Dynamics Chapter
... 1. Mass is intrinsic to an object. It does not depend on where the object is located. No matter whether it is; on earth, in outer space or deep under the ocean, the mass of an object will not change. 2. An object’s acceleration is inversely proportional to its mass. The more mass an object has, the ...
... 1. Mass is intrinsic to an object. It does not depend on where the object is located. No matter whether it is; on earth, in outer space or deep under the ocean, the mass of an object will not change. 2. An object’s acceleration is inversely proportional to its mass. The more mass an object has, the ...
FRICTION IN APPLICATIONS OF NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... 1a. Friction Needs Normal and Tangential Forces. In this module we introduce some effects of friction into some simple cases in mechanics.1 All such cases occur when there are two objects in contact and there are two force components that act on the objects: (1) a “normal force” which is perpendicul ...
... 1a. Friction Needs Normal and Tangential Forces. In this module we introduce some effects of friction into some simple cases in mechanics.1 All such cases occur when there are two objects in contact and there are two force components that act on the objects: (1) a “normal force” which is perpendicul ...
Momentum and Impulse Unit Notes
... The product of the average force acting on an object and the time during which it acts. Impulse is a vector quantity, and can also be calculated by finding the area under a force versus time curve. linear momentum The product of the mass of an object and its velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity, ...
... The product of the average force acting on an object and the time during which it acts. Impulse is a vector quantity, and can also be calculated by finding the area under a force versus time curve. linear momentum The product of the mass of an object and its velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity, ...
Momentum and Impulse Unit Notes
... IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM PREVIEW The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. If you want to change the momentum of an object, you must apply an impulse, which is the product of force and the time during which the force acts. If there are no external forces acting on a system of ob ...
... IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM PREVIEW The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. If you want to change the momentum of an object, you must apply an impulse, which is the product of force and the time during which the force acts. If there are no external forces acting on a system of ob ...
Circularmotionppt
... In the case of the whirling can, it is a common misconception to state that a centrifugal force pulls outward on the can. In fact, when the string breaks the can goes off in a tangential straight-line path because no force acts on it. So when you swing a tin can in a circular path, there is no force ...
... In the case of the whirling can, it is a common misconception to state that a centrifugal force pulls outward on the can. In fact, when the string breaks the can goes off in a tangential straight-line path because no force acts on it. So when you swing a tin can in a circular path, there is no force ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... • Imposed motion resulting from the action of forces that pushed or pulled. • Always had an external cause. • Once objects were in their natural resting places, they could not move by themselves. ...
... • Imposed motion resulting from the action of forces that pushed or pulled. • Always had an external cause. • Once objects were in their natural resting places, they could not move by themselves. ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... A box of mass m1 = 1 kg, initially at rest, is now pulled by a horizontal string having tension T = 10 N. This box (1) is on top of a second box of mass m2 = 2 kg. The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the 2 boxes are ms=1.5 and mk= 0.5. The second box can slide freely (frictionles ...
... A box of mass m1 = 1 kg, initially at rest, is now pulled by a horizontal string having tension T = 10 N. This box (1) is on top of a second box of mass m2 = 2 kg. The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the 2 boxes are ms=1.5 and mk= 0.5. The second box can slide freely (frictionles ...
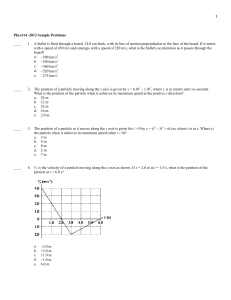
Phys114 -2013 Sample Problems ____ 1. A bullet is fired through a
... 42. The block shown is released from rest when the spring is stretched a distance d. If k = 50 N/m, m = 0.50 kg, d = 10 cm, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is equal to 0.25, determine the speed of the block when it first passes through the positio ...
... 42. The block shown is released from rest when the spring is stretched a distance d. If k = 50 N/m, m = 0.50 kg, d = 10 cm, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is equal to 0.25, determine the speed of the block when it first passes through the positio ...
Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... the same vertical level, find the difference in the air pressure between the two openings. ...
... the same vertical level, find the difference in the air pressure between the two openings. ...
PHY 203: Solutions to Problem Set 9
... to be 5000km/h (which is more than enough for all kinds of missiles and jets). The conclusion is that our results will be expressed with great accuracy to first order in those parameters. • Finally, since our paths are short, we will use the uncorrected parabolic trajectory when we calculate the for ...
... to be 5000km/h (which is more than enough for all kinds of missiles and jets). The conclusion is that our results will be expressed with great accuracy to first order in those parameters. • Finally, since our paths are short, we will use the uncorrected parabolic trajectory when we calculate the for ...
Short Answers to Questions
... text book. Instead it is a helping book to understand the text more clearly. Our standard of education is deteriorating very fast. The major factors are hand-books, keys, made-easy books, notes, and finally tuition. I know there is a war in progress. This Self Study Series is an attempt to enhance t ...
... text book. Instead it is a helping book to understand the text more clearly. Our standard of education is deteriorating very fast. The major factors are hand-books, keys, made-easy books, notes, and finally tuition. I know there is a war in progress. This Self Study Series is an attempt to enhance t ...
Ch. 6 Reading - Mr. Shaffer at JHS
... Push on an empty shopping cart. Then push equally hard on a heavily loaded shopping cart, as shown in Figure 6.2. The loaded shopping cart will accelerate much less than the empty cart. Acceleration depends on the mass being pushed. For a constant force, an increase in the mass will result in a decr ...
... Push on an empty shopping cart. Then push equally hard on a heavily loaded shopping cart, as shown in Figure 6.2. The loaded shopping cart will accelerate much less than the empty cart. Acceleration depends on the mass being pushed. For a constant force, an increase in the mass will result in a decr ...
Problem set 11
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...