Physics Final Review Problems 2014 *Note: the following problems
... c) What does a dot diagram look like for an object that is traveling with a constant velocity vs. speeding up vs. slowing down? d) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs ti ...
... c) What does a dot diagram look like for an object that is traveling with a constant velocity vs. speeding up vs. slowing down? d) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs ti ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... c) What does a dot diagram look like for an object that is traveling with a constant velocity vs. speeding up vs. slowing down? d) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs ti ...
... c) What does a dot diagram look like for an object that is traveling with a constant velocity vs. speeding up vs. slowing down? d) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs ti ...
You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
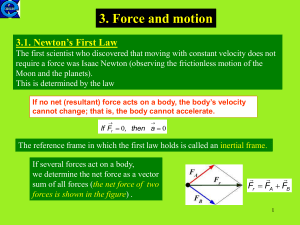
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
physics midterm review packet
... 13. What quantity is zero when a projectile is at its maximum height? 14. What are the units for: distance, velocity, acceleration, force, work, energy, power… 15. An object has a weight of 50 N on the Earth and a second object has a weight of 50 N on the moon. Which has the greater mass? 16. A car ...
... 13. What quantity is zero when a projectile is at its maximum height? 14. What are the units for: distance, velocity, acceleration, force, work, energy, power… 15. An object has a weight of 50 N on the Earth and a second object has a weight of 50 N on the moon. Which has the greater mass? 16. A car ...
KD-4 power point review
... Example: Calculate the maximum speed a 1200 kg car can travel around a curve of 35 m radius if the frictional force between the tires and the road surface is 2.4 X 103 N. Fc = m v2 / r 2.4 x 103 = 1200 v2 / 35 V = 8.4 m/s ...
... Example: Calculate the maximum speed a 1200 kg car can travel around a curve of 35 m radius if the frictional force between the tires and the road surface is 2.4 X 103 N. Fc = m v2 / r 2.4 x 103 = 1200 v2 / 35 V = 8.4 m/s ...
L20
... Parallel plates at different voltages produce a nearly constant field between them. Let V2 > V1. The distance between them is h. ...
... Parallel plates at different voltages produce a nearly constant field between them. Let V2 > V1. The distance between them is h. ...
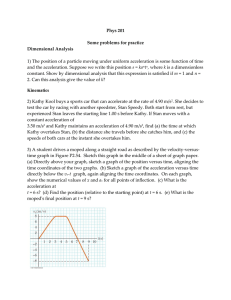
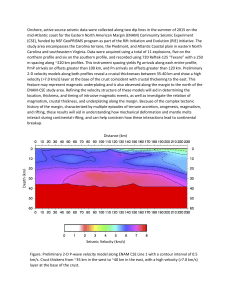
Phys 201 Some problems for practice Dimensional Analysis 1) The
... 11) A 72.0-kg man stands on a spring scale in an elevator. Starting from rest, the elevator ascends, attaining its maximum speed of 1.20 m/s in 0.800 s. It travels with this constant speed for the next 5.00 s. The elevator then undergoes a uniform acceleration in the negative y direction for 1.50 s ...
... 11) A 72.0-kg man stands on a spring scale in an elevator. Starting from rest, the elevator ascends, attaining its maximum speed of 1.20 m/s in 0.800 s. It travels with this constant speed for the next 5.00 s. The elevator then undergoes a uniform acceleration in the negative y direction for 1.50 s ...
FORCES AND MOTIONS TEST REVIEW FORCE BALANCED
... 8. IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING SCENARIOS USING YOUR MEMORY CUES FOR SPEED, VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 8. IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING SCENARIOS USING YOUR MEMORY CUES FOR SPEED, VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Chapter 2
... Instantaneous Velocity is the velocity of an object at ________________ Example: When you glance down at your speedometer while driving, the speed indicated by the speedometer is the magnitude of your instantaneous velocity. (or how fast you are going at that instant) ...
... Instantaneous Velocity is the velocity of an object at ________________ Example: When you glance down at your speedometer while driving, the speed indicated by the speedometer is the magnitude of your instantaneous velocity. (or how fast you are going at that instant) ...
Circular Motion
... When a particle moves along a straight line, it’s speed is calculated as the rate of change of distance. For a particle moving in a circle we find the speed by finding the rate at which the radius is turning. Tangential speed: A particle moving at constant speed v round a circle with centre O and r ...
... When a particle moves along a straight line, it’s speed is calculated as the rate of change of distance. For a particle moving in a circle we find the speed by finding the rate at which the radius is turning. Tangential speed: A particle moving at constant speed v round a circle with centre O and r ...
Content Area: Newtonian Mechanics Unit: 5 Topic (s): Circular
... 1) The Amazing Rando (m=85kg) is swinging through the air with the greatest of ease on a flying trapeze that has a string length of 3.1m. (a) What is the period of Rando's oscillation? (b) If the Amazing Rando was to sit on a seat that was attached to a spring, what would the spring constant need to ...
... 1) The Amazing Rando (m=85kg) is swinging through the air with the greatest of ease on a flying trapeze that has a string length of 3.1m. (a) What is the period of Rando's oscillation? (b) If the Amazing Rando was to sit on a seat that was attached to a spring, what would the spring constant need to ...
PowerPoint
... Angular Effects Let’s remain in 2-D plane for now In addition to kinematic variables • x, y positions ...
... Angular Effects Let’s remain in 2-D plane for now In addition to kinematic variables • x, y positions ...
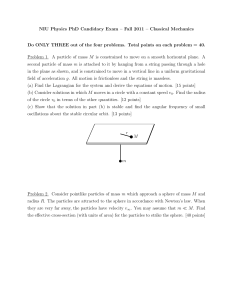
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam – Fall 2011 – Classical
... Do ONLY THREE out of the four problems. Total points on each problem = 40. Problem 1. A particle of mass M is constrained to move on a smooth horizontal plane. A second particle of mass m is attached to it by hanging from a string passing through a hole in the plane as shown, and is constrained to m ...
... Do ONLY THREE out of the four problems. Total points on each problem = 40. Problem 1. A particle of mass M is constrained to move on a smooth horizontal plane. A second particle of mass m is attached to it by hanging from a string passing through a hole in the plane as shown, and is constrained to m ...
1. The apparent weight of an object increases in an elevator while
... 4. Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle? Ans: No, Yes (If I move in circular path around the particle it will appear that the particle is moving in circular path around me.) [Sol. ...
... 4. Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle? Ans: No, Yes (If I move in circular path around the particle it will appear that the particle is moving in circular path around me.) [Sol. ...
lecture14
... Set initial position and linear/angular velocities Figure out all forces and their points of application Sum all forces and divide by mass to find COM’s linear acceleration For each force, compute perp-dot-product from COM to point of force application and add value into total torque of COM Divide t ...
... Set initial position and linear/angular velocities Figure out all forces and their points of application Sum all forces and divide by mass to find COM’s linear acceleration For each force, compute perp-dot-product from COM to point of force application and add value into total torque of COM Divide t ...