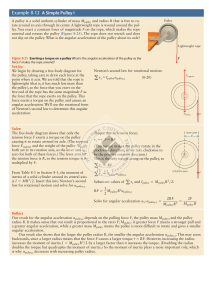
Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in
... - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or m ...
... - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or m ...
force - Cloudfront.net
... • Weight and mass are not the same. • Weight is a force and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. • Weight and mass are related. Weight increases as mass increases. ...
... • Weight and mass are not the same. • Weight is a force and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. • Weight and mass are related. Weight increases as mass increases. ...
4-1_to_4-3 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... • Ball veers to the side • No external force This is a non-inertial frame. • Observed motion inconsistent with Newton’s laws • Fictitious forces ...
... • Ball veers to the side • No external force This is a non-inertial frame. • Observed motion inconsistent with Newton’s laws • Fictitious forces ...
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
... When x =A, the potential energy is equal to E and the kinetic energy is zero. ...
... When x =A, the potential energy is equal to E and the kinetic energy is zero. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... More Laws of Motion • Newton’s First Law of Motion states that if you kick a ball, the ball will move. • Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that when a force acts on an object, the object accelerates. – If you kick the ball harder, it will move faster. – It also tells you that a heavy ball is harde ...
... More Laws of Motion • Newton’s First Law of Motion states that if you kick a ball, the ball will move. • Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that when a force acts on an object, the object accelerates. – If you kick the ball harder, it will move faster. – It also tells you that a heavy ball is harde ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... m/sec/sec? 132 N = 66 kg x 2 m/s/s 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/sec/sec? 9800 N = 1000 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
... m/sec/sec? 132 N = 66 kg x 2 m/s/s 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/sec/sec? 9800 N = 1000 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
OLE11_SCIIPC_TX_04D_TB_1
... 2010 TEKS 4D falls under science concept statement 4: The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. In this context, students will come to understand how to describe and measure the motion of an object. In addition, students will learn how an object’s motion is affected by ...
... 2010 TEKS 4D falls under science concept statement 4: The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. In this context, students will come to understand how to describe and measure the motion of an object. In addition, students will learn how an object’s motion is affected by ...
The Physics A course consists of 40 lessons, which address key
... Compare satellite motion to projectile motion; Calculate the speed needed for a satellite to maintain a circular orbit about a planet; Apply the dynamics of satellite motion to astronomical observations; Identify the contributions of scientists to the understanding of planetary motion Unit 6: Work ...
... Compare satellite motion to projectile motion; Calculate the speed needed for a satellite to maintain a circular orbit about a planet; Apply the dynamics of satellite motion to astronomical observations; Identify the contributions of scientists to the understanding of planetary motion Unit 6: Work ...
p250c04
... forces on an object arise from interactions with other objects. forces are vectors the net force on an object is the vector sum of the individual forces acting on that object The inertia of an object is its resistance to changes in its motion. Mass is a measure of inertia. Inertial Frame of Referenc ...
... forces on an object arise from interactions with other objects. forces are vectors the net force on an object is the vector sum of the individual forces acting on that object The inertia of an object is its resistance to changes in its motion. Mass is a measure of inertia. Inertial Frame of Referenc ...
Phys Sci Chapter 3 notes
... When you jump on a trampoline, you exert a force downward; the trampoline exerts an equal force upward—sending you back in the air. If forces are equal, how does anything ever happen? Action-reaction forces are acting on different objects! ...
... When you jump on a trampoline, you exert a force downward; the trampoline exerts an equal force upward—sending you back in the air. If forces are equal, how does anything ever happen? Action-reaction forces are acting on different objects! ...
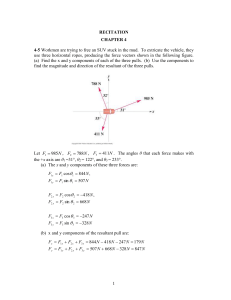
Recitation Ch 4-1
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law – Note Sheet
... we can either change its ___________ or change its speed. In either case, what we are really changing is the object’s ____________. Another name for a change in velocity is __________________. Newton’s 2nd Law takes into account the ____________ that is applied to an object and relates it to how the ...
... we can either change its ___________ or change its speed. In either case, what we are really changing is the object’s ____________. Another name for a change in velocity is __________________. Newton’s 2nd Law takes into account the ____________ that is applied to an object and relates it to how the ...