momentum
... The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables: how much stuff is moving and how fast the stuff is moving. In other words: The size of the momentum is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the size of the object's velocity. ...
... The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables: how much stuff is moving and how fast the stuff is moving. In other words: The size of the momentum is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the size of the object's velocity. ...
Unit 5 Part 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Notes
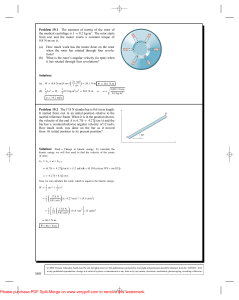
... Fs is known as the spring force (N) = the spring constant (in N/m) = the displacement of the body from its equilibrium (x = 0m) position (at equilibrium, = 0m so Fs= 0N ) ...
... Fs is known as the spring force (N) = the spring constant (in N/m) = the displacement of the body from its equilibrium (x = 0m) position (at equilibrium, = 0m so Fs= 0N ) ...
Lecture 7
... To show how to solve particle equilibrium problems using the equations of equilibrium ...
... To show how to solve particle equilibrium problems using the equations of equilibrium ...
Dynamics Problems - La Citadelle, Ontario, Canada
... what is the tension T at either end of the rope connecting both boxes? ...
... what is the tension T at either end of the rope connecting both boxes? ...
Chapter 4
... denoted by w. You may be used to thinking of your weight as a property of your body, but actually it is a force exerted on you by the earth. The gravitational attraction of two objects acts even when the objects are not in contact. We’ll discuss this concept at greater length in Section 4.4. Measuri ...
... denoted by w. You may be used to thinking of your weight as a property of your body, but actually it is a force exerted on you by the earth. The gravitational attraction of two objects acts even when the objects are not in contact. We’ll discuss this concept at greater length in Section 4.4. Measuri ...
Projectile Orbital Motion 2012 - EarthScienceNHS
... • Any object that moves forward due to its inertia and accelerates downward due to gravity. • Projectile Motion • The curved path of a projectile. The vertical and horizontal components of the motion are independent of each other. ...
... • Any object that moves forward due to its inertia and accelerates downward due to gravity. • Projectile Motion • The curved path of a projectile. The vertical and horizontal components of the motion are independent of each other. ...
Honors Review for Midterm
... A force of 100 N acting for 0.1 seconds would provide an equivalent impulse as a force of 5 N acting for 2.0 seconds. ...
... A force of 100 N acting for 0.1 seconds would provide an equivalent impulse as a force of 5 N acting for 2.0 seconds. ...
PHYSICS COURSE DESCRIPTION - McCall
... 16. Define free fall 17. Contrast free fall with non-free fall 18. Describe the relationship between air resistance and speed of a free-falling object Unit 5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion 1. Identify forces acting on an object 2. Identify the number of forces required for an interaction 3. Cite Newto ...
... 16. Define free fall 17. Contrast free fall with non-free fall 18. Describe the relationship between air resistance and speed of a free-falling object Unit 5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion 1. Identify forces acting on an object 2. Identify the number of forces required for an interaction 3. Cite Newto ...
Physics I - Rose
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...