q12 A 5.0 kg mass stretches a spring by 10 cm when the mass is attached to the spring. The mass is then displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) i ...
Chapter 15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... per second east. The bat and ball are in contact for 1.0 × 10−2 second. Calculate the magnitude of the average force the bat exerts on the ball while they are in contact. 7. A 2.0-kilogram laboratory cart is sliding across a horizontal frictionless surface at a constant velocity of 4.0 meters per se ...
... per second east. The bat and ball are in contact for 1.0 × 10−2 second. Calculate the magnitude of the average force the bat exerts on the ball while they are in contact. 7. A 2.0-kilogram laboratory cart is sliding across a horizontal frictionless surface at a constant velocity of 4.0 meters per se ...
Concept Review
... 5. Student diagrams should show vectors for weight and normal force from elevator; descent should show normal force less than weight; stopping should show normal force greater than weight; “weightlessness” feeling is due to acceleration. 6. 1050 s (17.5 min) ...
... 5. Student diagrams should show vectors for weight and normal force from elevator; descent should show normal force less than weight; stopping should show normal force greater than weight; “weightlessness” feeling is due to acceleration. 6. 1050 s (17.5 min) ...
Chapter 13 - apel slice
... are no longer exerting a force by pedaling. The early Greek philosophers made similar observations about objects in motion. It seemed to them that in order to set an object in motion, a force had to be exerted on the object. And if that force was removed, the object would come to rest. They logicall ...
... are no longer exerting a force by pedaling. The early Greek philosophers made similar observations about objects in motion. It seemed to them that in order to set an object in motion, a force had to be exerted on the object. And if that force was removed, the object would come to rest. They logicall ...
Friction - e
... ● We can walk on a surface only because of the frictional force exerted by that surface on our feet prevents slipping. If we try to walk on a wet surface or an oily surface, we tend to slip and fall, due to lack of friction. ● Grooves are etched on the surface of tire as shown in figure 5.7 in ord ...
... ● We can walk on a surface only because of the frictional force exerted by that surface on our feet prevents slipping. If we try to walk on a wet surface or an oily surface, we tend to slip and fall, due to lack of friction. ● Grooves are etched on the surface of tire as shown in figure 5.7 in ord ...
Haptic Rendering of Rigid Contacts Using Impulsive and Penalty
... perceived rigidity of contacts during the haptic manipulation of virtual rigid objects and linkages. It proposes a simulation approach that combines constraint-based and penalty-based techniques. Specifically, it computes constraint-based impulsive forces upon contact and penalty-based and friction ...
... perceived rigidity of contacts during the haptic manipulation of virtual rigid objects and linkages. It proposes a simulation approach that combines constraint-based and penalty-based techniques. Specifically, it computes constraint-based impulsive forces upon contact and penalty-based and friction ...
Going Down
... For each problem, draw a motion diagram and a free-body diagram labeling all forces with their agents and indicating the direction of the acceleration and the net force. Draw arrows the appropriate lengths. 7. A sky diver falls downward through the air at constant velocity (air drag is important). 8 ...
... For each problem, draw a motion diagram and a free-body diagram labeling all forces with their agents and indicating the direction of the acceleration and the net force. Draw arrows the appropriate lengths. 7. A sky diver falls downward through the air at constant velocity (air drag is important). 8 ...
Momentum, Impulse and Law of Conservation of Momentum
... zero before and after the firing? • The momentum in the system must be conserved; so if the system starts with zero momentum, it must end with zero momentum. ...
... zero before and after the firing? • The momentum in the system must be conserved; so if the system starts with zero momentum, it must end with zero momentum. ...