Notes - UMD Physics
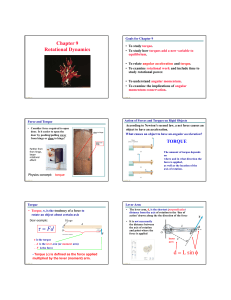
... Although torque is a force multiplied by a distance, it is very different from work and energy The units for torque are reported in N.m and not changed to Joules 9-Apr-28 ...
... Although torque is a force multiplied by a distance, it is very different from work and energy The units for torque are reported in N.m and not changed to Joules 9-Apr-28 ...
ExamView - S15--Physics Q4 Torque.tst
... 5. A heavy bank-vault door is opened by the application of a force of 3.0 × 10 2 N directed perpendicular to the plane of the door at a distance of 0.80 m from the hinges. What is the torque? a. 240 N•m b. 360 N•m c. 300 N•m d. 120 N•m 6. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the ...
... 5. A heavy bank-vault door is opened by the application of a force of 3.0 × 10 2 N directed perpendicular to the plane of the door at a distance of 0.80 m from the hinges. What is the torque? a. 240 N•m b. 360 N•m c. 300 N•m d. 120 N•m 6. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the ...
Ch 8 – Oscillation
... from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency is the number of cycles per second that an oscillator g ...
... from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency is the number of cycles per second that an oscillator g ...
Chap8
... Newton’s second law for rotational motion states that angular acceleration is directly proportional to the net torque and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia. This law is expressed by the following equation. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion ...
... Newton’s second law for rotational motion states that angular acceleration is directly proportional to the net torque and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia. This law is expressed by the following equation. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
Vectors in Two Dimensions (cont.)
... • Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. • For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. • The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the ...
... • Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. • For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. • The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the ...
Chapter #3 uniform-circular-motion
... A car is traveling at a velocity of 20 m/s. The driver of the car has a mass of 60 kg.The car is located at the bottom of a dip in the road. The radius of the dip is 80m. What is the apparent weight of the driver (the normal force supplied by the seat of the car to support him) at the bottom o ...
... A car is traveling at a velocity of 20 m/s. The driver of the car has a mass of 60 kg.The car is located at the bottom of a dip in the road. The radius of the dip is 80m. What is the apparent weight of the driver (the normal force supplied by the seat of the car to support him) at the bottom o ...
Physics 231 Topic 7: Oscillations Wade Fisher October 5-10 2012
... Newton’s second law: F=ma -kx=ma a=-kx/m acceleration(a) kA/m ...
... Newton’s second law: F=ma -kx=ma a=-kx/m acceleration(a) kA/m ...