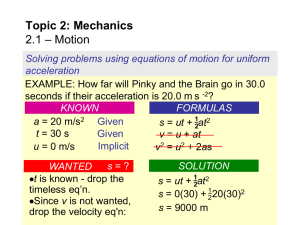
Horizontal Kinematics - The Woodlands High School
... 10. How fast must a bullet be shot to reach a height of 250 m? 11. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 8.9 m/s2. If balls on Mars and the Earth are thrown upward simultaneously with a speed of 10m/s, which would return to the ground first and by how much time would it beat the other ball? [th ...
... 10. How fast must a bullet be shot to reach a height of 250 m? 11. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 8.9 m/s2. If balls on Mars and the Earth are thrown upward simultaneously with a speed of 10m/s, which would return to the ground first and by how much time would it beat the other ball? [th ...
AB_Activity_03
... lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will collect your students’ answers to the lab problem warm-up questions 1-2 days prior to teaching the lab. Collecting the answers ...
... lab problem: Force and Motion. It is the first lab that addresses the physics concept of force. This particular set of solutions was from 2004. During the semester you will collect your students’ answers to the lab problem warm-up questions 1-2 days prior to teaching the lab. Collecting the answers ...
sy12_oct15_07
... A block of mass M is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. A bullet of mass m is fired at the block with a muzzle velocity (speed) v. The bullet lodges in the block, and the block ends up with a speed V. What is the initial energy of the system ? What is the final energy of the ...
... A block of mass M is initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. A bullet of mass m is fired at the block with a muzzle velocity (speed) v. The bullet lodges in the block, and the block ends up with a speed V. What is the initial energy of the system ? What is the final energy of the ...
Conservation of Angular Momentum
... If the internal forces between a pair of particles are directed along the line joining the two particles then the torque due to the internal forces cancel in pairs. int int ...
... If the internal forces between a pair of particles are directed along the line joining the two particles then the torque due to the internal forces cancel in pairs. int int ...
Powerpointreviewsolutuionschap16
... ConcepTest 16.11 Uniform Electric Field 22) In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
... ConcepTest 16.11 Uniform Electric Field 22) In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
Powerpoint Slides
... ConcepTest 19.11 Uniform Electric Field In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
... ConcepTest 19.11 Uniform Electric Field In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
Chap. 16 Conceptual Modules Giancoli
... ConcepTest 16.11 Uniform Electric Field In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
... ConcepTest 16.11 Uniform Electric Field In a uniform electric field in empty space, a 4 C charge is placed and it feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
Lecture 1 - GEOCITIES.ws
... as input the initial location, mass, and velocity of the sun, each of the planets and their moons, and some set of asteroids and comets. The program should then simulate the specified solar system in action by repeatedly computing the next position of each of the specified bodies over a period rangi ...
... as input the initial location, mass, and velocity of the sun, each of the planets and their moons, and some set of asteroids and comets. The program should then simulate the specified solar system in action by repeatedly computing the next position of each of the specified bodies over a period rangi ...
Lesson 1 - Physical Quantities and units - science
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
chapter 7
... b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinetic energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy ...
... b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinetic energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy ...
Final Momentum NRG Review
... which is moving in the same direction with a speed of 0.40 m/s. If the faster ball slows down to a speed of 0.65 m/s, then what is the speed of the second ball? PSYW 56. A 0.050-kg billiard ball moving at 1.5 m/s strikes a second 0.050-kg billiard ball which is at rest on the table. If the first bal ...
... which is moving in the same direction with a speed of 0.40 m/s. If the faster ball slows down to a speed of 0.65 m/s, then what is the speed of the second ball? PSYW 56. A 0.050-kg billiard ball moving at 1.5 m/s strikes a second 0.050-kg billiard ball which is at rest on the table. If the first bal ...