Outcomes Survey Begi.. - Aerospace Engineering Courses page
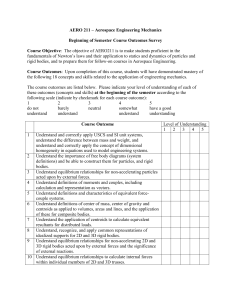
... and be able to model friction correctly, including the relationship between forces acting normal to a plane of contact and friction forces in the plane of contact. 13 Understand 2D (planar) definitions for velocity and acceleration for Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems, and be able to tra ...
... and be able to model friction correctly, including the relationship between forces acting normal to a plane of contact and friction forces in the plane of contact. 13 Understand 2D (planar) definitions for velocity and acceleration for Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems, and be able to tra ...
lab 6: work and energy - ITS
... force is not constant. For example, the force exerted by a spring increases the more you stretch the spring. In this lab you will learn how to measure and calculate the work done by any force that acts on a moving object (even a force that changes with time). Often it is useful to know both the tota ...
... force is not constant. For example, the force exerted by a spring increases the more you stretch the spring. In this lab you will learn how to measure and calculate the work done by any force that acts on a moving object (even a force that changes with time). Often it is useful to know both the tota ...
Ch03_Lecture_Outline - Saint Leo University Faculty
... Explain your answer to your neighbor. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Explain your answer to your neighbor. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
Anonymous-VibrationTheoryFundamentals.pdf
... mass and inertia for kinetic energy, and damper for dissipating mechanical energy. The vibration process alternatively converts energy between its potential and kinetic forms. In its general sense the vibration is a periodic motion that repeats itself in all its details after a certain interval of t ...
... mass and inertia for kinetic energy, and damper for dissipating mechanical energy. The vibration process alternatively converts energy between its potential and kinetic forms. In its general sense the vibration is a periodic motion that repeats itself in all its details after a certain interval of t ...