CTRIIa
... True A or False B: Whether the block makes it to the top of the ramp depends on the mass of block and on the angle . Answer: false. The block will make it to the top if (1/2)mv2 > or = mgh. The m’s cancel. Whether the block makes it to the top depends only on v and h. Suppose now that there is fric ...
... True A or False B: Whether the block makes it to the top of the ramp depends on the mass of block and on the angle . Answer: false. The block will make it to the top if (1/2)mv2 > or = mgh. The m’s cancel. Whether the block makes it to the top depends only on v and h. Suppose now that there is fric ...
AP Physics Review Sheet 1
... See Newton’s laws of motion in Table 4. Common forces on a moving object include an applied force, a frictional force, a weight, and a normal force. Contact forces are action-reaction pairs of forces produced by physical contact of two objects. Review calculations regarding contact forces betwee ...
... See Newton’s laws of motion in Table 4. Common forces on a moving object include an applied force, a frictional force, a weight, and a normal force. Contact forces are action-reaction pairs of forces produced by physical contact of two objects. Review calculations regarding contact forces betwee ...
Conceptual Physics
... 14. If a ball is thrown up at 10 m/s, what will be the speed of the ball when it’s caught back at the original point of the throw? 15. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s instantaneous speed at the top of its path? 16. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s acceleration ...
... 14. If a ball is thrown up at 10 m/s, what will be the speed of the ball when it’s caught back at the original point of the throw? 15. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s instantaneous speed at the top of its path? 16. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s acceleration ...
Theoretical questions
... differential in the appropriate figure. Describe its properties (magnitude, direction). 2. Define velocity of the mass point. Describe its properties. Define the acceleration of the mass point. Express its velocity and acceleration in the component form. 3. Define the angular velocity and angular ac ...
... differential in the appropriate figure. Describe its properties (magnitude, direction). 2. Define velocity of the mass point. Describe its properties. Define the acceleration of the mass point. Express its velocity and acceleration in the component form. 3. Define the angular velocity and angular ac ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 7, Mar 31, 2005 ns
... 1. Mass sliding down from Point 1 to point 2: The mass starts from rest (v1 = 0) at point ‘1’ and reaches point ‘2’ with velocity v2 . The goal of this section will be to evaluate v2 . (a) What is the expression for the change in kinetic energy in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’ ? (The superscript ...
... 1. Mass sliding down from Point 1 to point 2: The mass starts from rest (v1 = 0) at point ‘1’ and reaches point ‘2’ with velocity v2 . The goal of this section will be to evaluate v2 . (a) What is the expression for the change in kinetic energy in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’ ? (The superscript ...
EQUATIONS OF MOTION
... (continued) • Equations of Motion If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. ...
... (continued) • Equations of Motion If the forces can be resolved directly from the free-body diagram (often the case in 2-D problems), use the scalar form of the equation of motion. In more complex cases (usually 3-D), a Cartesian vector is written for every force and a vector analysis is often best. ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... If the distance between a point mass and the pivot point is tripled, the rotational inertia of the object about that point is multiplied by A) 9 B) 3 C) 1/3 ...
... If the distance between a point mass and the pivot point is tripled, the rotational inertia of the object about that point is multiplied by A) 9 B) 3 C) 1/3 ...
Metode Euler
... • In the “real world,” however, complications often arise that make analytical solutions difficult and perhaps beyond the mathematical abilities of most students taking introductory physics. • For example, the net force acting on a particle may depend on the particle’s position, as in cases where th ...
... • In the “real world,” however, complications often arise that make analytical solutions difficult and perhaps beyond the mathematical abilities of most students taking introductory physics. • For example, the net force acting on a particle may depend on the particle’s position, as in cases where th ...
work power energy - White Plains Public Schools
... Two blocks are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. The block of mass m1 lies on a horizontal surface and is connected to a spring of force constant k. The system is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. If the hanging block of mass m2 falls a distance h b ...
... Two blocks are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. The block of mass m1 lies on a horizontal surface and is connected to a spring of force constant k. The system is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. If the hanging block of mass m2 falls a distance h b ...
08-1 Note 08 Work and Kinetic Energy
... A System and its Environment In physics it is useful to envoke the concept of a system and its environment. A system is usually an object under study, while an environment is what lies outside a system and what is therefore irrelevant to the problem. In any problem it is useful to identify the syste ...
... A System and its Environment In physics it is useful to envoke the concept of a system and its environment. A system is usually an object under study, while an environment is what lies outside a system and what is therefore irrelevant to the problem. In any problem it is useful to identify the syste ...
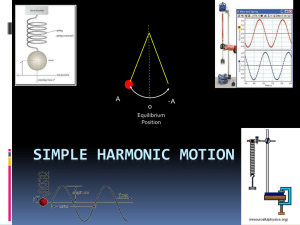
Abby AII1 C083 Ye, Zi Topic: Energy in Simple harmonic motion
... Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is the motion of a simple harmonic oscillator, a motion that is neither driven nor damped. The motion is periodic - as it repeats itself at standard intervals in a specific manner - and sinusoidal, with constant amplitude; the acceleration of a body executing SHM is dire ...
... Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is the motion of a simple harmonic oscillator, a motion that is neither driven nor damped. The motion is periodic - as it repeats itself at standard intervals in a specific manner - and sinusoidal, with constant amplitude; the acceleration of a body executing SHM is dire ...