Formula Sheet - Blank File
... Capacitance equations (If hooked up to a battery: V is constant. If battery is disconnected and capacitor isolated after charging: Q is constant): or Energy stored in a capacitor: ...
... Capacitance equations (If hooked up to a battery: V is constant. If battery is disconnected and capacitor isolated after charging: Q is constant): or Energy stored in a capacitor: ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... resistance, fall at the same rate of acceleration. 4. Explain the fundamentals of Newton’s 3rd law of motion 5. Analyze force pairs for any interaction Section 4 1. Explain the difference between mass and weight, and how weight is related to gravitational force. 2. Solve conversion problems for mass ...
... resistance, fall at the same rate of acceleration. 4. Explain the fundamentals of Newton’s 3rd law of motion 5. Analyze force pairs for any interaction Section 4 1. Explain the difference between mass and weight, and how weight is related to gravitational force. 2. Solve conversion problems for mass ...
physics midterm review
... Additional Review for Physics Midterm 9) A dog runs down the entire length of his driveway at a constant speed of 4 m/s for 5 s, then uniformly increases her speed to 8 m/s in 4 s. How long is the driveway? ...
... Additional Review for Physics Midterm 9) A dog runs down the entire length of his driveway at a constant speed of 4 m/s for 5 s, then uniformly increases her speed to 8 m/s in 4 s. How long is the driveway? ...
PowerPoint - University of Toronto Physics
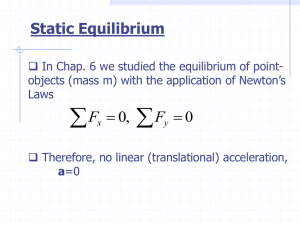
... of these choices should be done to simplify your calculations. • Each force has an x and y component and a torque. Sum all of these up. • Three equations which you can use are: ...
... of these choices should be done to simplify your calculations. • Each force has an x and y component and a torque. Sum all of these up. • Three equations which you can use are: ...
Part I
... • Fr is NOT a new kind of force. Exactly what it is depends on the problem. It could be string tension, gravity, etc. It is the right side of ∑F = ma, not the left side! (It is the form of ma for circular motion) ...
... • Fr is NOT a new kind of force. Exactly what it is depends on the problem. It could be string tension, gravity, etc. It is the right side of ∑F = ma, not the left side! (It is the form of ma for circular motion) ...
Physical Science
... 2. A car travels with zero acceleration along a road. What does this tell you about the car’s motion? 3. Describe the acceleration of a runner during a 100 m race. ...
... 2. A car travels with zero acceleration along a road. What does this tell you about the car’s motion? 3. Describe the acceleration of a runner during a 100 m race. ...
File
... g. an object at rest tends to stay a rest, an object in motion tends to stay in motion 8. ___ Velocity h. the speed of an object and the direction of its motion 9. ___ Acceleration i. the sum of all forces acting on an object 10. ___ Speed j. the tendency of an object to resist changes in motion 11. ...
... g. an object at rest tends to stay a rest, an object in motion tends to stay in motion 8. ___ Velocity h. the speed of an object and the direction of its motion 9. ___ Acceleration i. the sum of all forces acting on an object 10. ___ Speed j. the tendency of an object to resist changes in motion 11. ...
Newton`s 1st Law - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... velocity will continue to move at a constant velocity if no force is applied (ie, no acceleration). ...
... velocity will continue to move at a constant velocity if no force is applied (ie, no acceleration). ...
File - Martin Ray Arcibal
... Newton’s Second law – Constant Mass, Changing Force (Motion Sensor) 1. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to test the validity of Newton’s second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to the object and inversely propor ...
... Newton’s Second law – Constant Mass, Changing Force (Motion Sensor) 1. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to test the validity of Newton’s second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to the object and inversely propor ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The Law of Conservation of Momentum • The total momentum of any group of objects remains the same, or is conserved unless outside forces act on the object. – The total momentum of objects that interact does not change, in the absence of outside forces. – Momentum may be transferred from one to anot ...
... The Law of Conservation of Momentum • The total momentum of any group of objects remains the same, or is conserved unless outside forces act on the object. – The total momentum of objects that interact does not change, in the absence of outside forces. – Momentum may be transferred from one to anot ...
Impulse and Momentum
... gained nor loss. Momentum is transferred to another object. ½m1iv1i² + ½m2iv2i²= ½m1fv1f² + ½m2fv2f² m1v1i + m2v2i= m1v1f + m2v2f ...
... gained nor loss. Momentum is transferred to another object. ½m1iv1i² + ½m2iv2i²= ½m1fv1f² + ½m2fv2f² m1v1i + m2v2i= m1v1f + m2v2f ...