* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Stations
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
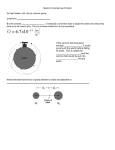
Physics Stations NAME:___________________________________ Station 1: Acceleration Background information; Acceleration describes how velocity changes over time. On the weather channel a hurricane’s path is explained in terms of velocity. People want to know how fast a hurricane is travelling but they also need to know in what direction it is travelling so that they can evacuate if necessary. For instance, the weatherman will report a hurricane’s velocity as five kilometers per hour moving in a northeasterly direction. Activity 1: Calculate the acceleration of the roller coater here. Show your work: Activity 2: Draw your 3 acceleration diagrams here: Station 2: Simple Machines The three pages for this station are attached to the very back of the packet. Station 3: Measuring Force Background information: Forces are pushes or pulls. If forces are unbalanced, they make objects move or stop moving. Forces are measured in Newtons. A Newton is the amount of force necessary to accelerate one kilogram of mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Weight is the downward force of gravity on an object. It is properly measures in Newtons. Record your data here. WEIGHT (G) FORCE NEEDED TO MOVE (N) What relationship do you see between weight and force:___________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Station 4: Air Pucks Use pages 43 – 51 for more information on Newton’s Laws. How did you use the air pucks to represent each of the three laws. Use illustrations if necessary. 1st Law: 2nd Law: 3rd Law: Station 5: Speed Walking Background information: Speed is a way to describe motion. It describes how much time it takes to travel a distance. Average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time it took to travel the distance. Distance can be calculated by multiplying the speed and time. Velocity is speed and direction. Activity – Speed Walking – Record data below. Trial 1 2 3 Distance (m) AVERAGE SPEED Time (sec) Speed (m/sec) Station 6: Work Background information: Work in physics means using a force to create movement or cause motion. Work is only done when a force moves an object and the motion of the object is in the same direction as the force. To measure the amount of work that you do, you multiply the force times the distance the object moved. Work = Force X Distance Activity; Are you working? Describe you observations below:__________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Station 7: Friction Background information: Friction is the resistance that happens when one object moves over or rubs against the surface or another. The force of friction can start things moving, slow them down, or stop them. Two things that affect the amount of friction are the roughness of the surface and the mass of an object, The heavier the object is, the more friction there is when you try to move the object. Surface Bare desk Wax paper Foil Plastic wrap Brown paper Prediction Total Mass Station 8: Speed Number of Blocks Length of ramp Time on Ramp Average Speed Distance from Ramp 1. When did the car move the fastest? 2. When did the car move the farthest? Station 9: Action-Reaction Background information ; The law of action and reaction states that whenever an object exerts a force (action) on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force (reaction) on the first. For example, when a jet engine is started or when a rocket is fired, rapidly expanding gases exert a force on them while they exert equal but opposite forces on the gases. The gases move backwards and the jet or rocket moves forward or upward. # of marbles # of marbles that move 1 2 3 4 What pattern do you see? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Station 10: Gravity Background Information: One force that affects everything on Earth is gravity. Gravity is a force that acts at a distance and pulls objects toward each other. The amount of matter in an object is called its mass. The force of gravity depends on the amount of mass a body has. The weight of an object is the measurement of the force of gravity on that object. You weigh something on a scale, according to the force that the Earth pulls it down. So the weight is actually the force of gravity on that object. If you drop an object, it will speed up because of acceleration due to gravity. Interestingly, mass does not have anything to do with acceleration due to gravity. Heavy objects fall just as fast as lighter objects. Air friction will slow some objects down, but if we didn’t have any air, all objects would fall at the same speed. Trial 1 Trail 2 Trail 3 Average Helicopter Helicopter + 1 paper clip Helicopter + 2 paper clips Helicopter + 3 paper clips Did the mass of the paper clip helicopter make a difference in the time it took to fall? Why or why not?_____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another way, first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity (speed & direction) will naturally remain constant. This means that if an object is moving along, untouched by a force of any kind, it will continue to move along in a perfectly straight line at a constant speed. This also means that if an object is standing still and is not contacted by any forces, it will continue to remain without moving. This is also known as The Law of Inertia. Newton's Second Law of Motion explains how an object will change velocity (speed & direction) if it is pushed or pulled upon. This law states that if you do apply a force on an object, it will accelerate (change velocity), and it will change its velocity in the direction of the force. Secondly, this acceleration is directly proportional to the force. For example, if you are pushing on an object, causing it to accelerate, and then you push twice as hard, the acceleration will be two times greater. Lastly, this acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. For example, if you are pushing equally on two objects, and one of the objects has five times more mass than the other, it will accelerate at one fifth the acceleration of the other. Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every force there is an equal and opposite force. For example, if you push on a wall, it will push back on you as hard as you are pushing on it. 1st Law � Description: 2nd Law � Description: 3rd Law � Description: Station 12; Internet Assignment Background Information: When an object rolls over a surface, the kind of friction that occurs is rolling friction. Skate boarders take advantage of this type of friction all the time. Reducing the amount of friction between the surface and the wheels allow skaters to go really fast. 1. What three forces are acting on a skateboard during an Ollie? a. _______________________________ b. _______________________________ c. _______________________________ 2. Describe any change in force that occurs during an Ollie. What does it do? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. What is a torque? _________________________________________________________ 4. What is the force that acts on you in midair? ____________________________________ 5. Record your observations of the activity: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 6. Describe how skateboarders build up speed in a half pipe. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Station 13; Speed Domino Dash Record the speed of the falling dominoes in the data table below; Length of domino row Time to fall Speed of Dominoes 1. What effect does distance have on the speed of a moving object?___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ 2. What affect does time have on the speed of a moving object? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Station 14; Balloon Rocket Data: Observations of completely inflated balloon ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Observations of partially inflated balloon ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Questions: 1. What is the action force in this investigation? ___________________________________________________________ 2. What is the reaction force in this investigation? ___________________________________________________________ 3. What is the action force acting on in this investigation? ___________________________________________________________ 4. What is the reaction force acting on in this investigation? ___________________________________________________________ 5. What happened when the amount of force (amount of air in the balloon) was changed? ___________________________________________________________ 6. Explain your answer to number 5 using Newton’s 3rd Law. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 7. Think about a real rocket launching at NASA. What are the action and reaction forces in the launch? What are the forces acting upon? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________