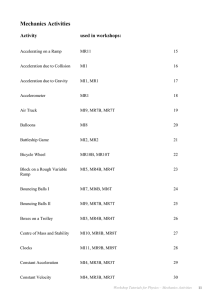
Physics Week 1(Sem. 2)
... attraction between them. If two negatively charged objects, or two positively charged objects, were brought near each other there would be a repulsive force between them. This force that is experienced between the objects can alter motion (cause acceleration). As seen in Newton’s second law ...
... attraction between them. If two negatively charged objects, or two positively charged objects, were brought near each other there would be a repulsive force between them. This force that is experienced between the objects can alter motion (cause acceleration). As seen in Newton’s second law ...
Ph 2001 Jan Key
... A coefficient of friction of 0.47 exists between the 5.0 kg block and the table. What is the maximum mass, m, that can be hung from the cords before the 5.0 kg block begins to move? (7 marks) ...
... A coefficient of friction of 0.47 exists between the 5.0 kg block and the table. What is the maximum mass, m, that can be hung from the cords before the 5.0 kg block begins to move? (7 marks) ...
Dynamic Analysis of Rodlike Object Deformation
... objects is presented. In manufacturing processes, there are many manipulative operations which deal with deformable objects. Evaluation of the shapes of these objects is important for their manipulative operations because their deformation can cause both success of such operations if it is utilized ...
... objects is presented. In manufacturing processes, there are many manipulative operations which deal with deformable objects. Evaluation of the shapes of these objects is important for their manipulative operations because their deformation can cause both success of such operations if it is utilized ...
Rotational Dynamics - Piri Reis Üniversitesi
... •An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
... •An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
05._UsingNewtonsLaws
... k & s of a tire on dry road are 0.61 & 0.89, respectively. If the car is travelling at 90 km/h (25 m/s), (a) determine the minimum stopping distance. (b) the stopping distance with the wheels fully locked (car skidding). ...
... k & s of a tire on dry road are 0.61 & 0.89, respectively. If the car is travelling at 90 km/h (25 m/s), (a) determine the minimum stopping distance. (b) the stopping distance with the wheels fully locked (car skidding). ...
form 4- 32 circular motion - kcpe-kcse
... Calculate (a) its angular speed in rad s-1; (b) its outer edge linear speed. (a) 7200 r.p.m. = [(7200 x 2 x π) / 60] rad s-1 angular speed = 754 rad s-1 ...
... Calculate (a) its angular speed in rad s-1; (b) its outer edge linear speed. (a) 7200 r.p.m. = [(7200 x 2 x π) / 60] rad s-1 angular speed = 754 rad s-1 ...