Unit 5 Review
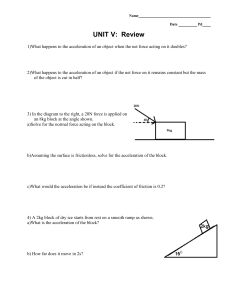
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Newton`s Laws
... 6. A 60 kg person on earth travels to a large planet that has a gravitational pull twice that of ...
... 6. A 60 kg person on earth travels to a large planet that has a gravitational pull twice that of ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... What are the proper units for: -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between t ...
... What are the proper units for: -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between t ...
F g - Humble ISD
... An object in motion remains in motion in a straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition ...
... An object in motion remains in motion in a straight line and at a constant speed OR an object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... • Laws of motion, can be used to analyze motion of ordinary objects. • Not valid for speeds close to the speed of light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
... • Laws of motion, can be used to analyze motion of ordinary objects. • Not valid for speeds close to the speed of light. Need to use the theory of relativity. • Not valid for atomic sized particles. Need to use quantum mechanics. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion 1st & 2nd
... 0.45 kg to her right along a smooth, level lunch counter. The bottle leaves her hand moving at 2.8 m/s, then slows down as it slides because of a constant horizontal friction force exerted on it by the countertop. It slides for 1.0 m before coming to rest. What are the magnitude and direction of the ...
... 0.45 kg to her right along a smooth, level lunch counter. The bottle leaves her hand moving at 2.8 m/s, then slows down as it slides because of a constant horizontal friction force exerted on it by the countertop. It slides for 1.0 m before coming to rest. What are the magnitude and direction of the ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... force applied to a 3 kg object? A 6 kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/s2? 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/s2? ...
... force applied to a 3 kg object? A 6 kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/s2? 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/s2? ...
Name - forehandspace
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
Chapter 11 Lesson 2- Forces and Motion Vocabulary force friction
... Gravity is the force that attracts all matter together. Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation ◦ Gravity depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. ◦ Increasing the mass increases the force, and increasing the distance decreases the force. Friction makes it difficult to slide ...
... Gravity is the force that attracts all matter together. Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation ◦ Gravity depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. ◦ Increasing the mass increases the force, and increasing the distance decreases the force. Friction makes it difficult to slide ...
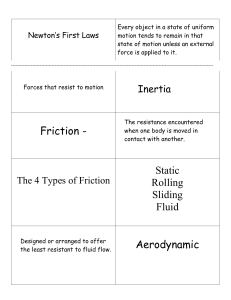
vocabulary
... A force on objects or substances in contact with each other that resists motion of the objects or substances relative to each other; a resistance encountered when one body moves relative to another body with which it is in ...
... A force on objects or substances in contact with each other that resists motion of the objects or substances relative to each other; a resistance encountered when one body moves relative to another body with which it is in ...