Slides - Powerpoint - University of Toronto Physics
... where A is the cross-sectional area of the object, ρ is the density of the air, C is called the drag coefficient, and v is the speed. • The direction of air resistance is opposite to the direction of motion relative to the air. • It depends on the size and shape of the object, and its speed, but not ...
... where A is the cross-sectional area of the object, ρ is the density of the air, C is called the drag coefficient, and v is the speed. • The direction of air resistance is opposite to the direction of motion relative to the air. • It depends on the size and shape of the object, and its speed, but not ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... **Misconception** - Normal Force is not equal and opposite to weight ...
... **Misconception** - Normal Force is not equal and opposite to weight ...
document
... • A force is exerted when one object pushes or pulls on another. • A force that is exerted only when two objects are touching is a contact force. • Non-contact forces are forces that can be exerted by one object on another even when the objects aren’t touching. ...
... • A force is exerted when one object pushes or pulls on another. • A force that is exerted only when two objects are touching is a contact force. • Non-contact forces are forces that can be exerted by one object on another even when the objects aren’t touching. ...
Test 6 - Circular - Blank
... 28. A space station rotates to simulate "gravitational forces" with normal forces of astronauts being up against the wall. Suppose the space ship wanted the astronauts to experience a normal force value which was equivalent to their typical gravitational weight. The rotating space ship has a radi ...
... 28. A space station rotates to simulate "gravitational forces" with normal forces of astronauts being up against the wall. Suppose the space ship wanted the astronauts to experience a normal force value which was equivalent to their typical gravitational weight. The rotating space ship has a radi ...
Multiple Choice 2 with Answers
... 1. A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is A. equal to its weight B. equal to its mass C. dependent ...
... 1. A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is A. equal to its weight B. equal to its mass C. dependent ...
An Investigation of a Model for Air Resistance
... Introduction: When an object falls near the Earth’s surface it experiences the force of gravity as well as a drag force due to air resistance. In first year physics, most students are told to “ignore” wind resistance. This lab is designed to show that a model equation may be tested. One of the simpl ...
... Introduction: When an object falls near the Earth’s surface it experiences the force of gravity as well as a drag force due to air resistance. In first year physics, most students are told to “ignore” wind resistance. This lab is designed to show that a model equation may be tested. One of the simpl ...
Physics principles
... 6.An object in equilibrium has no resultant force acting on it. The sum of all the x -components is zero, the sum of all the y -components is zero. 7.The equilibrant force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the resultant vector. 8.Static friction exists between two surfaces when moti ...
... 6.An object in equilibrium has no resultant force acting on it. The sum of all the x -components is zero, the sum of all the y -components is zero. 7.The equilibrant force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the resultant vector. 8.Static friction exists between two surfaces when moti ...
Momentum and Impulse
... 7) What is the impulse provided by a baseball bat providing a 450 N force over 0.3 seconds? 8) A rubber bumper provides an impulse of 540 N·s to stop a golf cart. a. What was the average force provided by the bumper if it acted over 1.2 seconds? ...
... 7) What is the impulse provided by a baseball bat providing a 450 N force over 0.3 seconds? 8) A rubber bumper provides an impulse of 540 N·s to stop a golf cart. a. What was the average force provided by the bumper if it acted over 1.2 seconds? ...
Straw Tower
... gravity is no longer located above the base then the structure cannot stand upright. A center of gravity that is low and close to the base also makes a structure very stable. Compression: The stress/force felt when an object is being pushed together (inward). When a tennis ball rests on a column of ...
... gravity is no longer located above the base then the structure cannot stand upright. A center of gravity that is low and close to the base also makes a structure very stable. Compression: The stress/force felt when an object is being pushed together (inward). When a tennis ball rests on a column of ...
Jeopardy Review
... A Honda Civic4-15A and an 18-wheeler moving at the same speed collide head-on. Which one experiences a greater force of impact? They both experience the same force, though the Civic, since it has less mass, will undergo a greater acceleration. ...
... A Honda Civic4-15A and an 18-wheeler moving at the same speed collide head-on. Which one experiences a greater force of impact? They both experience the same force, though the Civic, since it has less mass, will undergo a greater acceleration. ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
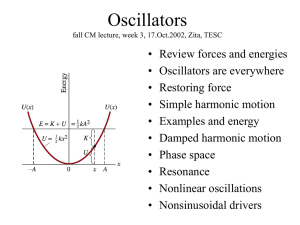
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
Guided Practice—Student Copy
... Before students can understand Newton’s laws, they must understand the following concepts. Force – a push or pull, mass -- the amount of matter in an object, Velocity – speed in a given direction, and acceleration – the rate at which velocity changes. Newton’s first law also called the Law of inerti ...
... Before students can understand Newton’s laws, they must understand the following concepts. Force – a push or pull, mass -- the amount of matter in an object, Velocity – speed in a given direction, and acceleration – the rate at which velocity changes. Newton’s first law also called the Law of inerti ...