Newton`s Laws
... Consider an elevator moving downward and speeding up with an acceleration of 2 m/s2. The mass of the elevator is 1000 kg. Ignore air resistance. What is the tension in the elevator cable? ...
... Consider an elevator moving downward and speeding up with an acceleration of 2 m/s2. The mass of the elevator is 1000 kg. Ignore air resistance. What is the tension in the elevator cable? ...
Monday, September 20, 2004
... Determine the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the puck whose mass is 0.30kg and is being pulled by two forces, F1 and F2, as shown in the picture, whose magnitudes of the forces are 8.0 N and 5.0 N, respectively. ...
... Determine the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the puck whose mass is 0.30kg and is being pulled by two forces, F1 and F2, as shown in the picture, whose magnitudes of the forces are 8.0 N and 5.0 N, respectively. ...
Force of Gravity
... and bicycle wheel, your feet and the floor, cars, and trains all keep in motion from friction…without friction you would not be able to move the bike, car, train, or walk on the road. Not helpful metal parts touching in a machine can ...
... and bicycle wheel, your feet and the floor, cars, and trains all keep in motion from friction…without friction you would not be able to move the bike, car, train, or walk on the road. Not helpful metal parts touching in a machine can ...
Forces with acceleration homework
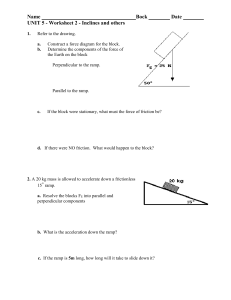
... 15° ramp. a. Resolve the blocks FE into parallel and perpendicular components ...
... 15° ramp. a. Resolve the blocks FE into parallel and perpendicular components ...
Force and Newton` s Laws Study Guide
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
Newton s Second and Third Laws and Gravity
... The gravitational force on an object near the surface of Earth is: Fgrav = m·g ...
... The gravitational force on an object near the surface of Earth is: Fgrav = m·g ...
Chapter 10-Forces - Solon City Schools
... Which of Newton’s Laws states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion at a constant velocity will continue in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by an outside force? ...
... Which of Newton’s Laws states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion at a constant velocity will continue in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by an outside force? ...
Ch6Lecture2
... 1) Side1: KE = 0, Total E = PE 2) Bottom: PE = 0, KE = Total E 3) Side2: KE = 0, Total E = PE F 4) Work to get this started, after that W = 0 a) Input E into the system b) ET = KE + PE = constant c) Sides: Initial Work gives us PE d) Bottom: Gravity moves bob down (KE) e) F = tension = centripetal f ...
... 1) Side1: KE = 0, Total E = PE 2) Bottom: PE = 0, KE = Total E 3) Side2: KE = 0, Total E = PE F 4) Work to get this started, after that W = 0 a) Input E into the system b) ET = KE + PE = constant c) Sides: Initial Work gives us PE d) Bottom: Gravity moves bob down (KE) e) F = tension = centripetal f ...
Forces
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (cont.) • Newton’s third law of motion says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of the same size but in the opposite direction on the first object. • E ...
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (cont.) • Newton’s third law of motion says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of the same size but in the opposite direction on the first object. • E ...
Chapter-6 Work and Energy
... gymnast leaves the trampoline at a height of 1.20 m and reaches a maximum height of 4.80 m before falling back down. All heights are measured with respect to the ground. Ignoring air resistance, determine the initial speed v0 with which the gymnast leaves the trampoline. ...
... gymnast leaves the trampoline at a height of 1.20 m and reaches a maximum height of 4.80 m before falling back down. All heights are measured with respect to the ground. Ignoring air resistance, determine the initial speed v0 with which the gymnast leaves the trampoline. ...
Physics I - Rose
... 4.10. Solve: (a) This problem calls for an estimate so we are looking for an approximate answer. Table 4.3 gives us no information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of ...
... 4.10. Solve: (a) This problem calls for an estimate so we are looking for an approximate answer. Table 4.3 gives us no information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of ...
Chapter 19 Outline The First Law of Thermodynamics - Help-A-Bull
... “Law I: Every body persists in its state of being at rest or of moving uniformly straight forward, except insofar as it is compelled to change its state by force impressed.” • From our text: A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and zero acceleration. ...
... “Law I: Every body persists in its state of being at rest or of moving uniformly straight forward, except insofar as it is compelled to change its state by force impressed.” • From our text: A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and zero acceleration. ...