Chapter 11 Forces
... every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. A. Forces always occur in pairs B. Force pairs do not act on the same object ...
... every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. A. Forces always occur in pairs B. Force pairs do not act on the same object ...
Version PREVIEW – Practice 8 – carroll – (11108) 1 This print
... and radius Rp = 6.55 × 106 m, and you may approximate it as a solid ball of uniform density. It rotates on its axis once every T = 16 hr. The asteroid has mass Ma = 3.99 × 1017 kg and speed va = 22500 m/s (relative to the planet’s center); its velocity vector points θ = 70◦ below the Eastward horizo ...
... and radius Rp = 6.55 × 106 m, and you may approximate it as a solid ball of uniform density. It rotates on its axis once every T = 16 hr. The asteroid has mass Ma = 3.99 × 1017 kg and speed va = 22500 m/s (relative to the planet’s center); its velocity vector points θ = 70◦ below the Eastward horizo ...
Student Word - Nuffield Foundation
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
- Science
... acted upon by an unbalanced force • Objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • The more mass an object has, the more inertia it ...
... acted upon by an unbalanced force • Objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • The more mass an object has, the more inertia it ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s second law, relating the unbalanced forces on a particle to its acceleration. If more than one force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the force ...
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s second law, relating the unbalanced forces on a particle to its acceleration. If more than one force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the force ...
Forces & Motion Review - Warren County Schools
... When acceleration is calculated, it may be a negative number ...
... When acceleration is calculated, it may be a negative number ...
Physics 201 Homework
... There are three forces here. The support force from the hands, the feet, and the person’s weight. We need to choose an axis of rotation. Any axis will work because the system is at rest, in equilibrium. There are three natural places to consider: each place where there is a force. Whichever point we ...
... There are three forces here. The support force from the hands, the feet, and the person’s weight. We need to choose an axis of rotation. Any axis will work because the system is at rest, in equilibrium. There are three natural places to consider: each place where there is a force. Whichever point we ...
Microsoft Word - 12.800 Chapter 4 `06
... original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the natural one, was misled by some experimental data on the discharge of flows in pipes and canals that di ...
... original formulation of the Navier Stokes equations, the validity of this condition was in doubt. Experimental verification was uncertain and Stokes himself, who felt the no slip condition was the natural one, was misled by some experimental data on the discharge of flows in pipes and canals that di ...
Conceptual Physics
... d) Newton’s first law- If net force = 0 then body is at rest or at constant velocity. If net force is NOT zero, then body will ...
... d) Newton’s first law- If net force = 0 then body is at rest or at constant velocity. If net force is NOT zero, then body will ...
Chapter 7 Rotating Frames
... the Earth’s surface, with position vector R relative to the centre of the Earth which rotates with (constant) angular velocity !. The particle is hanging at equilibrium in the lab frame. What is the tension in the string? Since (dx/dt)S 0 = 0, because the particle is at rest in the lab, T + mg = m! ...
... the Earth’s surface, with position vector R relative to the centre of the Earth which rotates with (constant) angular velocity !. The particle is hanging at equilibrium in the lab frame. What is the tension in the string? Since (dx/dt)S 0 = 0, because the particle is at rest in the lab, T + mg = m! ...
forces - jpsaos
... between all objects. The gravitational force between the Earth and the moon keeps the moon in orbit. It may be the most evident but it is the weakest of all the forces. ...
... between all objects. The gravitational force between the Earth and the moon keeps the moon in orbit. It may be the most evident but it is the weakest of all the forces. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air – fluid friction), it would never stop! ...
... unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air – fluid friction), it would never stop! ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
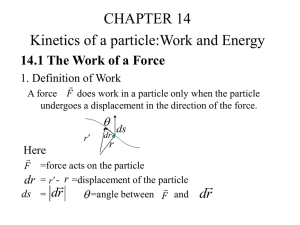
14.1 The Work of a Force
... (2)Work of a spring done on the particle A particle (or only) attached to a spring F.B.D of spring and particle spring force on the particle Fs ks work of a spring on the particle is ...
... (2)Work of a spring done on the particle A particle (or only) attached to a spring F.B.D of spring and particle spring force on the particle Fs ks work of a spring on the particle is ...
Forces-momentum
... net force. • When forces that act in the same direction, the net force can be found by adding the strengths of the individual forces. • When forces act in opposite directions, they also combine to produce a net force. (subtract) ...
... net force. • When forces that act in the same direction, the net force can be found by adding the strengths of the individual forces. • When forces act in opposite directions, they also combine to produce a net force. (subtract) ...
File
... Net force is the vector sum (so both mag & direction) of all the forces acting on an object at one time Last chapter we called this Resultant Force – FR If an object’s Fnet = 0, then the object satisfies the condition in Newton’s 1st Law to be maintaining its state of motion - either at rest or ...
... Net force is the vector sum (so both mag & direction) of all the forces acting on an object at one time Last chapter we called this Resultant Force – FR If an object’s Fnet = 0, then the object satisfies the condition in Newton’s 1st Law to be maintaining its state of motion - either at rest or ...