PHYSICS 211, Exam # 3 April 22, 2013 (Dr. Xinhua Bai`s session
... (Open book. No notes are allowed. You may use a calculator. There are twelve multiple-choice problems. For each of the multiple-choice questions below, choose the most correct answer.) 1. The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of a system of objects is conserved: A) only when no external forc ...
... (Open book. No notes are allowed. You may use a calculator. There are twelve multiple-choice problems. For each of the multiple-choice questions below, choose the most correct answer.) 1. The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of a system of objects is conserved: A) only when no external forc ...
Monday, September 24, 2007
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
Force - springsphysics
... Your new college roommate has put a box in front of your closet. The box is quite massive (60kg), so you slide it out of the way. The floor is dirty and rough, with a coefficient of friction .31. a) ...
... Your new college roommate has put a box in front of your closet. The box is quite massive (60kg), so you slide it out of the way. The floor is dirty and rough, with a coefficient of friction .31. a) ...
Dynamics Presentation
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. ...
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. ...
Force in Mechanical Systems
... Forces are quantities that are described in terms of 2 parameters: ...
... Forces are quantities that are described in terms of 2 parameters: ...
P4: Explaining Motion
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion 12.1 Forces
... Gravity is a force of attraction that acts between two objects. (examples: Earth and the sun, the moon and Earth, you and Earth) We will just look at the gravity Earth exerts on objects. Earth’s gravity acts downward toward the center of the earth. Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whil ...
... Gravity is a force of attraction that acts between two objects. (examples: Earth and the sun, the moon and Earth, you and Earth) We will just look at the gravity Earth exerts on objects. Earth’s gravity acts downward toward the center of the earth. Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whil ...
Physics Stations
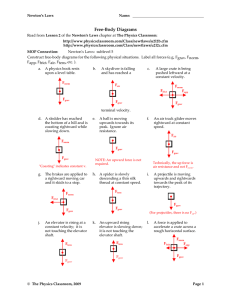
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
Wizard Test Maker - Canvas by Instructure
... 1. The position of a vehicle of mass 1000 kg moving on a straight track along the x-axis is given by the equation x(t) = t3 – t2 – 6t, where x is in meters and t is in seconds. What is the instantaneous force acting on the vehicle at t = 3 s? ...
... 1. The position of a vehicle of mass 1000 kg moving on a straight track along the x-axis is given by the equation x(t) = t3 – t2 – 6t, where x is in meters and t is in seconds. What is the instantaneous force acting on the vehicle at t = 3 s? ...
Notes on Terminal Velocity and Simple Harmonic Motion – Physics C
... At t=0, the acceleration is g, since the velocity is zero. This can be confirmed using Newton’s Second Law, mg-kv=ma, and mg-0=ma so therefore a=g at t=0. After a long time, the acceleration of the object is zero. It is important to help the students learn to plug in these limiting values to determi ...
... At t=0, the acceleration is g, since the velocity is zero. This can be confirmed using Newton’s Second Law, mg-kv=ma, and mg-0=ma so therefore a=g at t=0. After a long time, the acceleration of the object is zero. It is important to help the students learn to plug in these limiting values to determi ...