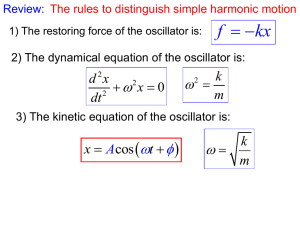
Chapter 2
... amplitude A=0.12m, period T=2s. When t=0, its displacement is x(0)=0.06m, moving to the positive direction of the equilibrium position. Find: 1) The kinetic equation of the simple harmonic motion. 2) t=T/4, the position, velocity and acceleration of the particle. 3) The time to arrive the equilibriu ...
... amplitude A=0.12m, period T=2s. When t=0, its displacement is x(0)=0.06m, moving to the positive direction of the equilibrium position. Find: 1) The kinetic equation of the simple harmonic motion. 2) t=T/4, the position, velocity and acceleration of the particle. 3) The time to arrive the equilibriu ...
chap 6 momentum
... than a car moving at the same speed because it has a greater mass. Which is more difficult to slow down? The car or the large truck? ...
... than a car moving at the same speed because it has a greater mass. Which is more difficult to slow down? The car or the large truck? ...
Rigid Body Simulation
... into a group of convex polyhedra. One way to do this is by using binary space partitioning, where we essentially recursively subdivide the polyhedron into convex smaller polyhedrons by using partitioning planes [16]. Convex decomposition is still an active area of research. This is because most part ...
... into a group of convex polyhedra. One way to do this is by using binary space partitioning, where we essentially recursively subdivide the polyhedron into convex smaller polyhedrons by using partitioning planes [16]. Convex decomposition is still an active area of research. This is because most part ...
Newton`s Laws: Determining the Motion
... If we follow such arguments to their logical conclusion we will decide that the first law is only valid in a non-accelerating reference frame. (This is also true of Newton’s other two laws.) A non-accelerating frame is called an inertial reference frame. Does such a reference frame actually exist? N ...
... If we follow such arguments to their logical conclusion we will decide that the first law is only valid in a non-accelerating reference frame. (This is also true of Newton’s other two laws.) A non-accelerating frame is called an inertial reference frame. Does such a reference frame actually exist? N ...
Document
... Notation and method for the vector sum—Figure 4.7 • We refer to the vector sum or resultant as the “sum of forces” R = F1 + F2 + F3 … Fn = ΣF. ...
... Notation and method for the vector sum—Figure 4.7 • We refer to the vector sum or resultant as the “sum of forces” R = F1 + F2 + F3 … Fn = ΣF. ...
AP Test Free Response Questions
... swung in a vertical circle, as shown in the diagram above. Point P, the lowest point of the circle, is 0.20 meter above the floor. The speed of the ball at the top of the circle is 6.0 meters per second, and the total energy of the ball is kept constant. a. Determine the total energy of the ball, us ...
... swung in a vertical circle, as shown in the diagram above. Point P, the lowest point of the circle, is 0.20 meter above the floor. The speed of the ball at the top of the circle is 6.0 meters per second, and the total energy of the ball is kept constant. a. Determine the total energy of the ball, us ...
CHAPTER 4
... FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the car: y-component: FTmin – mg = ma, or FTmin = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(– 0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2 ...
... FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the car: y-component: FTmin – mg = ma, or FTmin = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(– 0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2 ...