Circular motion
... - a force is necessary to keep an object moving along a circular path even when speed is constant (different from the one dimensional case) - this force acts on the body making the circular motion and it is directed toward the center of the circle - called: centripetal force (center-seeking force) - ...
... - a force is necessary to keep an object moving along a circular path even when speed is constant (different from the one dimensional case) - this force acts on the body making the circular motion and it is directed toward the center of the circle - called: centripetal force (center-seeking force) - ...
Experiment 5U: Kinetic Friction
... of the speed of the object. If the frictional force fk is less than fmax, the motion can still be maintained even though the force F is less than Fcrit. ...
... of the speed of the object. If the frictional force fk is less than fmax, the motion can still be maintained even though the force F is less than Fcrit. ...
$doc.title
... rest on a fricPonless air track. The force acts for a short Pme interval and gives the cart a final speed. To reach the same speed using a force that is half as big, the force must ...
... rest on a fricPonless air track. The force acts for a short Pme interval and gives the cart a final speed. To reach the same speed using a force that is half as big, the force must ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
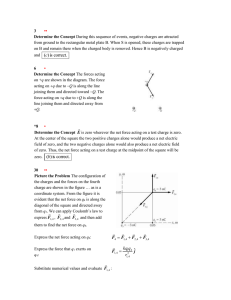
Fundamental Law of Electrostatics
... 5. The force is proportional to B 6. The force is proportional to the sign and magnitude of q The magnetic force Fon a moving charge is proportional to q, vp and B, where vp is the velocity component perpendicular to the field, while the direction of Fis perpendicular to both Band v and depends on t ...
... 5. The force is proportional to B 6. The force is proportional to the sign and magnitude of q The magnetic force Fon a moving charge is proportional to q, vp and B, where vp is the velocity component perpendicular to the field, while the direction of Fis perpendicular to both Band v and depends on t ...