exercises1
... D3) In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron revolves in circular orbits around the nucleus. If the radius of the orbit is 5.3x10-11 electron makes 6.6x1015 revolutions / s, find: (a) the acceleration (magnitude and direction) of the electron, (b) the centripetal force acting on the ele ...
... D3) In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electron revolves in circular orbits around the nucleus. If the radius of the orbit is 5.3x10-11 electron makes 6.6x1015 revolutions / s, find: (a) the acceleration (magnitude and direction) of the electron, (b) the centripetal force acting on the ele ...
Linear Motion
... When a flywheel speeds up, every point of the flywheel moves at increasing speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 ...
... When a flywheel speeds up, every point of the flywheel moves at increasing speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 ...
ppt
... Thus position of a particle is a rotation + translation from “object space” into “world space” We want to figure out what’s happening with ...
... Thus position of a particle is a rotation + translation from “object space” into “world space” We want to figure out what’s happening with ...
PHY820 Homework Set 5
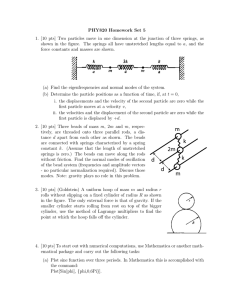
... (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displace ...
... (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displace ...
2nd 6-Weeks Test Review ANSWERS
... A quarterback takes the football and runs backward (perpendicular to the lines on the field) for 40 m. He then runs sideways (parallel to the lines on the field) for 15 m. The ball is thrown forward (perpendicular to the lines on the field) 60 m. When the receiver catches the football, how far is th ...
... A quarterback takes the football and runs backward (perpendicular to the lines on the field) for 40 m. He then runs sideways (parallel to the lines on the field) for 15 m. The ball is thrown forward (perpendicular to the lines on the field) 60 m. When the receiver catches the football, how far is th ...
speed momentum acceleration
... Formula: Acc= Final speed- Initial speed/time 10m/s – 30 m/s Acc = 10 sec = -2.0 m/s2 Newton’s Second Law Force = Mass X Acceleration for example: 1 Newton = 1Kg X 1 m/s2 Weight = Mass X Gravity Mass = Force/Acceleration Acceleration = Force/Mass 6. A force of 20 N acts upon a 5 kg block. Calculate ...
... Formula: Acc= Final speed- Initial speed/time 10m/s – 30 m/s Acc = 10 sec = -2.0 m/s2 Newton’s Second Law Force = Mass X Acceleration for example: 1 Newton = 1Kg X 1 m/s2 Weight = Mass X Gravity Mass = Force/Acceleration Acceleration = Force/Mass 6. A force of 20 N acts upon a 5 kg block. Calculate ...
King Abdulaziz University
... B) The total number of complete cycles divided by the time C) The time required to complete one circle ...
... B) The total number of complete cycles divided by the time C) The time required to complete one circle ...
You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
Chapter 7
... floor then drops away, leaving the riders suspended against the wall in a vertical position. What minimum coefficient of friction between a rider’s clothing and the wall is needed to keep the rider from slipping? (Hint: Recall that the magnitude of the maximum force of static friction is equal to μn ...
... floor then drops away, leaving the riders suspended against the wall in a vertical position. What minimum coefficient of friction between a rider’s clothing and the wall is needed to keep the rider from slipping? (Hint: Recall that the magnitude of the maximum force of static friction is equal to μn ...
Dynamics_NewtonLaws - University of Manchester
... What is Alice’s velocity as seen by Bob ? If Bob is on the boat it is just 1 m/s If Bob is on the shore it is 1+2=3m/s If Bob is on a boat passing in the opposite direction….. and the earth is moving around the sun… ...
... What is Alice’s velocity as seen by Bob ? If Bob is on the boat it is just 1 m/s If Bob is on the shore it is 1+2=3m/s If Bob is on a boat passing in the opposite direction….. and the earth is moving around the sun… ...
Newton`s first law of motion
... his three laws of motion. Like many other ‘laws’ they give the right answers for the majority of the time. For example, the paths of planets, moons and satellites are all calculated using Newton’s laws. ...
... his three laws of motion. Like many other ‘laws’ they give the right answers for the majority of the time. For example, the paths of planets, moons and satellites are all calculated using Newton’s laws. ...
Final Exam - Kuniv.edu.kw
... 18. A small object of m, on the end of a light cord, is held horizontally at a distance r from a fixed support as shown. The object is then released. What is the tension in the cord when the object is at the lowest point of its swing? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
... 18. A small object of m, on the end of a light cord, is held horizontally at a distance r from a fixed support as shown. The object is then released. What is the tension in the cord when the object is at the lowest point of its swing? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
Fall Final Study Guide Define a scalar quantity. A bicycle rider
... mass of 4.5 kg. What is the gravitational force between them? Assume G = 6.67×10-11 ...
... mass of 4.5 kg. What is the gravitational force between them? Assume G = 6.67×10-11 ...
CHAPTERS 3 & 4
... Components = the magnitude and sign of the component vectors. Algebraic calculations only involve the components of vectors not the ...
... Components = the magnitude and sign of the component vectors. Algebraic calculations only involve the components of vectors not the ...
Ch 3 Quiz (with KEY)
... 15. The momentum of a large bus is _____ that of a small car traveling at the same speed. a. greater than b. equal to c. less than d. none of the above 16. Force is expressed in units of ___. a. kg b. m/s c. m/s2 d. kg x m/s2 17. Newton's second law can be expressed in equation form as _______. a. v ...
... 15. The momentum of a large bus is _____ that of a small car traveling at the same speed. a. greater than b. equal to c. less than d. none of the above 16. Force is expressed in units of ___. a. kg b. m/s c. m/s2 d. kg x m/s2 17. Newton's second law can be expressed in equation form as _______. a. v ...